* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Chapter 5 Study Guide - Bennatti
Air well (condenser) wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Ocean acidification wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Meteorology wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
History of climate change science wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
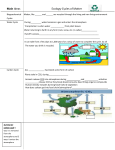
AP Chapter 5 Study Guide Vocabulary Biogeochemical cycle-cycling of carbon, water, nitrogen and other substances through the living and nonliving environment Combustion- rapid oxidation of organic molecules Nitrogen fixation- conversion of N2 to ammonia (NH3) by nitrogen-fixing bacteria or by lightening, combustion, industrial processes or volcanic activity Nitrification- conversion of ammonia (NH3) to ammonium (NH4+) to nitrates (NO3-) by soil bacteria Assimilation- absorption of nitrates, ammonia or ammonium and conversion into plant proteins and nucleic acids Ammonification- the conversion of biological nitrogen compounds into ammonia and ammonium ions. Denitrification- the reduction of nitrate to N2 Hydrologic cycle –water cycle Transpiration- evaporation of water from leaves Runoff-water running over the surface of the ground Watershed- all the land drained by a body of water Groundwater- water occupying cracks and pores in the ground Photochemical smog- brownish orange haze formed by chemical reactions involving sunlight, nitrogen oxides, and hydrocarbons. Some of the pollutants in photochemical smog include peroxyacetyl nitrates (PANs), ozone, and aldehydes. Acid deposition- sulfur dioxide and nitrogen dioxide emissions that react with water vapor in the atmosphere to form acids that return to the surface as either dry or wet deposition. Aerosols- tiny particles of natural or human-made pollution that are so small they stay suspended in the atmosphere for days or weeks Albedo- the proportional reflectance of Earth’s surface; glaciers and ice sheets have high albedos and reflect most of the sunlight hitting their surfaces while oceans and forests have low albedos Coriolois effect- the tendency of moving air or water to be deflected from its path to the right in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left in the Southern Hemisphere as a result of the rotation of the Earth Prevailing winds- major surface wind that blows more or less constantly Gyres- prevailing winds tend to blow in a circular pattern which create ocean currents in each ocean basin that flow in a circular pattern Upwelling- a rising ocean current that carries cold, nutrient-rich water to the surface Lithosphere – Earth’s outermost rigid rock layer that is composed of seven major and several minor plates Asthenosphere- the region of the mantle where rocks become hot and soft plate tectonics- the study of the processes by which the lithospheric plates move over the asthenosphere plate boundary- region where two tectonic plates meet subduction- process by which one tectonic plate descends under an adjacent plate seismic waves- vibrations that move through rock as a result of an earthquake faults- a fracture in the crust along which rock moves forward and backward, up and down, or side to side. Faults are often found along plate boundaries. focus- the place within the Earth that an earthquake originates epicenter-the location on the surface of the Earth directly above the focus magma- molten rock found within the Earth lava- molten rock that has reached the surface of the Earth 1. Describe the role organisms play in the carbon cycle. 2. Why are carbon, nitrogen, sulfur, phosphorus and water all important to living organisms? Which of these does not exist in a gaseous state as it cycles through the environment. 3 Describe two processes that remove carbon from the atmosphere. 4. List at least three processes that put carbon back into the atmosphere. 5. Describe one way humans can affect the carbon cycle. 6. The atmosphere is ____% nitrogen. 7. Why are plants unable to use nitrogen gas directly to form proteins and nucleic acids? 8. Which step of the nitrogen cycle does not involve bacteria? 9. What role do nitrogen-fixing bacteria play in the nitrogen cycle? 10. In which step of the nitrogen cycle do bacteria reverse the action of nitrogen-fixing and nitrifying bacteria by returning nitrogen (N2) back to the atmosphere? 11. Plants are able to absorb nitrogen when it is in the form of _________, __________ or _________. 12. Nitrogen is fixed by ________________, ____________________, _______________, ___________________, and _____________________. 13. Describe how humans can affect the nitrogen cycle. 14. Describe how humans can affect the phosphorus cycle. 15. Describe the role of organisms in the sulfur cycle. 16. Describe how humans have affected the sulfur cycle. 17. How are changes in global climate during the last century related to the carbon cycle? 18. Diagram the water cycle. 19. Describe the role of plants in the water cycle. 20. How have humans influenced the water cycle? 21. ____% of the sunlight that reaches Earth is reflected back as light and the remaining ____% is absorbed. 22. Compare the albedo of the following surfaces. Which has the highest albedo? a. ice; b. land; c. water 23. As polar ice caps melt, what does this suggest will happen to the percentage of sunlight that is absorbed by the Earth rather than reflected? 24. What causes seasons? 25. Why does Florida have a warmer climate than Maine? 26. What layer of the atmosphere is in contact with the surface of the Earth? How does the temperature change as altitude increases in this layer? 27. In what layer of the atmosphere is the ozone layer found? 28. Why is this ozone layer essential to life on Earth? 29. What layer of the atmosphere is hottest? 30. In what layer of the atmosphere does weather occur? 31. In what layer of the atmosphere do commercial jets fly? 32. List the layers of the atmosphere in order starting with the lowest. 33. What drives the circulation of the atmosphere? 34. What causes wind? 35. List three factors that affect air pressure. 36. Winds tend to blow from areas of ________ atmospheric pressure to areas of ______ atmospheric pressure. 37. Earth rotates from _______ to _________causing surface winds to be deflected. 38. Because of the Coriolis effect, winds curve to the _________ in the Northern Hemisphere and to the ___________ in the Southern Hemisphere. 39. Describe the location and direction of each of the three prevailing winds. 40. How does the Coriolis effect influence ocean currents? 41. What causes surface currents? 42. What causes deep ocean currents? 43. Explain how ocean currents influence climate. 44. What triggers an El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) event? 45. How does El Nino affect the fishing industry off the coast of South America? 46. How widespread geographically are the effects of El Nino? Choose one area of the world other than the Pacific coast of South America and describe how El Nino affects that area. 47. Describe how conditions change during a La Nina year. 48. Explain the difference between weather and climate. 49. Where would you observe a rain shadow effect? How does a rain shadow effect precipitation? 50. What conditions may lead to the formation of tornadoes? 51. In what regions of the world do tropical cyclones form? 52. Tropical cyclones are called ______ in the Atlantic, ________ in the Pacific and _______ in the Indian Ocean. 53. Why are tropical cyclones most common during summer and autumn months? 54. How has the intensity of tropical cyclones changed since 1970? What might contribute to this change? 55. Describe how the Himalayan mountains formed. 56. How much more energy is released by an earthquake that is 6 on the Richter scale compared to one that is 3 on the Richter scale? 57. What causes tsunamis? 58. Compare divergent, convergent and transform plate boundaries.