* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2. GLE 3.3.A.d: Describe how flowering plants reproduce sexually
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
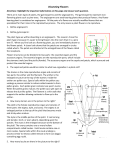
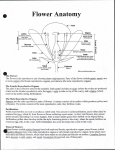
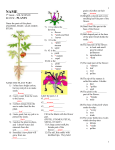
2. GLE 3.3.A.d: Describe how flowering plants reproduce sexually. Male Parts or reproductive organs of a plant. Stamen This is the male part of the flower. It is made up of the filament and anther: it is the pollen producing part of the plant. The number of stamen is usually the same as the number of petals. Anther This is the part of the stamen that produces and contains pollen. It is usually on top of a long stalk that looks like a fine hair. Filament This is the fine hair-like stalk that the anther sits on top of. Female Parts or reproductive organs of the plant Pistil This is the female part of the flower. It is made up of the stigma, style, and ovary. Each pistil is constructed of one to many rolled leaf-like structures. Stigma-One of the female parts of the flower. It is the sticky bulb that you see in the center of the flowers, it is the part of the pistil of a flower which receives the pollen grains and on which they germinate. Style Another female part of the flower. This is the long stalk that the stigma sits on top of. Ovary-The part of the plant, usually at the bottom of the flower, that has the seeds inside and turns into the fruit that we eat. The ovary contains ovules. Ovule-The part of the ovary that becomes the seeds. Carpels bear ovules, which are structures with the potential to develop into seeds. How does fertilization occur or how is a new seed made? Pollination has to occur before fertilization. Pollination: Pollen that comes from the anther lands on the sticky female stigma. Fertilization is the fusion (coming together) of nuclei from the male pollen grain with nuclei in the female ovule. Fertilization allows the flower to develop seeds. Each pollen grain begins to grow a tube down through the female style. Eventually, a sperm nucleus from the male pollen grain reaches and fertilizes the female egg cell or ovule in the ovary. The pollen and ovule fuse or come together as one. This is called fertilization and a new zygote (this is diploid = 2 sets of chromosomes) is the result. This zygote grows into a seed. An embryo is encased in the seed. From this seed and embryo a new plant will form.