* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - Science CALC
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
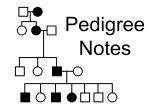
Name: __________________________________________ SBI3U 11 UNIVERSITY BIOLOGY PREP FINAL EXAM REVIEW Part A: Determine whether the following statements are true or false. Question One The small intestine produces bile. False Question Two The stomach contains folds called villi that allow it to expand. False Question Three Arteries carry blood away from the heart. True Question Four The main vein leading into the heart is called the vena cava. True Question Five The systemic circuit circulates blood to the body and back to the heart. True Question Six The voice box is located in the larynx. True Question Seven Gas exchange occurs by active transport. False Question Eight The organ that prevents food from entering the trachea is the epiglottis. True Question Nine Food moves down the esophagus by a process called peristalsis. True Question Ten Unsaturated fats contain only single bonds between carbon atoms. False Question Eleven Phagocytosis is the act of a cell engulfing a solid particle. True Question Twelve Exocrine gland secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream. False Question Thirteen Vasoconstriction occurs when the body is too hot. False Question Fourteen The pancreas produces insulin, bicarbonate and digestive enzymes. True Question Fifteen The respiratory defends the body against invading microbes. True Question Sixteen DNA is composed of a sugar, a nitrogen base and a phosphate group. True Question Seventeen The haploid number represents the number of chromosomes found in the somatic cell. False Question Eighteen By the end of meiosis there are 4 daughter cells. True Question Nineteen An organism with a diploid number of 46 would produce gametes cells with 23 chromosomes. True Question Twenty Alleles are genes that produce different expressions of a given trait. True Question Twenty One An individual’s phenotype is described as an individual’s genetic make up. False Question Twenty Two A genotype consisting of two identical genes for a given trait is said to be heterozygous. False Question Twenty Three The location of a gene on a chromosome is called a locus. True Question Twenty Four The diploid number represents the number of chromosomes found in the somatic cell. True Question Twenty Five The term used to describe an individual’s genetic makeup is called genotype. True Question Twenty Six An individual carries two copies of a gene called alleles. One copy from their mother, and one copy from their father. True Question Twenty Seven You only need one copy of a recessive allele in order to express a recessive trait. False Question Twenty Eight A trait that occurs in all of the males of a family and none of the females is probably X-linked. True Question Twenty Nine A mutation occurs when there is an error in the genetic code. True Question Thirty Because of complementary base pairing, if you know the base sequence of one DNA strand, you can predict the sequence of the other strand. True Question Thirty One Two species of pines releasing pollen at separate times in the same habitat is an example temporal isolation. True Question Thirty Two A population that meets the Hardy-Weinberg requirements has allele frequency in equilibrium. True Question Thirty Three A characteristic that better enables an organism to survive and reproduce is called a mutation. False Question Thirty Four Mechanical Isolation is an example of a pre-zygotic isolation mechanism. True Question Thirty Five Gene sequences in DNA of different animals tend to support evolution. True Question Thirty Six Genetic drift is a characteristic of a small population. True Question Thirty Seven Stabilizing selection does not cause change. False Question Thirty Eight Allopatric speciation is the relatively rapid evolution of a single species into many new species. False Question Thirty Nine The large-scale evolution of a group into many different forms is called divergent evolution. True Question Forty Lactose intolerance proves that biological evolution and cultural evolution can occur at the same time. True Question Forty One The remains of organisms preserved in rock are called vestigial structures. False Question Forty Two Darwin wrote “On the Origins of Species” to describe how species evolve over time. True Question Forty Three Catastrophism is the theory that changes are slow and gradual and that natural laws and processes have not changed over time. False Question Forty Four Lyell coined the phrase “survival of the fittest” because of his theory of natural selection. False Question Forty Five A human arm and a bat wing are examples of analogous structures. False Question Forty Six You REALLY like Biology. TRUE!!! Part B: Punnett Squares and Pedigree Charts. Question One In guinea pigs, black fur (B) is dominant over white fur (b). Smooth fur (r) is recessive to rough fur (R). a. Give the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F1 offspring of a homozygous black smooth guinea pig with a homozygous white rough coated guinea pig. Define all terms and include all Punnett squares. Homozygous white rough fur Br bR BbRr Homozygous black smooth fur Phenotype: 100% black rough guinea pigs Genotype: 100% heterozygous dominant for black fur and rough fur b. Conduct a dihybrid cross of the F1 offspring and state the genotypic and phenotypic ratios of the F2 offspring. BR Br bR br BR BBRR BBRr BbRR BbRr Br BBRr BBrr BbRr Bbrr bR BbRr BbRr bbRr bbRr br Bbrr Bbrr bbRr bbrr Phenotype: 9 black rough fur, 3 white rough fur, 3 black smooth fur, 1 white rough fur Genotype: too many Question Two Hand clasping left thumb over right thumb is a dominant trait (H). Hand clasping right thumb over left thumb is a recessive trait (h). Describe the phenotype and genotype of the offspring of the following crosses: a. A homozygous dominant individual crossed with a heterozygous dominant individual H H H h HH Hh HH Hh Phenotype: 100% hand clasping left thumb over right b. A heterozygous dominant individual crossed with a homozygous recessive individual H h h h Hh Hh hh hh Phenotype: 50% hand clasping left thumb over right, 50% hand clasping right thumb over left Genotype: 50% heterozygous dominant, 50% homozygous recessive Question Three Hemophilia became known as the “Royal disease” after it suddenly cropped up in some of the descendants of Great Britain’s Queen Victoria and spread through the royal families of Europe. Queen Victoria and her husband Prince Albert had 9 children – 5 girls (Beatrice, Victoria, Alice, Helena, and Louise – none of whom were hemophiliacs) and 4 boys (Edward, Alfred and Arthur had normal blood clotting; their son Leopold, however was a hemophiliac). Beatrice married a man named Henry and they had four children (sons Leopold and Maurice who were hemophiliacs, daughter Eugenie who was not a hemophiliac, and another son who was also not a hemophiliac). Eugenie married Alfonso XIII of Spain (nonhemophiliac) and they had 6 children (2 normal sons, 2 normal daughters and 2 hemophiliac sons). One of those normal sons married a non-hemophiliac woman and gave birth to one son – a non-hemophiliac they named Juan Carlos (the reigning King of Spain). a. Create a pedigree chart for the royal family. b. What kind of pedigree chart is this? Explain. This is an X-Linked pedigree chart. Boys are mostly affected. Daughters are most likely carriers. Question Four Look carefully at the pedigree drawn below and determine the type of pedigree chart. Defend your answer. This is an Autosomal Recessive pedigree chart. At first glance it looks autosomal dominant as the disease if found in every generation, and males and females are equally affected. However, in generation two individuals 2 and 3, one of the parents would have to carry at least one copy of the dominant gene to make a sick child. And if they did, they would be sick themselves. But they are not sick. Therefore, this must be an autosomal recessive chart. Part C: Anatomy Diagrams Question One Match the definitions with the organs below. a. This organ produces bile. Liver (11) b. This organ stores bile. Gall bladder (10) c. This organ produces hydrochloric acid. Stomach (12) d. This organ warms air to the correct body temperature of 37 oC. Oral or nasal cavity (1 or 2) e. This organ brings air to the lungs and is made out of cartilage. Trachea (5) f. This organ is the site for the bulk of absorption of nutrients by the body. Small intestine (15) g. This organ is part of the Pulmonary and Systemic circuits. Heart (8) h. This organ produces bicarbonate to neutralize the acidic chime. Pancreas (13) Part D: Cladograms Answer the following questions based on the cladogram below. Question One What trait separates perch from salamanders on this cladogram? Lungs Question Two Which organism is most related to the chimp? Mouse Question Four Based on your answer from question 2, what 4 traits do these two organisms share? Jaws, lungs, claws, fur and mammary glands Question Five Which organism’s DNA will differ the most from the mouse? Hagfish Question Six Create a cladogram given the table below. Species Bony Skeleton Sharks Fish Amphibians Primates Rodents Reptiles Birds + + + + + + Amphibians Characteristics Four Limb Amniotic Egg + + + + + Hair Two PostOrbital Fenestrae + + - + + + + + + Reptiles Rodents Birds Sharks Primates Fish Hair Amniotic egg Four limb Bony Skeleton Part E: Short Answer Question Question One What are differences and/or similarities between the following terms: a. directional selection and disruptive selection Direction selection favours one extreme or the other while disruptive selection favours both extremes. b. allopatric speciation and sympatric speciation Allopatric speciation occurs when a geological event separates a population of a species so that those individuals become more and more unalike over time. Sympatric speciation occurs when there is a mutation within a species that causes those individuals to be reproductively isolated from the rest of the species. c. dominant trait and recessive trait Dominant traits are expressed and recessive traits are not expressed. d. somatic cell and gamete cell Somatic cells contain a diploid number of chromosomes (2n) while gamete cells are sex cells that contain a haploid number of chromosomes (n). e. inhalation and exhalation Inhalation: Diaphragm lowers, thoracic cavity moves up and out, volume increases while pressure decreases and air rushes in. Exhalation: Diaphragm raises, thoracic cavity moves down and in, volume decreases and pressure increases and air rushes out. f. negative feedback and positive feedback Negative Feedback: corrects changes to the body Positive Feedback: amplifies changes to the body Question Two Is it possible for two individuals with Down Syndrome to have a child who does not have Down Syndrome? Yes. Since both individuals carry an extra chromosome, the division of the chromosomes will not be equal. Therefore, it is possible to produce sex cells with the correct number of chromosomes (23). If the sperm cell and the egg cell both have the correct number of chromosomes then it is possible to produce a zygote with the correct number of chromosomes (46). Question Three The pancreas and the liver are accessory organs in digestion. If these organs are not directly involved in digestion, why are the pancreas and liver important to digestion? The liver produces bile with helps to emulsify fats. The pancreas releases digestive enzymes which help to break down food for nutrients. The pancreas also releases bicarbonate which will neutralize the acidic chyme. Finally, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that is responsible for the uptake of glucose. Question Four Give five examples of how a population can deviate from the Hardy-Weinberg Principle of equilibrium. The population is small. The population is undergoing natural selection. There is emigration and immigration in the population. There is a mutation. Alleles are introduced into a population via other organisms.