* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EnvSci Chapter 3 Review Answers
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
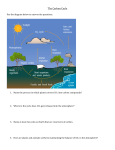
Environmental Science Name _Key_____________________ Period ___ Date _______ Chapter 3 - The Dynamic Earth Review The Geosphere Compositional Layers (list all three and give a brief description of each): 1. _Crust_ - _The hard outer surface of the Earth_ 2. _Mantle_ - _The moving inner portion of the Earth_ 3. _Core_ - _Dense center of the Earth_ Structural Layers (list all three and give a brief description of each): 1. _Lithosphere_ - _Cool rigid outer layer of the Earth, contains the Crust and the top of the Mantle_ 2. _Asthenosphere_ - _The Plastic layer that flows very slowly and causes techtonic motion_ 3. _Mesosphere_ - _The middle layer of the Earth_ 4. _Outer Core_ - _The dense liquid layer of the Earth made of liquid nickel and iron_ 5. _Inner Core_ - _The dense solid layer of the Earth made of nickel and iron, made solid by extreme pressure_ Define: Magma - _Molten rock found underground_ Tectonic Plate - _The large sections of lithosphere that float around on the mantle_ Earthquake - _Vibrations along faults as the plates slip past each other_ Volcano - _A mountain made from magma as it erupts through the surface of the Earth_ Mudflow - _When hot ash from a volcano mixes with water to form a deadly mudslide_ Erosion - _When wind or water or slowly deteriorate the surface of the Earth_ What is the temperature of the inner core? _4000oC -5000oC_ (make sure you give a unit!) What causes the inner core to be solid? _intense pressure_ In which geologic zone is 1/3 of the Earth’s mass found? _The Core (both Inner and Outer Core)_ Where does most geologic activity happen? _Tectonic plate boundaries_ What is the scale used to measure earthquakes? _Richter Scale_ How do mountain ranges form? _Collisions between two tectonic plates_ What two things cause erosion? _wind_ & _water_ How can volcanoes affect sunlight reaching the Earth? _They can emit large clouds of ash into the atmosphere and block incoming sunlight_ The Atmosphere List all four layers and describe the temperature variation as you go up: 1. _Thermosphere_ - _2000 oC+ zone of extremely thin Nitrogen and Oxygen_ 2. _Mesosphere_ - _The coldest layer of the atmosphere_ 3. _Stratosphere_ - _Home of the ozone and gradually warming from the Troposphere, warmer as you go up_ 4. _Troposphere_ - _The level we live in, becomes less dense and colder as you go up_ What is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere? _Nitrogen_ What is the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere? _Oxygen_ What is the ozone layer? _A layer of O3 (oxygen) that is really good at absorbing UV radiation_ Where is the ozone layer found? _The Stratosphere_ What causes the density of the troposphere to increase as you get closer to the Earth? _Gravity and the pressure of the layers above_ What organisms produce oxygen? _Plants, algae, phytoplankton_ What causes weather? _Movement of air in the Troposphere_ Define: Conduction - _Transfer of heat energy by direct contact_ Convection - _Transfer of heat by circular currents (happens in the oceans, the mantle and the atmosphere)_ Radiation - _Transfer of energy by electromagnetic waves, and it can happen through space_ What effect do Greenhouse gases have on the environment? _Trap heat in the atmosphere like a blanket_ How much of the sun’s radiation reaches the Earth? _2 billionths_ How much of that energy actually makes it through the atmosphere to the Earth? _About 50%_ What happens to the rest of that energy? _It is absorbed, scattered or reflected_ What is the hottest layer of the atmosphere? _Thermosphere_ The Hydrosphere The Water Cycle (list all three parts and give a brief description of each): 1. _Evaporation_ - _When liquid water is heated and becomes water vapor_ 2. _Condensation_ - _Water vapor forms droplets on dust particles_ 3. _Precipitation_ - _Large droplets join together and eventually fall from the sky (rain, snow, sleet or hail)_ Define: Salinity - _Salt concentration_ Tributary - _Smaller streams or rivers that flow into larger ones_ Groundwater - _Water that is filtered slowly into the Earth_ Aquifer - _A rock layer that stores and allows the flow of groundwater_ Recharge Zone - _The surface of the land where water enters an aquifer_ Where is most fresh water found? _Glaciers and polar ice_ Why does ocean water have a higher salinity than freshwater? _The salts build up as they are collected from rivers entering the ocean, and over time the evaporation of ocean water leaves the salt behind_ Are the oceans separate bodies of water? Why or why not? _We can consider them one World Ocean because they are all connected_ In the blanks below list the two types of currents, tell where they flow and why. 1. _surface current_ flows on the _surface of the ocean_because of _wind_ 2. _deep current_ flows on the _the ocean floor_because of _convection of water_ Which of these two has the greater effect on climate? _Surface currents_ How do the oceans help maintain the Earth’s temperature? _They absorb heat energy and slowly radiate it back into the atmosphere_ The Biosphere Define: Biosphere - _The part of the planet in which life can exist_ Open system - _One in which transfer of matter or energy can enter or leave_ Closed system - _One in which matter or energy do not enter or leave_ Which system is the Earth in regards to energy? _Open System_ Which system is the Earth in regards to matter? _Closed System_ What do plants require? _Sunlight_ What form of energy does sunlight take as it travels through space to the Earth? _Electromagnetic radiation_ Why is cycling of matter important to the biosphere? _There are limited resources available, as things die the matter in them goes back into the biosphere to be recycled in future generations of life_ What are the basic requirements of life? _Liquid water_, _ temperatures between 10oC and 40oC_ & _a source of energy_ What are phytoplankton? _Microorganisms that produce energy storing molecules using sunlight and release oxygen into the atmosphere_ Name three ways gravity helps all of these systems function the way they do: 1. _Causes increases in pressure and temperature as you get closer to the center of the Earth_ 2. _Allows convection in the mantle, atmosphere and hydrosphere_ 3. _It keeps the gases at the surface of the Earth and the solid materials in the center_