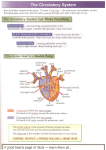
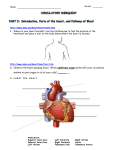
* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download When Oxygen Goes Bad or How Not to Kill a Small Child with O2
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
When Oxygen Goes Bad or How Not to Kill a Small Child with O2 Karim Rafaat, MD Nice Things Can Hurt You First, a simple example The PDA Fetal Circulation Fetal Circulation is Parallel Oxygenated Blood from the umbilical vein enters the RA Some mixes with systemic blood and is ejected by the RV into the PA Most gets preferentially shunted across the Foramen Ovale, joins with a touch of blood from the pulmonary veins in the LA, then is ejected by the LV The PA and Aortic flows are connected by the Ductus Arteriousus Relative resistances of systemic and pulmonary vascular beds ensure a well perfused body Transitional Circulation Once born, O2 ensures a decrease in the resistance of the pulmonary vasculature, to below the level of SVR The decrease in RVEDP, and thus RAP, leads to a functional closure of the formaen ovale Oxygen and a decrease of maternal prostaglandins leads to the closure of the ductus arteriosus But this closure does not always occur Usually we see this secondary to extreme prematurity PDA Now, there exists a path of variable size (we will assume big for this talk) through which blood from the aorta may shunt through to the pulmonary circulation Qp:Qs So, what determines our ratio of pulmonary to systemic blood flow? Or, Qp:Qs OHM’S LAW: V=IxR V is voltage, or, another way, driving force V = Pressure difference I is current or flow I = CO R is, in both cases, resistance Qp:Qs and PDAs Rearranged: I=V/R or Q = ΔP / R ΔP can be affected by way of inotropy, but this has little effect on the ratio of pulmonary to systemic flow The resistances of the two circuits are separate, and can thus be manipulated in a way that can effect flow differentially Resistance Resistance to Pulmonary flow is determined by Valvar or subvalvar pulmonary stenosis Pulmonary arteriolar resistance Pulmonary venous and left atrial pressure In part determined by: amount of pulmonary blood flow restriction of outflow through left atrioventricular valve Resistance Resistance to systemic flow determined by: Presence of anatomic obstructive lesions Aortic valve stenosis Arch hypoplasia or coarctation Subaortic obstruction Systemic arteriolar resistance Qp:Qs The most easily alterable aspects are thus the resistances of the respective vascular beds The problem of balancing the flows can be somewhat simplified to balancing the ratio of PVR:SVR Useful, as the majority of therapies available to us that affect flow differentially do so by way of manipulation of the resistance of the respective vascular beds Why is this important? Physiology with a high Qp:Qs brings with it a relatively low systemic oxygen delivery Low systemic DO2 leads to tissue hypoxia, anaerobic metabolism, and eventual end organ damage So…… Getting on with it Not only will O2 hurt the retina of tiny babies with ROP It will decrease their PVR, increase their Qp:Qs, thus decreasing their systemic oxygen delivery. This can lead quickly to acidosis and end organ damage It will also drastically decrease their DBP, to the point that LV perfusion is impaired This is why most NICU transporters have O2 blenders, so a concentration of O2 other than 100% can be delivered to the child. So What, just PDAs? Nope, this issue of balancing pulmonary and systemic flows in the face of a parallel circulation to ensure adequate peripheral DO2 occurs in quite a few other lesions Ill move through these quickly, as some of you may never ever hear of them again HLHS The most common is Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome 1. PFO 2. hypoplastic aorta 3. Patent PDA 4. aortic atresia 5. Hypoplastic left ventricle Mixing occurs via a patent PDA HLHS post Norwood Stage I We see this lesion usually after the stage 1 Norwood operation BTS supplies pulmonary flow Atrial septectomy Pulmonary trunk disconnected from MPA MPA and Aorta anastomosed to form a neo-aorta DORV Double Outlet Right Ventricle Both the aorta and pulmonary artery arise from the RV Accompanied by a VSD D-TGA with VSD Aorta and Pulmonary Artery arise from the wrong ventricle Mixing occurs through the VSD CAVC Complete AV Canal atrial septal defect abnormal tricuspid valve abnormal mitral valve ventricular septal defect Truncus Arteriosus single large arterial trunk arises from both ventricles, large VSD just below the trunk Tetralogy of Fallot ventricular septal defect (VSD) pulmonary (or right ventricular outflow tract) obstruction overriding aorta. Right ventricular hypertrophy Qp:Qs In lesions with parallel circulation, the total CO of the usually single ventricle is shared between pulmonary and systemic circulations The ratio of Qp:Qs describes the relative amount of pulmonary and systemic blood flow The absolute value, however, is a representation of total cardiac output Qp:Qs With complete mixing lesions, the ventricular output is the SUM of Qp and Qs Cause there’s, effectively, one ventricle The higher the ratio, the higher the demand on the heart So, a Qp:Qs of 2:1 means that the heart is pumping about 3 “cardiac outputs” It must maintain such a high output in an attempt to allow for acceptable systemic oxygen delivery What does this mean? Ventricular wall tension and myocardial oxygen demand are increased in the dilated, volume overloaded ventricle Leads to myocardial dysfunction and AV valve regurgitation Prolonged increased pulmonary volume will lead to pulmonary vascular bed remodeling can lead to increased pulmonary vascular resistance, which makes single ventricle surgical repair impossible So, even over the course of a 5 min transport from the NICU to the OR 100% O2 will Increase Qp:Qs increasing total myocardial workload and oxygen demand Decrease systemic oxygen delivery, leading to acidosis and end organ damage The combination of the above two can lead to myocardial ischemia How do we know when we should exercise caution? Our Clues for Caution The Cath Report If a pt has a complex cardiac lesion, they have probably either had an echocardiogram or gone to the cath lab The cath report will describe systemic and pulmonary resistences in Woods units, and even give you the Qp:Qs The Echo The lesion will be described. Look it up……. The Saturation that the ICU is allowing to be “acceptable” If the patient has a cardiac lesion, and the ICU is allowing a saturation of 70% as acceptable, this should (ideally and hopefully) indicate that this is the point of optimal Qp:Qs and thus optimal DO2. Keep it there Our Clues for Caution The Bedside Nurse If they insist theres a good reason for allowing this child to have sats of 75% and be on 21% O2, there may be a reason for it Bottom Line More isn’t always better Except if its cowbell Oxygen is a drug It can dramatically alter pulmonary vascular resistance and thus systemic perfusion in a way that may cause acidosis and end organ damage We can delve into more detail with Fick, graphs etc next time.