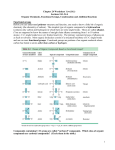
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Acid–base reaction wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Radical (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
Chemistry: A Volatile History wikipedia , lookup
Analytical chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
History of chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Green chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Electron configuration wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Molecular orbital diagram wikipedia , lookup
Bent's rule wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Molecular dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electronegativity wikipedia , lookup
Bond valence method wikipedia , lookup
Metallic bonding wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen bond wikipedia , lookup
Inorganic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Resonance (chemistry) wikipedia , lookup
IUPAC nomenclature of inorganic chemistry 2005 wikipedia , lookup
Stoichiometry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup