* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System Notes
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
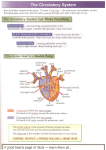
Circulatory System The heart, blood, and blood vessels make up the cardiovascular component of the circulatory system. It includes the pulmonary circulation, a "loop" through the lungs where blood is oxygenated. It also incorporates the systemic circulation, which runs through the rest of the body to provide oxygenated blood. The pulmonary circulatory system sends oxygen-depleted blood away from the heart through the pulmonary artery to the lungs and returns oxygenated blood to the heart through the pulmonary vein. Oxygen-deprived blood enters the right atrium of the heart and flows through the tricuspid valve (right atrioventricular valve) into the right ventricle. From there it is pumped through the pulmonary semilunar valve into the pulmonary artery on its way to the lungs. When it gets to the lungs, carbon dioxide is released from the blood and oxygen is absorbed. The pulmonary vein sends the oxygen-rich blood back to the heart. The systemic circulation is the portion of the circulatory system is the network of veins, arteries and blood vessels that transports blood from heart, services the body's cells and then re-enters the heart. Diseases of the circulatory system According to the American Heart Association, cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death in the United States. Because of its vastness and critical nature, it is one of the systems of the body most prone to disease. One of the most common diseases of the circulatory system is arteriosclerosis, in which the fatty deposits in the arteries causes the walls to stiffen and thicken the walls. The causes are too much fat, cholesterol and calcium. This can restrict blood flow or in severe cases stop it all together, resulting in a heart attack or stroke. Another circulatory is disease, hypertension — commonly called high blood pressure — causes the heart to work harder and can lead to such complications as a heart attack, a stroke, or kidney failure. An aortic aneurysm occurs when the aorta is damaged and starts to bulge or eventually tear, which can cause severe internal bleeding. This weakness can be present at birth or the result of atherosclerosis, obesity, high blood pressure or a combination of these conditions.