* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GCF and LCM - LCA Grade 7 Class 2014
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
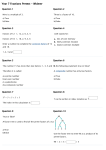
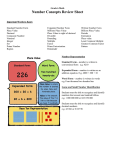
Name____________________ GCF and LCM The Greatest Common Factor - is the largest factor two or more numbers have in common. ***All numbers will have 1 in common*** There are two methods for finding GCF: 1) List the factors of the numbers then choose the largest Example: 12 and 18 12 = 1,2,3,4,6,12 18 = 1,2,3,6,9,18 The GCF of 12 and 18 is 6. 2) The other method involves prime numbers and prime factorization. a) list the prime factors of the numbers using a factor tree b) If a number appears on both lists, circle both numbers c) Multiply one of each pair of circled numbers and that is the GCF Example: 36 and 90 The prime factors of 36 = 2 • 2 • 3 • 3 The prime factors of 90 = 2 • 3 • 3 • 5 Since they have 2, 3, and 3 in common, we multiply 2 • 3 • 3 and the GCF is 18. ****If there are no numbers in common on both lists then the GCF is 1 Multiples The first 5 multiples of 7 are = 7, 14, 21, 28, 35 You get that by going: 7•1=7 7 • 3 = 21 7 •2 = 14 7 • 4 = 28 7 • 5 = 35 The first 6 multiples of 20 are = 20, 40, 60, 80. 100, 120 You get that by going: 20 • 1 = 20 20 • 3 = 60 20 • 5 = 100 20 • 2 = 40 20 • 4 = 80 20 • 6 = 120 Least Common Multiple - the smallest non zero multiple that two or more numbers have in common. There are two methods for finding LCM. 1) write out the multiples of the numbers and choose the smallest multiple in common that is greater than zero Example: Find the LCM of 18 and 27 The multiples of 18 are = 18, 36, 54, 72, 90 The multiples of 27 are = 27, 54, 81 The LCM = 54 2) You can also use prime numbers to find LCM a) write out the prime factors of both numbers using factor trees b) write each factor one time c) write out the greatest number of times that each factor appears when looking at separate lists Example: Find the LCM of 18 and 27 The prime numbers of 18 = 2 • 3 • 3 The prime numbers of 27 = 3 • 3 • 3 The factors are 2 and 3. 2 appears most on the list for 18 3 appears most on the list for 27 Multiply 2 • 3 • 3 • 3 = 54 The LCM is 54 Find the LCM of 16, 30, and 27. 16 = 2 • 2 • 2 • 2 30 = 2 • 3 • 5 27 = 3 • 3 • 3 The factors are 2, 3 and 5. 2 appears most on the list for 16 ( 2• 2 • 2 • 2) 3 appears most on the list for 27 (3 • 3 • 3) 5 appears most on the list for 30 (5) Multiply 2 • 2 • 2 • 2 • 3 • 3 • 3 • 5 = The LCM is 2160 Lowest Common Denominator Find the Least Common Multiple of the denominators and you’ve found the Lowest Common Denominator 3 11 Example: Find the lowest common denominator of and 15 24 The first step is to find the LCM of 15 and 24 which are the denominators 15 = 3 • 5 24 = 2 • 2 • 2 • 3 The factors are 2, 3, 5 3 appears most on 15 and 24. (3) 2 appears most on 24 (2 • 2 • 2) 5 appears most on 15 (5) Multiply 2 • 2 • 2 • 3 • 5 = 120 The Lowest Common Denominator is 120 Factors, Prime Factors, and Multiples Factors are numbers that divide evenly into another number. Example: The factors of 20 are --- 1,2,4,5,10,20 Each of the above factors divides evenly into 20. There are certain easy methods to test divisibility - to see if a number is a factor of another number. If the number is divisibly by: Test: Examples 2 The number ends in 2,4,6,8,0 1,350 or 21,988, or 752 3 Add up all the digits of the number and divide the sum by 3 4 Divide 4 into the last two digits 736 ---> 4 goes into 36 evenly 720 ---> 4 goes into 20 evenly 5 If the number ends in 5 or 0 430 or 3755 6 If both 2 and 3 are factors 780 ends in o so it's divisible by 2; The sum of the digits is 15 and that's divisible by 3 8 Divide 8 into the last 3 digits 20,504 --- divide 8 into 504. It goes in evenly so 8 is a factor 9 Add up all the digits of the number and see if 9 goes in evenly 8190 = 18; 9 goes into 18 evenly so 9 is a factor 573 = 15; 3 goes into it evenly If 9 is a factor of a number, 3 must also be a factor BUT if 3 is a factor, 9 is not always a factor*** 10 The number will end in 0. 230; 6000; 7540 For numbers 7, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, etc. you have to actually divide. Prime numbers and Composite Numbers Prime Numbers have only two factors - 1 and itself Example: The factors of 17 are 1 and 17 only. No other number divides in evenly. Other prime numbers are: 2,3,5,7,11,13,19,23,29,31 Composite numbers have more than 2 factors - 1, itself, and at least 1 other number Example: 51 - 1, 51 and 3 and 17 To find if a number is prime or composite, use the tests of divisibility. Practice Worksheet 1 Find all the factors of the following numbers: (Both prime & composite) 1. 26 2. 40 3. 56 4. 39 State whether each number is divisible by 2,3,4,5,6,8,9,10. List all the possibilities 5. 135 6. 891 7. 5455 8. 3720 9. 414 10. 3870 11. 15,408 12. 1527 Fill in the missing number to make the following divisible by 6: Then make each divisible by 4 13. 402_ 2 14. 71_ 4 15. 1000_ Tell whether each number is prime or composite. If it is composite, tell one other factor that it is divisible by. 16. 57 17. 37 18. 56 19. 11,121 20. 63 21. 117 22. 113 23. 12,543 Using a factor tree, find the prime factorization of each of the following numbers: 24. 210 25. 280 26. 336 27. 1024 28. 415 29. 550 30. 88 31. 67 Multiply: 32. .006 • .06 = 33. 4.5 • 65 = 34. 1.46 • 2.8 = 35. 14.89 • 1.8 = 36. .3002 • .7 = 37. 1.62 • .009 = 38. 21.1 • 6 = 39. 98 • 1.4 = 40. .08 • .0004 = Divide 41. 2418 Solve: 45. n + 2 = 3.98 1.25 .6.0498 42. 46. 7y - 5 = 30 43. 47. 3025 44. .18.54036 1.5n = 3.9 48. y - 3 = 48 .271 Practice Worksheet 2 Find the GCF and LCM of the following numbers using the factor method: 1. 8 and 14 2. 14 and 21 3. 24 and 42 Find the GCF and LCM of the following numbers using prime factorization: 4. 28 and 45 5. 45, 60, 160 6. 32, 80, 120 7. 21 and 28 8. 18 and 32 9. 70 and 120 10. 20 and 50 11. 120 and 35 12. 9, 12, and 15 13. 240 and 300 14. 80 and 180 15. 70 and 160 16. 17 and 53 17. 175 and 150 18. 135 and 65