* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worksheet Key - UCSB C.L.A.S.
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
Enantioselective synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Polythiophene wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
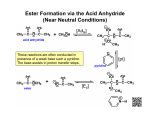
Chem 1C - CLAS - Chapter 21 b. 3-chloro-3,4,4-trimethyl-1-pentyne 1. Classify the following compounds as saturated or unsaturated. O OH Cl saturated unsaturated unsaturated unsaturated 2. What is the general formula for a hydrocarbon with one ring and a triple bond? a. CnH2n+2 b. CnH2n c. CnH2n–2 d. CnH2n–4 e. CnH2n–6 3. Name the following alkanes: a. 4-ethyl-3-methylheptane 6. Which of the following is not a structural isomer of 2-heptene? a. b. c. d. e. 3-heptene 2,4-dimethyl-2-pentene 3-methylcyclohexene 1-methylcyclohexane 2-heptyne 7. Which of the following can have geometric isomers? a. 2-pentene b. 2-pentyne c. cyclopentene d. 1-pentene e. 2,3-dimethyl-2-pentene 8. How many dibromobenzenes can you have? Draw and name them. Br b. 5-bromo-2,2-dimethylhexane Br ortho-dibromobenzene Br c. 2,4-dichloro-1-ethyl-1-propylcyclopentane Br meta-dibromobenzene para-dibromobenzene 4. Name the following alkenes: a. 5-bromo-3-ethyl-2-hexene Br b. 6-tert-butyl-1-isopropylcyclohexene 5. Name the following alkynes: a. 5-ethyl-6-methyl-3-octyne 9. How many compounds can be produced if you mix chlorine with ethane in the presence of high energy photons? 9 monochlorination CH3CH2Cl dichlorination ClCH2CH2Cl or CH3CHCl2 trichlorination Cl2CHCH2Cl or CH3CCl3 tetrachlorination Cl2CHCHCl2 or ClCH2CCl3 pentachlorination Cl2CHCCl3 hexachlorinationCl3CCCl3 10. Predict the product for the following addition reactions: a. 1-pentene + Br2 → Br Br2 Br b. 2-pentene + HBr → c. 6-cyclopentyl-5-methyl-1-hexanol H HBr Br Br OH H c. 1-butene + HCl → O H HCl 6-cyclopentyl-5-methylhexanal Cl OH Cl H O 11. Which of the following transitions does not represent a hydrogenation reaction? a. 1-butene → butane b. 1-pentyne → pentane c. pentane → 2-pentene 6-cyclopentyl-5-methylhexanoic acid 14. Name the following: a. 12. Identify the functional groups that are present in the following compounds: O 5,6-dimethyl-3-hexanone b. Br O OH 4-bromopentanoic acid c. Carboxylic acid Amine Amide Ester Alcohol Ketone Alcohol Ether Aldehyde H 3,4,4-trimethylpentanal 13. For each of the following (1) provide a name (2) draw the products of oxidation and (3) name the products: a. O 15. Classify the following amines as primary, secondary or tertiary a. tertbutylamine tertiary b. ethylhexylamine secondary 3,4,4-trimethyl-2-pentanol 16. Predict and name the products for the following: a. propanoic acid + 2-methyl-2-propanol → O OH O 3,4,4-trimethyl-2-pentanone b. 1-isopropylcyclohexanol tertiary alcohols cannot be oxidized O + H2O b. methanoic acid + 2-butanol → O H OH O OH + HO O OH + HO H O + H2O c. hexanoic acid + 2,3-dimethyl-1-pentanol → O O OH + HO O + H2O 17. What compounds would you use to synthesize the following esters? a. methyl ethanoate O O OH + CH 3OH 22. Draw a short segment of the polymer that is the result of the following monomers: a. tetrafluoroethene -[-CF2- CF2- CF2- CF2- CF2- CF2- CF2-]nb. 4-methyl-2-pentene + H2O O b. cyclohexyl propanoate iPr O O OH + HO iPr iPr iPr n c. 1,1-dichloro-1-butene + H2O O Cl Cl Cl Cl Cl ClCl Cl 18. Circle the chiral carbons in the following: O H H H OH OH OH OH Carbons 2,3 and 4 are all chiral 19. Peptide bonds in proteins are the result of Condensation reactions between carboxylic and amines What’s the difference between the primary, secondary and tertiary structure of a protein? Primary – sequence of amino acids Secondary – hydrobonding within the back bone resulting in coiling or helices and pleated sheats Tertiary – overall shape of a protein How many possible tripeptides will result if you were to mix valine, leucine and cysteine together? 27 O O NH2 Valine SH O NH2 Leucine b. F F Cl F c. OH OH OH 23. Draw the monomer used to make the following polymers. a. NH2 d. Cysteine O HO 20. What type of monomers are used to make addition polymers? OH e. a. b. c. d. Alkanes Alkenes Alcohols and carboxylic acids Amines and carboxylic acids 21. What type of monomers are used to make condensation polymers? a. Alkanes b. Alkenes c. Alcohols and carboxylic acids d. Amines and carboxylic acids HO H2N O NH2 O 24. Which of the following are examples of condensation polymers? a. Proteins b. DNA c. Polysaccharides d. Polystyrene OH