* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture Presentation Outline
Drug rehabilitation wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of binge drinking wikipedia , lookup
Health effects of wine wikipedia , lookup
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder wikipedia , lookup
The Natural History of Alcoholism Revisited wikipedia , lookup
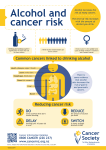
Alcohol and cancer wikipedia , lookup
Disease theory of alcoholism wikipedia , lookup
Long-term effects of alcohol consumption wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Alcoholism in family systems wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol withdrawal syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol abuse wikipedia , lookup
Alcohol and health wikipedia , lookup
Lecture Presentation Outline I. Alcohol Facts Instructor Resources: Unit 14 Nutrition Scoreboard transparency master; Unit 14 PowerPoint presentation on Multimedia Manager A. B. C. D. E. F. Alcohol is a food, an energy source for humans Alcohol is a drug; it modifies body functions People consume ethanol, termed alcohol Alcohol is produced from carbohydrates in grains, fruits, and other foods by fermentation Wines, beers and ales, and other alcohol-containing beverages are a traditional part of the food supply of many cultural groups In high doses alcohol is harmful to the body and causes a variety of nutritional, social, and physical health problems II. The Positive Side Instructor Resources: CNN Today Nutrition Vol. 2: Alcohol Benefits (2:26) A. Consumption of moderate amounts of alcohol by healthy adults who are not pregnant appears to cause no harm B. Moderate alcohol consumption may protect against heart disease 1. Moderate alcohol consumption is one standard-sized drink per day for women and two drinks for men Instructor Resources: transparency #40: A Standard “Drink” 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Alcohol increases the body’s production of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL) HDL eliminates cholesterol and reduces plaque build-up in arteries All types of alcohol-containing beverages reduce the risk of heart disease Red wine reduces the risk more for women a. Red wine includes deep red, blue, or purple pigments b. Pigments may decrease the tendency of blood to clot c. May decrease ability of plaque to form in the arteries d. Purple grape juice may also help prevent heart disease But not an excuse to drink alcohol, because diets low in saturated fat, liberal intakes of vegetables and fruits, ample physical activity, and not smoking also reduce the risk of heart disease II. The Negative Side A. Heavy drinking threatens the health of drinkers and others B. Ill effects of alcohol are most obvious in people with alcoholism C. Habitual high alcohol intake and alcoholism increase risk of: 1. High blood pressure 2. Stroke 3. Cirrhosis of the liver 4. Throat, stomach, and bladder cancer 5. Central nervous system disorders 6. Vitamin and mineral deficiency diseases D. Alcohol abuse associated with deaths from Instructor Resources: transparency #41: Violence and Injuries Associated with Alcohol 1. Homicide 2. Drowning 3. Fires 4. Traffic accidents 5. Suicide 6. Involved in rapes and assaults 7. Alcohol poisoning can cause death - and does for a number of college students each year E. Drinking during pregnancy may harm the fetus Instructor Resources: transparency #42: Child with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome 1. Drinking causes Fetal Alcohol Syndrome in fetus 2. Children with Fetal Alcohol Syndrome experience long-term growth and mental retardation 3. Severity depends on amount consumed and if intake occurred early or late in pregnancy 4. It is recommended that women who are, or may become, pregnant not drink alcohol F. Alcohol and Diet Quality 1. Alcohol provides seven calories per gram 2. Alcohol-containing beverages provide calories but few or no nutrients, they are considered “empty-calorie” foods 3. Alcohol accounts for 3 to 9% of the caloric intake of U.S. adults who drink 4. Average goes to 50% among heavy drinkers 5. Beer, wine, and mixed drinks contain alcohol and provide calories G. Do alcohol calories contribute to weight gain? Alcohol Calories Count 1. Calorie intake of heavy drinkers high 2. Chronic alcohol abuse is associated with weight loss and muscle wasting a. Effect appears due to inhibition of fat tissue accumulation 3. But calories do count for light and moderate drinkers III. Alcoholism Effects A. As calories from alcohol increase, quality of the diet decreases 1. Heavy drinkers receive too little thiamin, vitamins A and C, calcium, and iron 2. Deficiencies of nutrients and toxic effects of alcohol produce physical health problems associated with alcoholism 3. Lack of thiamin impairs the utilization of glucose by the brain a. Thiamin deficiency results in “delirium tremens” b. People with “DTs” experience convulsions and hallucinations and are severely confused c. Thiamin injections are a treatment for DTs B. Alcohol in excess is directly toxic to body tissues C. Consuming adequate diet won’t protect from the harmful effects of alcohol D. The Body and Alcohol 1. Alcohol easily and rapidly absorbed in stomach and small intestine 2. Alcohol enters the circulatory system and goes to liver, brain, and other tissues in the body 3. Alcohol remains in blood and tissues until broken down for energy or converted to fat and stored 4. Process of converting alcohol to energy takes several hours 5. Due to lag time between intake and utilization, blood levels of alcohol build up Instructor Resources: Activity 14-1: Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Blood Alcohol Level; Handout 14-1: Effect of Alcohol Consumption on Blood Alcohol Level a. After 1 to 2 drinks, blood levels reach 0.03% in 150-pound people 1. Mild intoxication: people lose control over muscle movement, have slowed reaction times and impaired thought processes 2. Ability to drive or operate equipment is decreased at this level b. 0.06% leads to increased involvement in traffic accidents c. At 0.13%, speech is slurred, “double vision” occurs, reflexes are dulled, and body movements become unsteady d. If blood alcohol continues to increase, drowsiness occurs and people may lose consciousness e. Levels of blood alcohol above 0.6% can cause death, especially in individuals who have not developed a tolerance for alcohol 6. Many medications interact harmfully with alcohol a. Three drinks per day with pain relievers may cause stomach ulcers or liver damage 7. Alcohol in women produces higher blood levels of alcohol than for men of the same body weight a. Women’s bodies have less water; alcohol levels in women increase faster than in men b. Women experience intoxicating effects of alcohol on lower amounts of alcohol than men require E. Acute Alcohol Poisoning 1. Very high blood levels of alcohol can be extremely dangerous 2. Drinking large amounts of alcohol in a short time causes unconsciousness 3. Sufferers have rapid pulse, low blood pressure, and dilated pupils IV. Drink Safely if You Drink A. Many problems related to alcohol intake can be prevented by not drinking 1. Not drinking if you are or could become pregnant 2. Not drinking on empty stomach (intoxication fast) 3. Slowly sipping rather than gulping drinks 4. Limiting alcohol to an amount that doesn’t make you lose control over your mind and body 5. Never driving a car or boat, hunting, or operating heavy equipment while under the influence of alcohol V. What Causes Alcoholism? 1 in 13 adults in the U.S. abuse alcohol or have alcoholism Instructor Resources: Activity 14-3: Is Alcohol a Problem for You? A. Alcoholism runs in families, so there is a genetic component to the disease B. Development influenced by environmental factors 1. Individuals who begin drinking very young will develop a drinking problem at some point in life 2. Individuals drinking before age 15 are 400% more at risk of alcohol dependence than people who do not drink before age 21 3. Friends or peers who drink, high levels of stress, and availability of alcohol may also increase risk of alcoholism 4. Television ads depicting youth-oriented parties, fun, and beer may increase underage drinking C. Alcohol Use in Adolescents Instructor Resources: Activity 14-2: Who Is to Blame? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Alcohol use among adolescents increasing Age when teens drink is going down Underage drinking is 20% of alcohol consumed in the U.S. Average age teens begin drinking now 14 Trends suggest higher rates of alcoholism and alcohol-related problems soon Reduction in alcohol intake by adolescents is a major initiative of 2010 Health Objectives for the Nation Treatment programs such as Alcoholics Anonymous and educational programs that stress safe drinking can lessen impact of alcohol abuse on personal and public health