* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CIVICS AND ECONOMICS
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
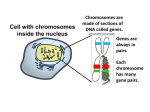
BIOLOGY STUDENT LEARNING PACKET RIO UNIT: SC BIO I UP07: Meiosis and Heredity ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How do genes and the environment interact to produce a phenotype? How are traits passed from parent to offspring? How does one single cell with a set number of chromosomes become thousands of different types of cells in a mature multi-cellular organism? What should you know/be able to do at the end of this unit? Describe the cell division process that reduces chromosome number in half (meiosis). Explain the cause of genetic variation within a population of organisms. Compare and contrast meiosis and mitosis. Explain how an organism’s phenotypes and genotypes are determined. Interpret and explain patterns in a karyotype. Describe how recessive traits are expressed. Investigate and explain the inheritance patterns of Sickle cell, Huntington’s disease, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs. Explain what distinguishes the different blood types: A, B, AB, O Identify several examples of traits controlled by more than one gene (skin, hair, and height) and how these polygenic traits are expressed. Explain how the sex of organism is determined. Explain why males are more likely to express a sex-linked trait such as color blindness or hemophilia. Investigate the importance of genes being located on separate chromosomes how this leads to greater genetic variability. KEY VOCABULARY: Allele Genotype Phenotype Dominant Recessive Sex-Linked Traits Cell Cycle Karyotype IMPORTANT CONCEPT(S): Mendel’s experiments and laws The process of meiosis The significant differences between mitosis and meiosis The structure and production of haploid and diploid cells The characteristics of asexual and sexual reproduction Causes of genetic variation, including random assortment, crossing over, and mutations. Applications of the following: Punnett squares, test cross, and pedigrees. LEARNING OPPORTUNITIES: Investigate Mendel’s principles of dominance and segregation. Using the “Five Habits of Mind” explain the application and significance of these principles. Imagine that you came upon a tall pea plant similar to those Mendel used in his experiments. Demonstrate the application of a test cross and how it is used to determine the plant’s genotype with respect to its height. Your answer should include a written description at least two Punnett squares. Using Punnett squares and a written explanation, prove the following statements. The genotype of a tall plea plant is determined by allowing the plant to selfpollinate. If the plant is heterozygous, there is a 25% chance that an offspring will be short. If the plant is homozygous, then all the offspring will be tall. Create a poster, divided into 4 sections, that illustrates the following five types of inheritance: incomplete dominance, codominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits and sex-linked traits. The poster should include both written descriptions and pictorial representations for each type of inheritance. Investigate the four heritable diseases listed below and create an informative pamphlet that explains their inheritance patterns, symptoms, and treatments. Sickle cell, Huntington’s disease, cystic fibrosis, Tay-Sachs. Write a short story about a chromosome going through meiosis. The story should be divided up so that each paragraph represents one step of meiosis, and the journey should span from interphase I to telophase II. Create a Venn diagram to demonstrate the differences and similarities between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction. Choose one of the “Five Habits of Mind” to evaluate what you see in the diagram. Explain how a pedigree can be used to determine an organism genotype. Include a visual representation of a pedigree as well as the patterns observed in the cases of dominant, recessive, and sex-linked traits. Research PolyHeme and its applications. Using the “Five Habits of Mind” evaluate and explain its development, significance, and potential applications. Create table that illustrates the inheritance patterns and symptoms of the following disorders: Down syndrome, Turner’s Syndrome, Colorblindness, Hemophilia, and Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. FIVE HABITS OF MIND 1. Evidence (How do you know that?) How do we know what’s true and false? What evidence counts? How sure can we be? What makes it credible to us? This includes using the scientific method and more. 2. Viewpoint (Who said it and why?) How else might this look if we stepped into other shoes? If we were looking at it from a different direction? If we had a different history or expectation? This requires the exercise of informed “empathy” and imagination. It requires flexibility of mind. 3. Cause and Effect (What led to it? What else happened?) Connections? Is there a pattern? Have we seen something like this before? What are the possible consequences? 4. Hypothesizing (What if? Suppose that?) Could it have been otherwise/ Supposing that? What if…? This habit requires use of the imagination as well as knowledge of alternative possibilities. It includes the habits described above. 5. Matter (Who cares?) Relevance? Does it matter? LINKS TO RELATED RESOURCES… . WEBSITES, GAMES, LITERATURE, VIDEOS, DOCUMENTARIES Cells Alive shows mitosis and meiosis in action! http://www.cellsalive.com/ On this site you can review the stages and events of mitosis with pictures of real cells dividing. http://www.bishopstopford.com/faculties/science/arthur/mitosis%20drag%20&% 20drop.swf This is a great site that allows you to practice moving chromosomes through the processes of mitosis and meiosis. www.biologyinmotion.com/cell_division/ This is a site where you can work with virtual flashcards to practice you vocabulary. http://www.studystack.com/matching-13355 Punnett square practice. http://www.athro.com/evo/gen/punexam.html A really cool tutorial about how traits are passed from parent to offspring. http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/units/basics/tour/inheritance.swf SAMPLE TEST QUESTIONS: 1. Which of the following best represents the process of meiosis? a. 2n 2n b. 2n n c. n 2n d. n n 2. Different forms of a gene are called a. alleles b. hybrids c. mutations d. phenotypes 3. In a genetics laboratory, two heterozygous tall plants are crossed. If tall is dominant over short, what are the expected phenotypic ratios? a. 100% tall b. 25% tall, 75% short c. 75% tall, 25% short d. 50% tall, 50% short 4. In a species of corn, the diploid number of chromosomes is 20. What is the number of chromosomes found in each of the normal egg cells produced by this species? a. 5 b. 10 c. 40 d. 20 5. A cross between two plants that have pink flowers produced plants that have red, pink or white flowers. Which is the most likely explanation for these results? a. Nondisjunction of the homologous pairs of chromosomes resulted in the production of abnormal offspring. b. Crossing-over of white and red alleles occurred during meiosis. c. Mutations occurred during gamete development. d. Incomplete inheritance involved alleles that were not dominant or recessive. 6. Which of the following process includes two cellular divisions and results in four haploid cells? a. meiosis b. mitosis c. fertilization d. DNA replication 7. Traits that are caused by the interactions of many genes are said to be a. linked b. polygenic c. autosomal d. codominant 8. Which parental pair could produce females with colorblindness? a. homozygous normal-vision mother, father with colorblindness b. mother with colorblindness, normal vision father c. heterozygous normal-vision mother, normal vision father d. heterozygous normal-vision mother, father with colorblindness 9. A situation, such as human blood type, where a gene has more than two alleles is known as a. incomplete dominance b. codominance c. polygenic dominance d. multiple alleles 10. The appearance of an organism due to its genetic makeup is referred to as its a. phenotype b. genotype c. hybrid d. karyotype Answer Key: 1. B 2. A 3. C 4. B 5. D 6. A 7. B 8. D 9. D 10. A