* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Evolutionary Classification Notes (17.2)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
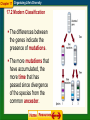
Evolutionary Classification (17.2) State Standard SB3C. Examine the evolutionary basis of modern classification systems. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Phylogenetic Species Concept Phylogeny is the evolutionary history of a species. The phylogenetic species concept defines a species as a cluster of organisms that is distinct from other clusters and shows evidence of a pattern of ancestry and descent. It also takes into account DNA similarities. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Characters To classify a species, scientists construct patterns of descent by using characters. Characters can be morphological or biochemical. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Morphological Characters Shared morphological characters suggest that species are related closely and evolved from a recent common ancestor. Ex. Hawks & Eagles Analogous characters are those that have the same function but different underlying construction. No indication of common ancestry Homologous characters might perform different functions, but show an anatomical similarity inherited from a common ancestor. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Homologous Structures Between Birds and Dinosaurs Hollow bones Haliaeetus leucocephalus Theropods have leg, wrist, hip, and shoulder structures similar to birds. Some theropods may have had feathers. Oviraptor philoceratops Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Biochemical Characters Scientists use biochemical characters, such as amino acids and nucleotides, to help them determine evolutionary relationships among species. Chromosome structure & number is a powerful clue for determining species similarities. DNA and RNA analyses are powerful tools for reconstructing phylogenies. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification The similar appearance of chromosomes among chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans suggests a shared ancestry. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification Molecular Clocks Scientists use molecular clocks to compare the DNA sequences or amino acid sequences of genes that are shared by different species. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity 17.2 Modern Classification The differences between the genes indicate the presence of mutations. The more mutations that have accumulated, the more time that has passed since divergence of the species from the common ancestor. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity Chapter Assessment Questions What does this image represent? A. phylogeny of species B. molecular clock C. cladogram D. tree of life 0% D 0% C 0% B A 0% 1. 2. 3. 4. A B C D Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity Chapter Assessment Questions What do the colored bands in the figure represent? A. mutations B. molecular clock C. time D. gene 1. 2. 3. 4. 0% D 0% C 0% B A 0% A B C D Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity Standardized Test Practice Which pair of organisms is more closely related? 1. 2. 3. A 0% 0% B A. 1 and 2 B. 2 and 3 C. 1 and 3 A B C 0% C 1. Quercus alba 2. Cornus alba 3. Quercus rubra Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity Standardized Test Practice How do systematists use this model to determine the degree of relationship among species? A B C D 0% 0% D 0% C 0% B 1. 2. 3. 4. A A. It shows the chromosomal structure of different species. B. It shows the genetic makeup of a common ancestor. C. It shows the rate of mutation for different species. D. It shows the relative time of divergence of a species. Chapter 17 Organizing Life’s Diversity Vocabulary Section 2 phylogeny character molecular clock cladistics cladogram