* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 9 - Marketing Strategies
Market analysis wikipedia , lookup
Visual merchandising wikipedia , lookup
Product placement wikipedia , lookup
Digital marketing wikipedia , lookup
Sales process engineering wikipedia , lookup
Youth marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multi-level marketing wikipedia , lookup
Neuromarketing wikipedia , lookup
Guerrilla marketing wikipedia , lookup
Grey market wikipedia , lookup
Price discrimination wikipedia , lookup
First-mover advantage wikipedia , lookup
Customer relationship management wikipedia , lookup
Dumping (pricing policy) wikipedia , lookup
Product lifecycle wikipedia , lookup
Darknet market wikipedia , lookup
Marketing mix modeling wikipedia , lookup
Perfect competition wikipedia , lookup
Direct marketing wikipedia , lookup
Service parts pricing wikipedia , lookup
Customer engagement wikipedia , lookup
Customer satisfaction wikipedia , lookup
Marketing plan wikipedia , lookup
Integrated marketing communications wikipedia , lookup
Target audience wikipedia , lookup
Pricing strategies wikipedia , lookup
Street marketing wikipedia , lookup
Multicultural marketing wikipedia , lookup
Green marketing wikipedia , lookup
Supermarket wikipedia , lookup
Target market wikipedia , lookup
Segmenting-targeting-positioning wikipedia , lookup
Advertising campaign wikipedia , lookup
Sensory branding wikipedia , lookup
Marketing channel wikipedia , lookup
Market penetration wikipedia , lookup
Services marketing wikipedia , lookup
Global marketing wikipedia , lookup
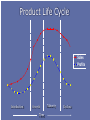
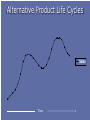
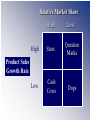
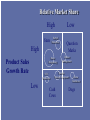
Chapter 9 Marketing Strategies Chapter 9 slides for Marketing for Pharmacists, 2nd Edition Learning Objectives Describe three generic marketing strategies. Explain product life cycles and their implications for pharmacy products and pharmacist services. Discuss product portfolio management and how pharmacists might use it. Compare and contrast convenience strategies used by pharmacies. Discuss the potential downside of overreliance on convenience strategies. Define relationship marketing and explain its advantages over transactional marketing. Suggest ways of identifying innovative products and services. Generic Marketing Strategies All other strategies are just variations. TIP Be cheaper or different. Three generic strategies Forms of Competitive Advantage Broad Number of Target Markets (Scope) Narrow Cost Differentiation Cost Leadership Differentiation Focus •Low price •Efficiency •Broad product offering •Broad market Wal-Mart Cost Leadership •Higher price •Unique mix •Broad market Medicine Shoppe Differentiation Focus •Higher price •Unique mix, •Narrow market Independents Choosing an approach No strategy is inherently better. Depends on one’s capabilities and environment Porter says to choose one. Others disagree. What differentiates you from other pharmacists? Product Life-Cycle Strategies Products, like plants and animals, have a life. TIP Don’t let your product die an early death. Product Life Cycle Sales Profits Introduction Growth Time Maturity Decline Alternative Product Life Cycles Sales Time Lessons for PLC Any new idea takes time and effort to bear fruit (e.g., pharmaceutical care). If successful, time and effort must be expended to keep them successful. All products and innovations eventually die. Portfolio Strategies A portfolio is all products and services offered by a business. TIP Consider the mix of your portfolio. Relative Market Share High Low High Stars Question Marks Low Cash Cows Dogs Product Sales Growth Rate Relative Market Share High Stars Low Herbal Medicines High Basic Dispensing Product Sales Growth Rate OTC Medicines Low Question Marks Disease Management Durable Medical Equipment Cash Cows Home Healthcare Dogs Managing your portfolio 1. Identify your primary target markets. 2. Inventory your current service offerings. 3. Identify which of your current services are viable with your target markets. The goal is to offer different levels of services to the target markets. 4. Identify which services you need to add or subtract to round out your service portfolio. Convenience Strategies Pharmacy convenienc e is an important factor in pharmacy patronage. TIP Convenience varies among people and situations. The downside of convenience Fast will soon be slow. It can be expensive. Affects professional image. Types of convenience Access - easy to reach Search - easy to identify and select Possession - easy to obtain Transaction - easy to purchase and return Conduct a convenience audit Go through a pharmacy with the eyes of customer. How easy is it to Get into and through the pharmacy? Find what you want? Get what you want? Purchase what you want? Relationship Marketing Strategies The goal is to keep customers . TIP Loyal customers are more profitable. Goal of relationship marketing (RM) Build and maintain a base of committed, profitable customers Attract Retain Enhance Bucket Theory of RM Attract business through sales, advertising, promotion Bucket = a company whose goal is to be filled with business Lose business through poor service and not meeting needs Benefits of RM To your patients Greater value and less hassle Reduces search Special needs of customer accommodated Customer knows what to expect Simplifies and reduces stress of buying process To your business Loyal customers Purchase more Provide positive word of mouth (WOM) Are less price sensitive Cost less Are more profitable The $100,000 customer (1) $ Spent/yr by avg pt. (1)__________ (2) Avg # yrs as customer (2)__________ (3) Customers from WOM (4)__________ (1) x (2) x (3) = Lifetime value (3)__________ Do you practice RM? Do you have formal RM strategies? Do you commit enough resources to RM? Are existing patients given concrete reasons to stay with you? Do you keep a database of patient preferences, likes, and dislikes? Do you know the lifetime value of customers? Innovation Strategies: Innovate to differentiate. Any change in the 4 P’s offered that customers perceive as new. It’s not an innovation unless someone thinks it is. Innovations can be used to Find new customers for the product (e.g., pets). Increase usage for existing products (e.g., loyalty card). Expand a product line (e.g., offer disease management). Expand distribution intensity (e.g., more pharmacies). Expand distribution over a wider geographic area. Penetrate markets of competitors (e.g., develop a service that will draw away a competitor’s target customers). Innovations can be used to Find new uses for a product (e.g., baking soda). Disruptive innovations Technological innovation, product, or service that overturns current market leaders. When customers are overserved in the market, they seek lower cost, lower quality (but good enough) products. Substitute OTC for Rx medicine, midwife for obstetrician, ATM pharmacy for local pharmacist. Lower-end disruptive innovations: dominate an existing market by filling a role in a new market that the older technology could not fill (expensive physician practices competing with low-cost store clinics) holistic medicine, 24-hour services, convenient health care. New-market disruptive innovation: fulfills new, unmet need Treating allergies Specialists Family Physicians Nurse Practitioners/ Physician Assistants Self-Care Providers Treating allergies Specialists Office Diagnostics Family Physicians Minute Clinics Nurse Practitioners/ Physician Assistants Self-Care Providers Rx-to-OTC Identifying innovations Challenge everything. Focus on the customer’s viewpoint. Make things easier, faster, cheaper, better. Tap into emotions. New Market: Travel clinics New Market: Pet Medicine In the United States, $35.9 billion was spent on pet-related products in 2005; this is increasing 5% each year. 63% of households have at least one pet. 73 million dogs (32% of households) Average vet bill $187 per year 90 million cats (27% of households) Average vet bill $147 per year Source: Brandweek.com Expand service intensity: specialty pharmacy Change the experience: holistic pharmacies Increase usage for existing products: customer relationship management (CRM) Loyalty cards Summary Pharmacists have traditionally relied on a limited number of marketing strategies in the marketing of their services. This chapter presents several new strategies. Questions?