* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study Guide: Plants
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
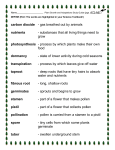
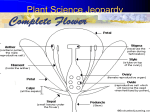
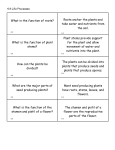
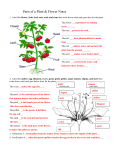
Name____________________________ Date______________________ #____ Science Study Guide ~ Plants Chapter 6, Lessons 1 & 2 Test Day__________________ Be able to match the vocabulary words below: Classify Genus Species Sepals Pistil Stamen Pollination Fertilization Germinate arrange or sort objects or living things according to their properties or characteristics a group of closely related living things group of similar organisms that can mate & produce offspring that can also produce offspring one of the leaflike parts that cover and protect the flower bud a female structure in plants that produces egg cell male structure in plants that makes pollen the movement of pollen from stamen to pistil the process in which a sperm cell and an egg cell combine to start to grow Answer the following questions. 10. What two characteristics do scientists use to classify plants? (1) how they transport nutrients (2) how they reproduce 11. Plant Type: Vascular Nonvascular Definition: Have a tubelike structure Nontubular; pass nutrients from cell to cell 12. Compare seeds & spores: ALIKE: (1) grow into new plants, (2) have a protective covering DIFFERENT: seeds have many cells, spores only have one cell 13. Label the parts of a flower. stamen Male Part anther Function: produce pollen Example: Ferns, wildflowers, bamboo pistil Female Part Function: produce egg Function: protect and cover the flower bud 14. Why are flower petals often colorful? To attract animals to help with pollination 15. Name 3 ways pollen is carried from the stamen to the pistil. Wind , water, animals 16. What is a bulb? An underground stem that stores food 17. What three things does a seed need to germinate? Oxygen, water, the right temperature Chapter 6, Lesson 3 & 4 **This will be combined with Chapter 6, Lessons 1 & 2 for one test on plants. Be able to match the vocabulary words below: Photosynthesis the process in which plants make sugar Chlorophyll the substance in plants that makes their parts green and captures energy from sunlight Answer the following questions. 1. What are the four needs of a plant? Water, sunlight, carbon dioxide, nutrients 2. Explain the jobs of each part of the plant: Job Roots (1) collect water (2) hold plant in place Stem (1) transports water and nutrients (2) supports plant structure Leaves (1) collect sunlight and carbon dioxide 3. What 4 things does a plant need for photosynthesis? Sunlight, carbon dioxide, chlorophyll, water 4. What is the product of photosynthesis? (What food does a plant make?) sugar 5. What is the waste product of photosynthesis? oxygen 6. How do plants and animals depend on each other? Plants give off oxygen, which animals need to breathe. Animals give off carbon dioxide, which plants need to live. 7. What are the three stages of a plant life cycle? (1) seed, (2) young plant (called a seedling), (3) adult plant 8. Plants grow from seeds and spores, but can also grow from plant parts. Give an example: Tulips - Grow from bulbs (underground stems) Strawberries – Grow from stems (called runners) Grass – Can grow from underground roots