* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch.-2-notes - North Star Academy
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
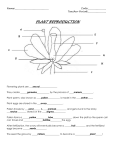
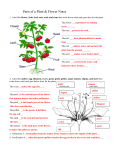
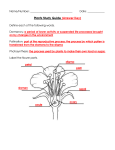
Name: ________________________________ Date: _________________________________ Topic: Chapter2-Energy from Plants Questions/Main Ideas: Notes: VOCABULARY Photosynthesis How plants make their own food using light chlorophyll Makes plants green, captures energy from sunlight for photosynthesis sepal Small leaves below flowers pistil Knoblike structure in center of flower stamen Stalks that surround pistils, makes pollen ovary Part of plant that contains egg cells fertilization When a plant cell and egg combine dormant Resting Lesson 1: What are plants’ characteristics? Cells Plants need: Chloroplast Describe process of photosynthesis Lesson 2: What are the parts of plants? Leaves Stems Roots: fibrous vs. taproots Lesson 3: How do plants reproduce? Stamen Nectar Wind Lesson 4: What is the life cycle of a plant? Plants need: - A multi-celled organism that has leaves, stems, and roots Plants are multi-celled organisms (have many cells) o All plants have cells Sunlight, water, carbon dioxide (from the air) Where photosynthesis takes place Contains chlorophyll, which makes plants green 1. plants take in carbon dioxide, water, and sunlight energy 2. turn those things into sugar (food) Pine needle and tulip leaves both are leaves - Carries water, minerals, and food (materials) - Supports the plant Fibrous-roots grow away from the stem and spread out (grasses and trees) Taproot- large main root that contains stored food (carrots, turnips, radishes) SIMILAR: both anchor plants and absorb water and minerals from soil Makes pollen - Helps flowers become pollinated - Animals looking for nectar spread pollen - blows the pollen from grass into the pistil of another grass plant - a pollen tube grows from the pollen into the ovary - the cell from the pollen and the egg cell in the ovary combine for fertilization to make a new plant Water, oxygen, right temperature, Plants turn sunlight into energy for reproduction Spores Seeds How do plants reproduce without seeds? A single tiny cell Can stay dormant for many years, needs moist environment Ex. Ferns, moss, Separate from the parent plant - Summary: From stems/ runners (strawberries, African violet plant), roots, or leaves Bulbs (tulip) Buds (potato) Grafting branches to another tree