* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Circulatory System has Three Functions good
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Your circulatory system's pretty great. It comes in two bits - the pulmonary and systemic circuits.
The blood goes round one, then the other, passing through each side of the heart in turn.
The Circulatory System has Three Functions
:tRANSPORT
- moving things around the body in the
bloodstream, like oxygen, nutrients (like glucose), water and waste.
BODY TEMPERATU R('CONTRO(
-
more blood near the skin
cools the body quicker. That's why your skin looks redder after exercise.
- moving antibodies around the
body to fight disease. Blood clotting seals cuts.
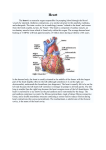
The Human Heart is a Double Pump I
pulmonary
artery
inferior
vena cava
semilunar valves
bicuspid (mitral)
valve
septum
_
Oxygenated blood has more oxygen.
It's found in all arteries (except the pulmonary artery).
_
Deoxygenated blood has less oxygen.
It's found in all veins (except the pulmonary vein).
The stroke volume is the amount of blood pumped per beat.
You can use it to work out the amount pumped per minute:
The heart rate is the number oftimes the heart beats in one minute.
CARDIAC OUTPUT = STROKE VOLUME x HEART RATE
good hearty page of facts -
learn them all...
I
Humans have a Double Circulation
I
Each time a blood cell goes right round your body, it goes through the heart twice
- that's double circulation.
It happens because there are two circuits:
The systemic circuit
It carries:
1) oxygenated
is the main circuit.
blood around the body in the arteries.
E'---
2) deoxygenated blood back to the heart along the
this then gets reoxygenated in the pulmonary circu'Lo
The pulmonary circuit
lungs. It carries:
t
I.
,At;
includes the heart and
1) deoxygenated blood from the heart to the
lungs to be oxygenated.
The oxygenated blood
then goes back to the heart to be pumped around
the systemic circuit.
The Blood is Under Pressure-I
,.
.@.
.
~~
Your pulse is just the increase and decrease in pressure in the artery as your heart pumps blood.
Blood pressure can be measured using a sphygmomanometer.
It gives two readings:
SYSTOLIC
PRESSURE -
DIASTOLIC
PRESSURE -
the pressure of the blood
the pressure of the blood
in the arteries when the left ventricle
in the arteries when the left ventricle
I·Blood Pressure is Affected by Loads of Things I
These things affect your blood pressure:
AGE -
blood pressure tends to increase with age.
GENDER
generally
-
EXERCISE
-
higher in men.
increases blood pressure in the short term, but reduces it in the long term.
increases blood pressure.
STRESS -
If your blood pressure remains high, you're at higher risk of these:
ANGINA
-
sharp pains in the chest, caused by the heart not getting enough oxygen.
HEART ATTACKS
STROKES
-
-
the heart stopping
because of oxygen starvation.
damage to the brain because of oxygen starvation.
contracts,
relaxes,
Warm-up Questio
1) Which one of the following is not a function of the circulatory system transporting oxygen, controlling body temperature or improving muscle size?
2)
How many circuits are there in the circulatory system -
one, two or five?
3)
What type of blood is carried back to the heart (except in the pulmonary vein)?
4)
Which type of blood vessel carries blood away from the heart?
5)
Which type of blood cell carries oxygen?
6)
Which type of blood cell fights disease?
Worked Exam Questi
Have a look at these, then move on to the next page for some real work ...
1
List the three functions of the circulatory system.
Tr.~m.~pqrt~tkm
..(qf l?xyg,~n!nf.!:t.r.~~n.~?(w~t.~r.fw~?t.~
J.
fP.!J."t.r.9.!.
qf
.l?,9,qy.
t~lJ!p~r.~t.l:I.J:'.~)
.
\
.
prp..~~ftlQn!f~gh.~~lJg
..~!!.~~g.~~
.
(3 marks)
2
a)
Name the parts labelled A to E in the diagram of a human heart below
A
l(.~lJg
..f~yg
.
B
.t:'/gh.~.~t.r:!.l:I.lJ!
.
c
D
left ventricle
.........................................................
p~!mp.!J.~rY
..l!.~~n
.
E .........................................................
aorta
(5 marks)
b)
Describe the differences between the pulmonary circulation and the systemic
circulation of blood.
.=..
~f.!/fJ1PlJ.qr.y q,~!:r.(~f?
.4~p,~yg.~lJ.q.~~4.
.!?!pP,4.
lr9.!!1..
fh.~.h~qt:'."P..
fp ."P.h~
.
qlJ.4. p'~yg.~lJ.qJ~4.
.!?!pP,4. .!?~q.~
J9.. ~b~.
h.~~rf: f?Y?~.~fJ1!.q,
.=.p~rr(~~
l~!,!.g?.
l?~yg~!,!q"p'~4..
p!t?9.4. .~r9.~p4..~h~.r.~?f.
pf .~~~. P..t?qy
Say what type of blood is being moved, not just where it's going.
.
(3 marks)