* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download JEWISH HISTORY
Jewish views on evolution wikipedia , lookup
Index of Jewish history-related articles wikipedia , lookup
Jewish religious movements wikipedia , lookup
Supersessionism wikipedia , lookup
Pardes (Jewish exegesis) wikipedia , lookup
Origins of Rabbinic Judaism wikipedia , lookup
Jewish views on sin wikipedia , lookup
JUDAISM
Judaism
Worldwide: 14,551,000 Jews
– US: 5.6 million
– Asia: 4.5 million
– Europe: 2.4 million
Many different groups/divisions of
Judaism that exist
– Conflicting beliefs about observances, etc.
Importance of History
*The basis of the Jewish religion is its history. It is
the most important aspect.
– demonstrated through the celebration of life cycle
events in people’s lives
– holiday celebrations commemorate historic events
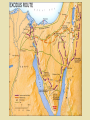
The key event is the Exodus from Egypt
(recorded Book of Exodus)
– Many important aspects of observances are linked to
this event
From the beginning, the
Jewish people have
interpreted acts of history
as God acting on behalf of
the Jewish people
– Either to promote them or to
punish them
– History is seen as the story
of God’s intervention in the
lives of His “Chosen
People”
Six Periods of Jewish History
The Patriarchs: AbrahamMoses (19th - 13th
cent. BCE)
Mosesthe Hebrew Monarchy (13th - 6th cent.
BCE)
The Babylonian Exile and Post Exilic Judaism
(6th cent BCE - 1st cent. CE) ("Second Temple"
period)
Rabbinic period (1st - 7th cent CE)
Medieval Judaism (7th - 18th cent. CE)
Modern Judaism (18th cent. - current)
Judaism as a Race
Judaism is an ethnic religion
Began as a religion of an extended family, a tribe
of peoples known as the Hebrews
Jewish people today continue to think of
themselves as a family, a nation of peoples, as
well as a religion
God is understood by the Jews to intervene, to
act, in and through history time and again,
especially in the history of Israel (the people)
Jews look to God’s action in the world
Sacred Texts
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh
– Known by Christians as "Old Testament“
– contains the same books as the Christian version but in a
different order after the first five
Considered revealed and inspired by God
– Interpretation of early history of the Hebrew people,
establishment of a nation
– Story of God’s interaction with His "Chosen People" (His-Story)
– Foundation of Jewish life
Called the Bible
– (Biblia) means "little books“
– Actually a library of 39 independent books divided into 3
categories:
The 3 Categories
1. Torah
Most important text
Divine instruction and guidance or "Written Law”
Books are Genesis, Exodus, Leviticus, Numbers,
Deuteronomy
Covers history from creation through the Exodus and
wandering in the desert
613 commandments from God
Continued…
2. Prophets: Words and revelations of the minor
and major prophets
Ezekiel, Isaiah, Amos, Jonah, etc.
3. Writings: poetic and devotional material written
and used during the same time as the Prophets,
words and works of the sages
Psalms, Proverbs, Job, Ruth, Esther, Daniel, etc.
The Talmud
– Oral tradition passed to Moses and beyond
– Finally written down in the 2nd century
– Contains info on rituals, marriages,
agricultural laws, festivals, etc.
The Nature of God
Covenants with good people
– Responds to their needsdeliverance
Guides & directs His people
Compassionate
Controls with justice
Source of forgiving, redeeming love
Establishes peace on earth
The “Name” of God
Written by Hebrew consonants YHVH
– Means “I am”
Jews do not have a personal name for God
– Christians and others have Anglicized it to Yahweh or
Jehovah
– Written by Orthodox Jews as G-d
God referred to as:
– Adonai (The Lord)
– Elohim, or HaShem (the Name) - the unpronounceable
name of God
A Few Main Beliefs
Jews do not believe in
"original sin" (no need for
a "savior" in the Christian
sense)
The Ten Commandments
– first 4 have to do with our
relationship with God
– Next 6 refer to our
relationship with other
people
continued
Importance of family
Story/experience of exile and exodus
– "Let my people go."
– Compassion and concern for freedom of all
peoples
– history of continual fight for freedom and
continued survival
Humans
God’s highest creatures
– Earth has been given to them for food & pleasure
– They are the “caretakers”
Created in God’s image
– Each is a soul and body united
– Each should have a fellowship with God
Responsible
– Answer to God for conduct
– Humans have choices/can make decisionssuffer
consequences
Problem for Humans
Rebellion against God
and consequential
expulsion
– Adam and Eve
Who is the Messiah?
– Has not arrived yet to
usher in a new age
– He is expected
Life after Death
Emphasis on good life on earth more than
good afterlife
References in Psalms to heaven and hell
– Influenced by Zoroastrians?
– Lack specific descriptions of life beyond death
Rituals
Jewish calendar based on lunar month
Sabbath/Shabbat
– Observed each week
– Sundown on Fridaysundown on Saturday
Rosh Hashanah
– New year
– Begins the Days of Awe
– Concentrate on prayer, contemplation, self-searching
Yom Kippur
– 10th day (of awe)
– Holiest day observed
– Repentance: 24 hours of atonement and fasting
Shabbat dinner
Sweets for a sweet new year
continued
Chanukkah
– Celebrated
rededication of
Jerusalem temple in
164 BCE (after
destruction by Greeks)
– Sacred oil lasted 8
days for celebration
– Minor festival
Passover
Most important holiday
Marks deliverance form slavery in Egypt
under Moses’ leadership
Sacred meal: seder
– Unleavened bread (matzah)
Mitzvah
613 mitzvot
258 positive, 365 negative
Boys: 13+1 day, girls 12+1 day
– Bar Mitzvah means “son of the commandment”
Commands from God
– No immediate reward
– Obedience rewards in afterlife