* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download i. Electronic Polarization
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
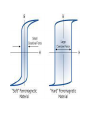
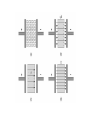
Dielectric Materials Dielectric materials are also called as insulators. In dielectric materials, all the electrons are tightly bound to their parent molecules and there are no free charges. Not possible for the electrons in the valence band to excite to the conduction band, by crossing the energy gap, even with normal voltage or thermal energy. A dielectric material (dielectric for short) is an electrical insulator that can be polarized by an applied electric field When a dielectric is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the material as they do in a conductor, but only slightly shift from their average equilibrium positions causing dielectric polarization Note that during the polarization the charges in the dielectric medium are displaced from their equilibrium positions by distances that are considerably less than the atomic diameter . Thus there is no net transfer of charge over large distances which occurs when s current is sent up in conductor WHAT IS Electric POLARIZATION??? The displacement of positive and negative charges in opposite directions in a dielectric. P=p/V Basic Definitions in Dielectrics Electric Field The region around the charge within which its effect is felt or experienced is known as electric field. The electric field is assumed to consist of imaginary electric lines of force. These lines of force originate from the positive charges and terminate to the negative charges . Relative permittivity is the factor by which the electric field between the charges is decreased relative to vacuum In electromagnetism, permittivity or absolute permittivity is the measure of that is encountered when forming an electric field in a medium. In resistance other words, permittivity is a measure of how an electric field affects, and is affected by, a dielectric medium. The permittivity of a medium describes how much electric field is 'generated' per unit charge in that medium. More electric flux exists in a medium with a low permittivity because of polarization effects. Permittivity is directly related to electric susceptibility, which is a measure of how easily a dielectric polarizes in response to an electric field. Thus, permittivity relates to a material's ability to resist an electric field r 0 Dielectric Constant The dielectric constant or relative permittivity of a material determines its dielectric characteristics. It is the ratio of the permittivity of the medium and the permittivity of free space Various Polarization mechanisms Dielectric material is made up of atoms or molecules that possess one or more these types of electric polarization, Polarization come when centre of gravity of charges shifts and its overlapped for symmetrical materials and centre of gravity can be shifted when materials is deformed and . Four types of microscopic polarization mechanisms. Electronic polarization Ionic polarization Orientation polarization and Space-charge polarization. i. Electronic Polarization Electronic Polarization occurs due to the displacement of positively charged nucleus and negatively charged electrons in opposite directions, when an external electric field is applied, and thereby a dipole moment is created in the dielectric. The induced dipole moment µ = eE where e = electronic polarizability. Monoatomic gases exhibit this kind of polarization, Electronic polarizability is proportional to the volume of the atoms and is independent of temperature. The electronic polarizability = e = 4e0R3 ( Farad.m2) where R is the radius of the atom. Nucleus Displaced Equilibrium position Nucleus x Sphere of electronic charge +Ze -Ze Field direction Original Position Fig. (a) Position of +ve and –ve charges in an atom without field (b) Position of +ve and –ve charges in an atom with field Suppose that the electron cloud of charges -Zq is uniformly distributed in a sphere of radius R and that its center of gravity originally coincided with that of the nucleus, and suppose that it is displaced by the field to a distance d from the center of the nucleus, This displacement of the electrons Dx, resulting from electronic polarization, always generates an elastic restoring force tending to bring the electrons back to their equilibrium position. The noble gas atoms, such as He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, H, Li, Na, K, Rb, Single atoms in gases may be considered spherical in shape, but molecules, each comprising two or more atoms, are generally not spherical. The field strength produced by the nucleus charges and experienced by the electrons is Zq/4peoR2 is larger than 109 V/cm. This field strength is far larger than the applied field. This may be the reason why the induced dipole moment for electronic polarization is proportional to the applied field and independent of frequency, because the time required for this polarization to occur is of the order of 10-15 sec Temperature independent intermolecular phenomenon since to make it shift again the nuclear force an equal and but in opposite direction force has to be applied ii. Ionic Polarization Ionic polarization arises due to the displacement of -ve ions and + ve ions in opposite directions and it occurs in ionic solids, in the presence of electric field. The displacement is independent of temperature. Example : NaCl crystal - + Cl Na - + x2 x1 Fig. (a) Without field (b) With field Each Na+ - Cl– pair is a natural dipole, no matter how you pair up two atoms. The polarization of a given volume, however, is exactly zero because for every dipole moment there is a neighboring one with exactly the same magnitude, but opposite sign.Note that the dipoles can not rotate; their direction is fixed. In an electric field, the ions feel forces in opposite directions. For a field acting as shown, the lattice distorts a little bit Na+ ions moved a bit to the right, the Cl– ions to the left. The dipole moments between adjacent NaCl pairs in field direction are now different and there is a net dipole moment in a finite volume now dielectric material consisting of polyatomic molecules usually has electronic polarization and ionic polarization, and in some cases, also orientational polarization when it is subjected to an electric field. In general, there are two groups of ionic solids. One group does not possess permanent dipoles, such as NaCl, which forms a simple cubic lattice so that the lattice symmetry and the overall charge neutrality ensure that electric dipoles formed by each ion pair everywhere cancel each other. The other group possesses permanent dipoles, because the crystal lattice in this case is less symmetrical, as with HCl The time required for electronic polarization is about 10-15 sec, and that required for the ionic polarization is about 10-13 sec, simply because ions are heavier than electrons by more than 103 times. This is why the resonances for these two polarizations occur in different frequency iii. Orientation Polarization The orientation polarization arises due to the presence of polar molecule in the dielectric medium. Fig. (a) Without field (b) With field Explanation: In the case of a CH3Cl molecule, the positive and negative charges do not coincide. The Cl- has more electro negativity than hydrogen. Therefore, the chlorine atoms pull the bonded electrons towards them more strongly than hydrogen atoms. Therefore, even in the absence of field, there exists a net dipole moment. Now, when the field is applied, positive portion align along the direction of field and negative portion align in the opposite direction of the field. This kind of polarization is called as orientation polarization. This depends on temperature; when temperature is increased, the thermal energy tends to randomize the alignment orientation of a molecule involves the energy required to overcome the resistance of the surrounding molecules, so the orientation process is strongly temperature dependent. Explanation Without the application of external field, the ions are orderly arranged as shown in the Fig. Now, when the field is applied, the ions diffuse with respect to the direction of applied field. Thus the polarization occurs, known as space charge polarization. Normally, this type of polarization occurs in ferrites and semiconductors and will be very small. Which polarization is slower and why??? It was seen that in some materials dielectric constant are some tow orders of larger magnitude than the normal dielectric Barium titnate has di cons of 2000 than normal dieletric it was due to the ferroelectricity in them The term ferroelectrics arose by analogy with ferromagnetic, mainly because they have similar characteristics: under electric fields for ferroelectric phenomena and under magnetic fields for ferromagnetic phenomena Like ferromagnetics, ferroelectrics exhibit a spontaneous electric polarization below the Curie temperature, Occurs in non-centro-symterial molecules In general, all materials undergo a small change in dimension when subjected to an external force, such as an applied electric field, a mechanical stress, or a change in temperature. This implies that non -centrosymmetric crystals are nonpolar and thus do not possess a finite polarization or dipole moment. Depending on the material structure, such a small change in dimension may result in a change in electric polarization and hence give rise to the occurrence of the ferroelectric, This implies that centrosymmetric crystals are nonpolar and thus do not possess a finite polarization or dipole moment. In such cubic systems centre of gravity of positive charge coincide with negative charges and centered of gravity shifts as system