* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Year 8 - Portland Place School
Abuse of notation wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
A New Kind of Science wikipedia , lookup
History of statistics wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
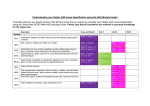
Mathematics Scheme of Work Year 7 New Mathematics Framework Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 1 YEAR 7: Overview of year 7 scheme of work New Maths Frameworking YEAR 7 Term 1 Term 2 Term 3 Assessment Tests Algebra 1 Sequences and functions (6 hours) Number 2 Fractions, decimals, percentages, ratio and proportion (5 hours) Number 1 Place values, integers, calculations (6 hours) Statistics 1 Geometry and Measures 1 Mensuration (perimeter and area) (4 hours) Algebra 2 Statistics including probability (5 hours) Equations and formulae (5 hours) Geometry and Measures 2 Coordinates, geometrical reasoning: lines, angles and shapes (3 hours) Algebra 3 Integers, powers and roots. Sequences, functions and graphs (5 hours) Statistics 2 Statistics (4 hours) Geometry and Measures 3 Number and Measures 3 Place value, calculations, calculator methods, measures (7 hours) Number 4 Geometrical reasoning: lines, angles and shapes. Construction (3 hours) Fractions, decimals, percentages, ratio and proportion (4 hours) Algebra 4 Equations and formulae (3 hours) Number 5 Place value, calculations including calculator methods, fractions, decimals, percentages, ratio and proportion, solving problems (6 hours) Geometry and Measures 4 Transformations (5 hours) Algebra 5 Statistics 3 Statistics, including probability (5 hours) Geometry and Measures 5 Sequences, functions and graphs, equations and formulae (4 hours) Geometrical reasoning: lines, angles and shapes; construction (3 hours) Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 2 Test 1 Test 2 Test 3 Test 4 Test 5 End of year test YEAR 7: AUTUMN TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Algebra 1 (6 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 1.1 Sequences and rules 1.2 Finding missing terms 1.3 Functions and mappings 1.4 Using letter symbols to represent functions 1.5 The general term (nth term) 1.6 An nth term investigation 1.1 Describe integer sequences. 1.2 Generate terms of a simple sequence given a rule (for example, finding a term from the previous term; finding a term given its position in the sequence). 1.3 Express simple functions in words, then using symbols; represent them in mappings. 1.4 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. 1.5 Generate sequences from patterns or practical contents and describe the general term in simple cases. 1.6 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures. Classify and visualise properties and patterns; generalise in simple cases by working logically. 1.1 Sequences and rules 1.2 Finding missing terms 1.3 Finding the general term (nth term) 1.4 Functional and mappings 1.5 Using letter symbols to represent functions 1.6 A function investigation Number 1 (6 hours) 2.1 Decimals 2.2 Ordering decimals 2.3 Directed numbers 2.4 Estimates 2.5 Column method for addition and subtraction 2.6 Solving problems 2.1 Understand and use decimal notation and place value. Multiply and divide integers and decimals by 10, 100, 1000, and explain the effect. 2.2 Compare and order decimals in different contexts. Know that when comparing measurements the units must be the same. 2.3 Understand negative numbers as positions on a number line. Order, add and subtract integers in context. 2.4 Make and justify estimates and approximations of calculations. 2.5 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. 2.6 Represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words and diagrams; use appropriate procedures and tools. 2.1 Decimals 2.2 Ordering decimals 2.3 Directed numbers 2.4 Estimates 2.5 Column method for addition, subtraction and multiplication 2.6 Solving problems 1.1 Describe integer sequences; generate terms of a simple sequence. 1.2 Generate terms of a simple sequence, given a rule (for example, finding a term from the previous term, finding a term given its position in the sequence). 1.3 Generate sequences from patterns or practical contexts and describe the general term in simple cases. 1.4 Express simple functions in words, then using symbols; represent them in mappings. 1.5 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. 1.6 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures. Classify and visualise properties and patterns; generalise in simple cases by working logically. Recall number facts, including positive integer complements to 100 and multiplication facts to 10 × 10, and quickly derive associated division facts. 2.1 Understand and use decimal notation and place value; multiply and divide integers and decimals by 10, 100, 1000, and explain the effect. 2.2 Compare and order decimals in different contexts; know that when comparing measurements the units must be the same. 2.3 Understand negative numbers as positions on a number line; order, add and subtract integers in context. 2.4 Strengthen and extend mental methods of calculation to include decimals, fractions and percentages. Make and justify estimates and approximations of calculations. 2.5 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. Extend to multiplying decimals with one or two places by single-digit whole numbers. 2.6 Classify and visualise properties and patterns; generalise in simple cases by working logically; draw simple conclusions and explain reasoning; understand the significance of a counter-example; take account of feedback and learn from mistakes. Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 3 YEAR 7: AUTUMN TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Geometry & Measures 1 (4 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 3.1 Length, perimeter and area 3.2 Areas of some 2-D shapes 3.3 3-D shapes 3.4 Surface area and volume of cuboids 3.1 Length, perimeter and area 3.2 Areas of some 2-D shapes 3.3 3-D shapes 3.4 Surface area and volume of cuboids 3.1 Know and use the formula for the area of a rectangle; calculate the perimeter and area of shapes made from rectangles. 3.2 Derive and use formulae for the area of a triangle, parallelogram and trapezium; calculate areas of compound shapes (Year 8 Framework objective). 3.3 Use 2-D representations to visualise 3-D shapes and deduce some of their properties. 3.4 Calculate the surface area of cubes and cuboids. Know and use the formula for the volume of a cuboid; calculate volumes and surface areas of cuboids and shapes made from cuboids (Year 8 Framework objective). Number 2 (5 hours) 4.1 Fractions 4.2 Fractions and decimals 4.3 Adding and subtracting fractions 4.4 Equivalences 4.5 Solving problems 3.1 Choose and use units of measurement to measure, estimate, calculate and solve problems in everyday contexts. 3.2 Choose and use units of measurement to measure, estimate, calculate and solve problems in everyday contexts. Know and use the formula for the area of a rectangle; calculate the perimeter and area of shapes made from rectangles. 3.3 Use 2-D representations to visualise 3-D shapes and deduce some of their properties. Make accurate mathematical diagrams, graphs and constructions on paper and on screen. 3.4 Know and use the formula for the area of a rectangle. Calculate the perimeter and area of shapes made from rectangles. Calculate the surface area of cubes and cuboids. 4.1 Express a smaller whole number as a fraction of a larger one. Simplify fractions by cancelling all common factors and identify equivalent fractions. 4.2 Convert terminating decimals to fractions: for 4.1 Fractions 4.2 Fractions and decimals 4.3 Adding and subtracting fractions 4.4 Calculations and equivalences 4.5 Solving problems 4.1 Express a smaller whole number as a fraction of a larger one; simplify fractions by cancelling all common factors and identify equivalent fractions. 4.2 Convert terminating decimals to fractions, for 23 example 0.23 = 100 . Use a diagram to compare two or more simple fractions. 4.3 Add and subtract simple fractions and those with common denominators. 4.4 Calculate simple fractions of quantities and measurements (whole-number answers). Multiply a fraction by an integer. Understand percentage as the ‘number of parts per 100’. Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. 4.5 Check results by considering whether they are of the right order of magnitude and by working the problem backwards. Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 4 23 example, 0.23 = 100 . Use diagrams to compare two or more simple fractions. 4.3 Add and subtract simple fractions and those with common denominators. 4.4 Calculate simple fractions of quantities and measurements (whole number answers); multiply a fraction by an integer. Calculate simple percentages. Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. Calculate percentages and find the outcome of a given percentage increase or decrease (Year 8 Framework objective). 4.5 Interpret information from a mathematical representation or context; relate findings to the original context; check the accuracy of the solution; explain and justify methods and conclusions; compare and evaluate approaches. Check results by considering whether they are of the right order of magnitude and by working problems backwards. YEAR 7: AUTUMN TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Statistics 1 (5 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 5.1 Mode, median and range 5.2 The mean 5.3 Statistical diagrams 5.4 Probability 5.5 Experimental probability 5.1 Calculate statistics for small sets of discrete data. Find the mode, median and range, and the modal class for grouped data. Explain and justify methods and conclusions; compare and evaluate approaches. 5.2 Calculate statistics for small sets of discrete data. Calculate the mean, including from a simple frequency table, using a calculator for a larger number of items. 5.3 Interpret diagrams and graphs (including pie charts), and draw conclusions based on the shape of graphs and simple statistics for a single distribution. Interpret information from a mathematical representations or context. 5.4 Use vocabulary and ideas of probability, drawing on experience. Understand and use the probability scale from 0 to 1. Find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts. Identify all the possible mutually exclusive outcomes of a single event. 5.5 Estimate probabilities by collecting data from a simple experiment and recording it in a frequency table. Compare experimental and theoretical probabilities in simple contexts. 5.1 Mode, median and range 5.2 The mean 5.3 Statistical diagrams 5.4 Probability 5.5 Experimental probability Algebra 2 (5 hours) 6.1 Algebraic terms and expressions 6.2 Rules of algebra 6.3 Simplifying expressions 6.4 Formulae 6.5 Equations 6.1 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Know the meanings of the words term, expression and equation. 6.2 Understand that algebraic operations follow the rules of arithmetic. 6.3 Simplify linear algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Multiply a single term over a bracket (integer coefficients). 6.4 Use simple formulae from mathematics and other subjects. Substitute positive whole numbers into linear expressions and formulae and, in simple cases, derive a formula. 6.5 Give simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 6.1 Algebraic terms and expressions 6.2 Rules of algebra 6.3 Expanding and simplifying expressions 6.4 Formulae 6.5 Equations 5.1 Calculate statistics for small sets of discrete data: find the mode, median and range, and the modal class for grouped data. 5.2 Calculate statistics for small sets of discrete data: calculate the mean, including from a simple frequency table, using a calculator for a larger number of items. 5.3 Interpret diagrams and graphs (including pie charts), and draw simple conclusions based on the shape of graphs and simple statistics for a single distribution. 5.4 Use vocabulary and ideas of probability, drawing on experience. Understand and use the probability scale from 0 to 1; find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts; identify all the possible mutually exclusive outcomes of a single event. Know that if the probability of an event occurring is p, then the probability of it not occurring is 1 – p; use diagrams and tables to record in a systematic way all possible mutually exclusive outcomes for single events and for two successive events (Year 8 Framework objective). 5.5 Estimate probabilities by collecting data from a simple experiment and recording it in a frequency table. 6.1 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables; know the meanings of the words term, expression and equation. 6.2 Understand that algebraic operations follow the rules of arithmetic. 6.3 Simplify linear algebraic expressions by collecting like terms; multiply a single term over a bracket (integer coefficients). 6.4 Use simple formulae from mathematics and other subjects; substitute positive integers into linear expressions and formulae and, in simple cases, derive a formula. 6.5 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures and tools, including ICT. 31 Hours Teaching Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 5 YEAR 7: SPRING TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Geometry & Measures 2 (3 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 7.1 Lines and angles 7.2 Calculating angles 7.3 Coordinates 7.1 Lines and angles 7.2 Calculating angles 7.3 Coordinates 7.1 Use correctly the vocabulary, notation and labelling conventions for lines, angles and shapes. Identify parallel and perpendicular lines. Identify alternate angles and corresponding angles (Year 8 Framework objective). 7.2 Know the sum of angles at a point, on a straight line and in a triangle; recognise vertically opposite angles. Understand a proof that: the angle sum of a triangle is 180° and of a quadrilateral is 360°; the exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the two interior opposite angles (Year 8 Framework objective). 7.3 Use conventions and notation for 2-D coordinates in all four quadrants; find coordinates of points determined by geometric information. Statistics 2 (4 hours) 8.1 Using a tally chart 8.2 Using the correct data 8.3 Grouped frequencies 8.4 Data collection 7.1 Use correctly the vocabulary, notation and labelling conventions for lines, angles and shapes. Identify parallel and perpendicular lines. Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals. Distinguish between and estimate the size of acute, obtuse and reflex angles. Represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words and diagrams. 7.2 Use correctly the vocabulary, notation and labelling conventions for lines, angles and shapes. Know the sum of angles at a point, on a straight line and in a triangle, and recognise vertically opposite angles. 7.3 Use conventions and notation for 2-D coordinates in all four quadrants. Find coordinates of points determined by geometric information. 8.1 Suggest possible answers given a problem that can be addressed by statistical methods. 8.2 Decide which data would be relevant to an enquiry and possible sources. Plan how to collect and organise small sets of data; design a data collection sheet or questionnaire to use in a simple survey. 8.3 Construct frequency tables for discrete data, grouped where appropriate in equal class intervals. 8.4 Collect small sets of data from surveys and experiments, as planned. 8.1 Using a tally chart 8.2 Using the correct data 8.3 Grouped frequencies 8.4 Data collection 8.1Suggest possible answers, given a question that can be addressed by statistical methods. 8.2 Decide which data would be relevant to an enquiry and possible sources. Plan how to collect and organise small sets of data from surveys and experiments: design data collection sheets or questionnaires to use in a simple survey. 8.3 Plan how to collect and organise small sets of data from surveys and experiments: construct frequency tables for gathering discrete data, grouped where appropriate in equal class intervals. 8.4 Collect small sets of data from surveys and experiments, as planned. Decide which data to collect to answer a question, and the degree of accuracy needed; identify possible sources; consider appropriate sample size (Year 8 Framework objective). Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 6 YEAR 7: SPRING TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Numbers & Measures 3 (7 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 9.1 Rounding 9.2 The four operations 9.3 BODMAS 9.4 Long multiplication and long division 9.5 Efficient calculations 9.6 Calculating with measurements 9.7 Solving problems 9.1 Round positive whole numbers to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000 and decimals to the nearest whole number or one decimal place. 9.2 Understand and use the rule of arithmetic and inverse operations in the context of positive integers and decimals. 9.3 Use the order of operations, including brackets. 9.4 Multiply and divide three-digit by two-digit whole numbers. 9.5 Check results by considering if they are of the right order of magnitude and by working problems backwards. Carry out calculations with more than one step using brackets and the memory; use the square root and sign change keys. 9.6 Choose and use units of measurement to measure, estimate, calculate and solve problems in everyday contexts. Convert one metric unit to another (for example grams to kilograms); read and interpret scales on a range of measuring instruments. 9.7 Draw simple conclusions and explain reasoning, communicate own findings effectively in writing. 9.1 Rounding 9.2 The four operations 9.3 BODMAS 9.4 Long multiplication and long division 9.5 Efficient calculations 9.6 Calculating with measurements 9.7 Solving problems Algebra 3 (5 hours) 10.1 Square numbers and square roots 10.2 Triangle numbers 10.3 From mappings to graphs 10.4 Naming graphs 10.5 Naming sloping lines 10.1 Recognise and use multiples, factors, primes (less than 100), common factors, highest common factors and lowest common multiples in simple cases. Recognise the squares of numbers to at least 12 × 12, and the corresponding roots. 10.2 Recognise the first few triangle numbers. 10.3 Generate terms of a simple sequence, given a rule. (For example, find a term from the previous term; find a term given its position in the sequence). 10.4 Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a simple linear rule. Recognise straight-line graphs parallel to the x-axis or y-axis. 10.5 Plot the graphs of simple linear functions, where y is given explicitly in terms of x, on paper and using ICT. 10.1 Square numbers and square roots 10.2 Triangle numbers 10.3 From mappings to graphs 10.4 More about graphs 10.5 Questions about graphs 9.1 Round positive whole numbers to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000, and decimals to the nearest whole number or one decimal place. 9.2 Understand and use the rules of arithmetic and inverse operations in the context of positive integers and decimals. 9.3 Use the order of operations, including brackets. 9.4 Multiply and divide three-digit by two-digit whole numbers. 9.5 Carry out calculations with more than one step using brackets and the memory; use the square root and sign change keys. Check results by considering whether they are of the right order of magnitude and by working problems backwards. 9.6 Choose and use units of measurement to measure, estimate, calculate and solve problems in everyday contexts; convert one metric unit to another, for example, grams to kilograms; read and interpret scales on a range of measuring instruments. 9.7 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures and tools, including ICT. Interpret information from a mathematical representation or context; relate findings to the original context; explain and justify methods and conclusions. Communicate own findings effectively, orally and in writing. 10.1 Recognise and use multiples, factors and primes (less than 100). Recognise the squares of numbers to at least 12 × 12 and the corresponding roots. Use positive and negative square roots for small positive integer powers (Year 8 Framework objective). 10.2 Recognise the first few triangular numbers. 10.3 Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a simple linear rule; plot the graphs of simple linear functions, where y is given explicitly in terms of x. Recognise that equations of the form y = mx + c correspond to straight-line graphs (Year 8 Framework objective). 10.4 Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a simple linear rule; plot the graphs of simple linear functions, where y is given explicitly in terms of x, on paper and using ICT; recognise straight-line graphs parallel to the x-axis or y-axis. 10.5 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures and tools, including ICT. Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 7 YEAR 7: SPRING TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Geometry & Measures 3 (3 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 11.1 Measuring and drawing angles 11.2 Constructions 11.3 Solving geometrical problems 11.1 Use a ruler and protractor to: measure and draw lines to the nearest millimetre and angles, including reflex angles, to the nearest degree. 11.2 Use a ruler and protractor to: measure and draw lines to the nearest millimetre and angles to the nearest degree; construct a triangle, given two sides and the included angle (SAS) or two angles and the included side (ASA). Explore these constructions using ICT. Make accurate mathematical diagrams and constructions on paper and screen. 11.3 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals. Explore geometrical problems involving these properties, using step-by-step deduction supported by diagrams. Make accurate mathematical diagrams and constructions on paper. Classify and visualize in patterns. 11.1 Measuring and drawing angles 11.2 Constructions 11.3 Solving geometrical problems Number 4 (4 hours) 12.1 Percentages 12.2 Ratio and proportion 12.3 Calculating ratios and proportions 12.4 Solving problems 12.1 Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. 12.2 Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. 12.3 Understand the relationship between ratio and proportion; use ratio notation, simplify ratios and divide a quantity into two parts in a given ratio. 12.4 Solve simple problems about ratio and proportion using informal strategies. 12.1 Percentages 12.2 Ratio and proportion 12.3 Calculating ratios and proportions 12.4 Solving problems 11.1 Use a ruler and protractor to measure and draw lines to the nearest millimetre and angles, including reflex angles, to the nearest degree. 11.2 Within the appropriate range and content make accurate mathematical constructions. Use a ruler and protractor to construct a triangle, given two sides and the included angle (SAS) or two angles and the included side (ASA). Use ICT to explore constructions. Use straight edge and compasses to construct: the midpoint and perpendicular bisector of a line segment; the bisector of an angle (Year 8 Framework objective). 11.3 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; explore geometrical problems involving these properties, explaining reasoning orally, using step-by-step deduction supported by diagrams. Classify quadrilaterals by their geometrical properties (Year 8 Framework objective). 12.1 Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. 12.2 Understand the relationship between ratio and proportion; use direct proportion in simple contexts; use ratio notation. 12.3 Simplify ratios and divide a quantity into two parts in a given ratio. 12.4 Solve simple problems involving ratio and proportion using informal strategies. 26 Hours Teaching Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 8 YEAR 7: SUMMER TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Algebra 4 (3 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 13.1 Solving ‘brick wall’ problems 13.2 Solving square-and-circle problems 13.3 Triangle-and-circle problems 13.1 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Simplify linear algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Construct and solve linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 13.2 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 13.3 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers. Understand the significance of a counterexample. 13.1 Solving ‘brick wall’ problems 13.2 Square-and-circle problems 13.3 Triangle-and-circle problems Geometry & Measures 4 (5 hours) 14.1 Line symmetry 14.2 Rotational symmetry 14.3 Reflections 14.4 Rotations 14.5 Translations 14.1 Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections, translations and rotations. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. 14.2 Understand and use the language and notation associated with rotations. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by rotating about a given point. 14.3 Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by reflecting in given mirror lines. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 14.4 Understand and use the language and notation associated with rotations. Recognise and visualise the transformation and symmetry of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by rotating about a given point. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 14.5 Understand and use the language and notation associated with translations. Recognise and visualise the transformation and symmetry of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by translating. Explore the transformations and symmetries using ICT. 14.1 Line symmetry and rotational symmetry 14.2 Reflections 14.3 Rotations 14.4 Translations 14.5 Enlargements 13.1 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Simplify linear algebraic expressions by collecting like terms; multiply a single term over a bracket (integer coefficients). Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 13.2 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 13.3 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Understand the significance of a counter-example. 14.1 Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections and rotations. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. 14.2 Understand and use the language and notation associated with reflections. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by reflecting in given mirror lines. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 14.3 Understand and use the language and notation associated with rotations. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by rotating about a given point. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 14.4 Understand and use the language and notation associated with translations. Recognise and visualise the symmetries of a 2-D shape. Transform 2-D shapes by translating. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. Try out mathematical representations of simple combinations of rotation, reflection and translation (Year 8 Framework objective). 14.5 Understand and use the language and notation associated with enlargement; enlarge 2-D shapes, given a centre of enlargement and a positive integer scale factor (Year 8 Framework objective). Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 9 YEAR 7: SUMMER TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Statistics 3 (5 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 15.1 Pie charts 15.2 Comparing data 15.3 and 15.4 Statistical surveys 15.5 Probabilities from two way tables 15.1 Construct, on paper and using ICT, graphs and diagrams to represent data, including simple pie charts. Use ICT to generate pie charts. Interpret diagrams and graphs (including pie charts). 15.2 Compare two simple distributions using the range and one of the modes, median or mean. Interpret information from a mathematical representation or context; relate findings to the original context; check the accuracy of the solution; explain and justify methods and conclusions; compare and evaluate approaches. 15.3 & 15.4 Decide which data would be relevant to an enquiry and possible sources. Plan how to collect and organise small sets of data from surveys and experiments. Design data collection sheets or questionnaires to use in a simple survey. Write a short report of a statistical enquiry and illustrate with appropriate diagrams, graphs and charts, using ICT as appropriate; justify the choice of presentation. 15.5 Understand and use the probability scale from 0 to1; find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts; identify all the possible mutually exclusive outcomes of a single event. 15.1 Pie charts 15.2 Comparing data 15.3 and 15.4 Statistical surveys 15.5 Comparing experimental and theoretical probabilities 15.1 Construct, on paper and using ICT, graphs and diagrams to represent data, including simple pie charts. Interpret diagrams and graphs (including pie charts). Compare two simple distributions using the range and one of the mode, median or mean. Recognise when it is appropriate to use the range, mean, median and mode (Year 8 Framework objective). 15.3 & 15.4 Within the appropriate range and content make accurate mathematical diagrams, graphs and constructions on paper and on screen. Decide which data would be relevant to an enquiry and possible sources. Plan how to collect and organise small sets of data from surveys and experiments: design data collection sheets or questionnaires to use in a simple survey. Write a short report of a statistical enquiry, including appropriate diagrams, graphs and charts, using ICT as appropriate; justify the choice of presentation. 15.5 Understand and use the probability scale from 0 to 1; find and justify probabilities based on equally likely outcomes in simple contexts; identify all the possible mutually exclusive outcomes of a single event. Estimate probabilities by collecting data from a simple experiment and recording it in a frequency table; compare experimental and theoretical probabilities in simple contexts. Compare estimated experimental probabilities with theoretical probabilities, recognising that: if an experiment is repeated the outcome may, and usually will, be different; increasing the number of times an experiment is repeated generally leads to better estimates of probability (Year 8 Framework objective). Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 10 YEAR 7: SUMMER TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Number 5 (6 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 16.1 Adding and subtracting decimals 16.2 Multiplying and dividing decimals 16.3 Using a calculator 16.4 Fractions of quantities 16.5 Percentages of quantities 16.6 Solving problems 16.1 Use efficient written methods to add and subtract whole numbers and decimals with up to two places. 16.2 Multiply and divide three-digit by two-digit whole numbers; extend to multiplying and dividing decimals with one or two places by single-digit whole numbers. 16.3 Carry out calculations with more than one step using brackets and the memory; use the square root and sign change keys. 16.4 Calculate simple fractions of quantities and measurements (whole-number answers); multiply a fraction by an integer. 16.5 Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. 16.6 Draw simple conclusions and explain reasoning. Communicate own findings effectively, orally and in writing. 16.1 Multiplying decimals 16.2 Dividing decimals 16.3 Using a calculator 16.4 Fractions of quantities 16.5 Percentages of quantities 16.6 Solving problems Algebra 5 (4 hours) 17.1 Solving equations 17.2 Formulae 17.3 Dotty investigations 17.4 Graphs from the real world 17.1 Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 17.2 Use simple formulae from mathematics and other subjects; substitute positive integers into linear expressions and formulae and, in simple cases, derive a formula. 17.3 Generate sequences from patterns or practical contexts and describe the general term in simple cases. 17.4 Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a simple linear rule; plot the graphs of simple linear functions, where y is given explicitly in terms of x. 17.1 Solving equations 17.2 Formulae 17.3 Dotty investigations 17.4 Graphs from the real world 17.5 Other types of problem 16.1 Multiply three-digit by two-digit whole numbers; extend to multiplying decimals with one or two places by single-digit whole numbers. Understand where to position the decimal point by considering equivalent calculations (Year 8 Framework objective). 16.2 Divide three-digit by two-digit whole numbers; extend to dividing decimals with one or two places by single-digit whole numbers. Understand where to position the decimal point by considering equivalent calculations (Year 8 Framework objective). 16.3 Carry out calculations with more than one step using brackets and the memory; use the square root and sign change keys. 16.4 Calculate simple fractions of quantities and measurements (whole number answers); multiply a fraction by an integer. 16.5 Calculate simple percentages and use percentages to compare simple proportions. Recognise the equivalence of percentages, fractions and decimals. 16.6 Identify the necessary information to understand or simplify a context or problem; represent problems, making correct use of symbols, words, diagrams, tables and graphs; use appropriate procedures and tools, including ICT. Enter numbers and interpret display in different contexts (documents, percentages, money, metric measures). 17.1 Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). 17.2 Use simple formulae from mathematics and other subjects; substitute positive integers into linear expressions and formulae and, in simple cases, derive a formula. 17.3 Generate sequences from patterns or practical contexts and describe the general term in simple cases. 17.4 Generate coordinate pairs that satisfy a simple linear rule. Plot and interpret the graphs of simple linear functions arising from real-life situations, for example, conversion graphs. 17.5 Use letter symbols to represent unknown numbers or variables. Simplify linear algebraic expressions by collecting like terms. Construct and solve simple linear equations with integer coefficients (unknown on one side only) using an appropriate method (for example, inverse operations). Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 11 YEAR 7: SUMMER TERM MATHEMATICAL TOPIC - Context Geometry & Measures 5 (3 hours) ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 2 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 2 ►OVERVIEW – Teacher Pack 3 ► FRAMEWORK OBJECTIVES – Teacher Pack 3 18.1 Polygons 18.2 and 18.3 Tessellations 18.4 and 18.5 Constructing 3-D shapes 18.1 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; explore geometrical problems involving these properties, explaining reasoning orally, using step-by-step deduction supported by diagrams. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 18.2 and 18.3 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; explore geometrical problems involving these properties explaining reasoning orally, using step-bystep deduction supported by diagrams. 18.4 and 18.5 Make accurate mathematical diagrams and constructions on paper. Use a ruler and protractor to construct simple nets of 3-D shapes; for example, cuboid, regular tetrahedron, square-based pyramid, triangular prism. 18.1 Polygons 18.2 and 18.3 Tessellations 18.4 and 18.5 Constructing 3-D shapes 18.1 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; explore geometrical problems involving these properties, explaining reasoning orally, using step-by-step deduction supported by diagrams. Explore these transformations and symmetries using ICT. 18.2 and 18.3 Identify and use angle, side and symmetry properties of triangles and quadrilaterals; explore geometrical problems involving these properties, explaining reasoning orally, using stepby-step deduction supported by diagrams. 18.4 and 18.5 Use ruler and protractor to construct simple nets of 3-D shapes, for example, cuboid, regular tetrahedron, square-based pyramid, triangular prism. 26 Hours Teaching Year 7 Mathematics – Scheme of Work (22-06-2010) 12