* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diseases of Muscular System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
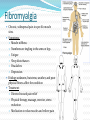
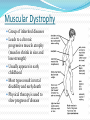
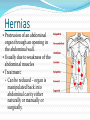
Fibromyalgia Chronic, widespread pain in specific muscle sites. Symptoms: Muscle stiffness Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs Fatigue Sleep disturbances Headaches Depression Etiology unknown, but stress, weather, and poor physical fitness affect the condition Treatment: Directed toward pain relief Physical therapy, massage, exercise, stress reduction Medication to relax muscles and relieve pain Muscular Dystrophy Group of inherited diseases Leads to a chronic progressive muscle atrophy (muscles shrink in size and lose strength) Usually appears in early childhood Most types result in total disability and early death Physical therapy is used to slow progress of disease Dushenne Muscular Dystrophy genetic disease passed in an X-linked recessive fashion - affects almost exclusively males Symptoms do not usually show up until child is 5-6 years old. Milder form called Becker muscular dystrophy Initial symptoms include: not being able to keep up with other children when running; developing a “waddling” run and eventually a “waddling” walk; difficulty going up stairs Later symptoms include walking on tiptoes; developing a lordosis; more frequent falling; and progressive weakness in the legs and later in the arms Final stages include weakness of chest muscles that lead to respiratory problems including pneumonia and eventually respiratory or cardiac failure Posture changes during progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy Myasthenia Gravis Chronic condition in which nerve impulses are not transmitted properly to the muscles Leads to progressive muscular weakness and paralysis Fatal when it affects respiratory muscles Etiology unknown May be autoimmune disease Antibodies attack the body’s own tissues No cure, and treatment is supportive Muscle Spasms or Cramps Sudden, painful, involuntary contractions of muscles Usually occur in legs or feet May result from overexertion, low electrolyte levels, or poor circulation Use gentle pressure and stretching of muscle to relieve spasm Strain/Sprain Overstretching or injury to a muscle and/or tendons Frequent sites include the back, arms, and legs Prolonged or sudden muscle exertion is usually cause Symptoms: Myalgia or muscle pain Swelling Limited movement Treatment Rest and elevation of extremity Muscle relaxants or pain medications Alternating heat and cold applications Hernias Protrusion of an abdominal organ through an opening in the abdominal wall. Usually due to weakness of the abdominal muscles Treatment: Can be reduced – organ is manipulated back into abdominal cavity either naturally or manually or surgically.