* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Control
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
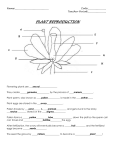
VOCABULARY Transpiration- the process by which water is given off from plants through evaporation Variable- what you change in an experiment (what you are testing!) Control- the standard to which an experiment is compared; it is not subjected to the variable (the change) Controlled Experiment- only one variable is being tested Xylem- the tube-like structures that carry water from the roots throughout the plant Stomates- pores or holes in the leaves that open and close to regulate the amount of water passing out of the plant Guard Cells- control the size of the openings on leaves QUESTIONS TO THINK ABOUT 1. What are the openings on the leaves that let gases in and out? Why does a plant need these openings? 2. What controls the size of the openings on these leaves? 3. Why is the transpiration process so important to a plant? 4. Describe the process of transpiration in detail from how water enters the plant all the way to how it leaves the plant. (think about roots, vascular channels, xylem, and stomates) 5. During a drought, would you expect a plant to pass a lot of water through the stomates? Why or why not? VOCABULARY • Ovary- where seeds develop • Ovules- tiny preseeds in the ovary • Pistil- center of the flower, ovary is located at the base (female part) • Egg- female sex cell in the ovule • Fertilized- ovule joins with sperm to create an egg (embryo) • Sperm- male sex cell located in pollen grain • Pollen grain- contains the sperm cell • Anthers- produces the pollen grains, located at the end of the stamen • Pollination- the process by which pollen gets from the male anther to the female pistil and down to the egg • Stigma- sticky tip of the pistil • Pollen tube- grows from pollen grain the length of the pistil. QUESTIONS TO THINK ABOUT 6. Describe the pollination process and tell why it is important. 7. What is the purpose of flowers? 8. What is sexual reproduction in plants? 9. What is a pollinator and can you name 5 of them? 10. What are the seed-dispersal methods plants use to spread seeds around? 11. Why is it important for seeds to be able to move away from the parent plant? 12. Label all the parts of the flower on the back of this sheet and be able to tell the function of each (what each does).