Harold Shipman, Dr. Death
... are lost as a result of the erratic and frequently uncontrollable behavior of individuals under the influence of drugs. But one should not automatically attribute these occurrences to the wide proliferation of illicit-drug markets. For example, in the United States alone, drug manufacturers produce ...
... are lost as a result of the erratic and frequently uncontrollable behavior of individuals under the influence of drugs. But one should not automatically attribute these occurrences to the wide proliferation of illicit-drug markets. For example, in the United States alone, drug manufacturers produce ...
Toxicology Notes 2012
... • After consumption, alcohol concentration slowly decreases back to zero. • Factors such as time taken to consume the drink, the alcohol content, the amount consumed, and food present in the stomach determine the rate at which alcohol is absorbed. ...
... • After consumption, alcohol concentration slowly decreases back to zero. • Factors such as time taken to consume the drink, the alcohol content, the amount consumed, and food present in the stomach determine the rate at which alcohol is absorbed. ...
Alcohol intake and risk of incident gout in men: a
... Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis in men.1 The association between heavy alcohol consumption and increased risk of gout has long been suspected; however, the association has not been prospectively confirmed. Metabolic studies have shown that hyperuricaemia (not gout per se) can be induc ...
... Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis in men.1 The association between heavy alcohol consumption and increased risk of gout has long been suspected; however, the association has not been prospectively confirmed. Metabolic studies have shown that hyperuricaemia (not gout per se) can be induc ...
Full-Text PDF
... DNA methylation, synthesis and repair that subsequently reduces the risk of developing cancer [13]. Numerous epidemiologic studies have shown that folate is protective against colorectal, gastric, and other cancers. However, epidemiologic studies examining the relationship between folate intake and ...
... DNA methylation, synthesis and repair that subsequently reduces the risk of developing cancer [13]. Numerous epidemiologic studies have shown that folate is protective against colorectal, gastric, and other cancers. However, epidemiologic studies examining the relationship between folate intake and ...
Alcohol Toxicology
... substance and co-ingestant with other drugs in suicide attempts Ethanol is a common solvent for both prescribed and over-the-counter medications Also serve as the diluent for many household products such as mouthwashes, colognes, perfumes, and extracts “Proof”……is the term used to describe the ethan ...
... substance and co-ingestant with other drugs in suicide attempts Ethanol is a common solvent for both prescribed and over-the-counter medications Also serve as the diluent for many household products such as mouthwashes, colognes, perfumes, and extracts “Proof”……is the term used to describe the ethan ...
WEEK 8
... Mercaptans are the sulfur analogs of alcohols. These compounds contain the sulfhydryl group, -SH, instead of the hydroxyl group, -OH. The general formula for thioalcohols is R-SH. An example of a mercaptan is ethyl mercaptan: CH3CH2SH. The presence of sulfur produces obnoxious odors. Ethyl mercaptan ...
... Mercaptans are the sulfur analogs of alcohols. These compounds contain the sulfhydryl group, -SH, instead of the hydroxyl group, -OH. The general formula for thioalcohols is R-SH. An example of a mercaptan is ethyl mercaptan: CH3CH2SH. The presence of sulfur produces obnoxious odors. Ethyl mercaptan ...
The Effects of Moderate Beer Consumption.
... a substantially (30 – 40%)1 reduced risk of coronary heart disease when compared to teetotallers and heavy drinkers. Similar results have been shown by many studies throughout the world. The WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol (2004) describes this as the “most important health benefit of alcohol” 5 ...
... a substantially (30 – 40%)1 reduced risk of coronary heart disease when compared to teetotallers and heavy drinkers. Similar results have been shown by many studies throughout the world. The WHO Global Status Report on Alcohol (2004) describes this as the “most important health benefit of alcohol” 5 ...
Alcoholic liver disease
... metabolism, synthesis and storage of nutrients. The liver is essential in the metabolism of alcohol. Alcohol is produced through the fermentation of yeast, sugars and starches, and it can be divided in three main categories. Liver damage is a common consequence of chronic alcoholism. Alcoholism is a ...
... metabolism, synthesis and storage of nutrients. The liver is essential in the metabolism of alcohol. Alcohol is produced through the fermentation of yeast, sugars and starches, and it can be divided in three main categories. Liver damage is a common consequence of chronic alcoholism. Alcoholism is a ...
Alcohol and Cancer - UCLA Fielding School of Public Health
... Prevalence of Alcohol Use Almost half of Americans aged 12 and older reported being current drinkers of alcohol in the 2000 survey (46.6%). This translates to an estimated 104 million people. About 35% of the adult US population abstains from alcohol use, about 60% are occasional to moderate dr ...
... Prevalence of Alcohol Use Almost half of Americans aged 12 and older reported being current drinkers of alcohol in the 2000 survey (46.6%). This translates to an estimated 104 million people. About 35% of the adult US population abstains from alcohol use, about 60% are occasional to moderate dr ...
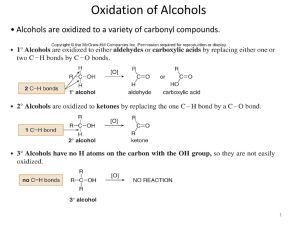
Oxidation of Alcohols
... Metabolism of Ethanol • In the body, ingested ethanol is oxidized in the liver first to CH3CHO (acetaldehyde), and then to CH3COO− (the acetate anion) catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase. • If more ethanol is ingested than can be metabolized, the concentration of acetaldehyde increases. • Acetaldehy ...
... Metabolism of Ethanol • In the body, ingested ethanol is oxidized in the liver first to CH3CHO (acetaldehyde), and then to CH3COO− (the acetate anion) catalyzed by alcohol dehydrogenase. • If more ethanol is ingested than can be metabolized, the concentration of acetaldehyde increases. • Acetaldehy ...
Fructose and its effect on alcohol elimination
... presence of alcohol. This shift has been linked to the production in the liver of NAD+ which facilitates alcohol oxidation (17, 18, 20). Therefore, in the presence of alcohol, the metabolism of fructose in the liver is diverted from NAD+ to NADH requiring pathways, which in turn generates the NAD+ n ...
... presence of alcohol. This shift has been linked to the production in the liver of NAD+ which facilitates alcohol oxidation (17, 18, 20). Therefore, in the presence of alcohol, the metabolism of fructose in the liver is diverted from NAD+ to NADH requiring pathways, which in turn generates the NAD+ n ...
NICOTINE: - Alkaloid in tobacco (~5% by weight): major
... - Sustained activation of NMDA receptors at critical stages in development activates programmed cell death-this can lead to fetal alcohol syndrome; we see this effect with PCP, Ketamine, and ethanol Glutamate excitotoxicity - Neurons, when overactivated, can die- hypoxia (drop in blood oxygen level) ...
... - Sustained activation of NMDA receptors at critical stages in development activates programmed cell death-this can lead to fetal alcohol syndrome; we see this effect with PCP, Ketamine, and ethanol Glutamate excitotoxicity - Neurons, when overactivated, can die- hypoxia (drop in blood oxygen level) ...
Chapter 8 - Ltcconline.net
... • Drinking moderate amounts appears to be healthy for people who do not have problems with alcohol abuse or dependency. • People who consume one to two drinks daily have lower mortality rates than nondrinkers. • Like any other drug, there is a beneficial dose and a level (dose) that will cause harm. ...
... • Drinking moderate amounts appears to be healthy for people who do not have problems with alcohol abuse or dependency. • People who consume one to two drinks daily have lower mortality rates than nondrinkers. • Like any other drug, there is a beneficial dose and a level (dose) that will cause harm. ...
10_Toxicology
... that leads into a metal cylinder. The pressure of the breath raises a piston. As the breath ends, the piston settles to a position that traps the last portion of air. When the valve is in the ANALYZE position, the piston drops causing the sample of air to pass into a glass ampoule that contains pota ...
... that leads into a metal cylinder. The pressure of the breath raises a piston. As the breath ends, the piston settles to a position that traps the last portion of air. When the valve is in the ANALYZE position, the piston drops causing the sample of air to pass into a glass ampoule that contains pota ...
Ethyl Alcohol - LyondellBasell
... Toxicity after repeated exposure Oral / inhalation / dermal Genotoxicity / Mutagenicity Carcinogenicity Toxicity for reproduction ...
... Toxicity after repeated exposure Oral / inhalation / dermal Genotoxicity / Mutagenicity Carcinogenicity Toxicity for reproduction ...
Alcohol - Florida Alcohol and Drug Abuse Association
... • Gender. Women appear to be more vulnerable than men to many adverse consequences of alcohol use according to an Alcohol Alert from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Women achieve higher concentrations of alcohol in the blood and become more impaired than men after dri ...
... • Gender. Women appear to be more vulnerable than men to many adverse consequences of alcohol use according to an Alcohol Alert from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (NIAAA). Women achieve higher concentrations of alcohol in the blood and become more impaired than men after dri ...
Chemistry of Alcohol Slides
... aldehyde and organic acid formed from methanol are more toxic substances than those formed from ethanol. ...
... aldehyde and organic acid formed from methanol are more toxic substances than those formed from ethanol. ...
Chapter 6
... Main Pathway for Alcohol Metabolism At relatively low doses, the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase convert alcohol to acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA can be used to form glucose or fatty acids. ...
... Main Pathway for Alcohol Metabolism At relatively low doses, the enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase convert alcohol to acetyl CoA. Acetyl CoA can be used to form glucose or fatty acids. ...
Critique 179: Response to proposed guidelines
... drink/day for women and just over 2 drinks/day for men. Thus, heavy drinking is indeed a factor for many cancers, but moderate drinking is not. “For breast cancer, the incidence has repeatedly been shown to be slightly increased among women reporting only 1 drink/day. In many studies, this risk is a ...
... drink/day for women and just over 2 drinks/day for men. Thus, heavy drinking is indeed a factor for many cancers, but moderate drinking is not. “For breast cancer, the incidence has repeatedly been shown to be slightly increased among women reporting only 1 drink/day. In many studies, this risk is a ...
Living with Alcohol by Steven Wm. Fowkes
... When alcohol is metabolized, it has a powerful effect on cellular energy production pathways. The conversion of alcohol into acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde into acetate by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase results in the generation of NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) ...
... When alcohol is metabolized, it has a powerful effect on cellular energy production pathways. The conversion of alcohol into acetaldehyde by alcohol dehydrogenase and acetaldehyde into acetate by acetaldehyde dehydrogenase results in the generation of NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) ...
The breakdown of alcohol and your body How do you prevent a
... What is a hangover? When someone drinks more than their body can handle, there is a big chance of waking up the next day with a hangover. A hangover often implies having one or more of the following symptoms: headache, feeling weak, being lethargic, nauseous, shaky and spending the day bed-bound. Af ...
... What is a hangover? When someone drinks more than their body can handle, there is a big chance of waking up the next day with a hangover. A hangover often implies having one or more of the following symptoms: headache, feeling weak, being lethargic, nauseous, shaky and spending the day bed-bound. Af ...
Lecture No. 2
... gills. Chloride ions always have primacy. It means that in water with abundance of chloride ions, the chloride cells are all occupied by chlorides, which block the absorption of NO2- to the bodies of fish and negative effects related with it • Another example is the competition between methyl alcoho ...
... gills. Chloride ions always have primacy. It means that in water with abundance of chloride ions, the chloride cells are all occupied by chlorides, which block the absorption of NO2- to the bodies of fish and negative effects related with it • Another example is the competition between methyl alcoho ...
Unit 10-Toxicology
... “All substances are poisons: there is none which is not a poison. The right dose differentiates a poison from a remedy.” ...
... “All substances are poisons: there is none which is not a poison. The right dose differentiates a poison from a remedy.” ...
Long-term effects of alcohol consumption
The long-term effects of alcohol (ethanol) consumption range from cardioprotective health benefits for low to moderate alcohol consumption in industrialized societies with higher rates of cardiovascular disease to severe detrimental effects in cases of chronic alcohol abuse. Health effects associated with alcohol intake in large amounts include an increased risk of alcoholism, malnutrition, chronic pancreatitis, alcoholic liver disease and cancer. In addition, damage to the central nervous system and peripheral nervous system can occur from chronic alcohol abuse. The long-term use of alcohol is capable of damaging nearly every organ and system in the body. The developing adolescent brain is particularly vulnerable to the toxic effects of alcohol. In addition, the developing fetal brain is also vulnerable, and fetal alcohol spectrum disorders (FASDs) may result if pregnant mothers consume alcohol.The inverse relation in Western cultures between alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease has been known for over 100 years. Many physicians do not promote alcohol consumption, however, given the many health concerns associated with it, some suggest that alcohol should be regarded as a recreational drug, and promote exercise and good nutrition to combat cardiovascular disease. Others have argued that the benefits of moderate alcohol consumption may be outweighed by other increased risks, including those of injuries, violence, fetal damage, liver disease, and certain forms of cancer.Withdrawal effects and dependence are also almost identical. Alcohol at moderate levels has some positive and negative effects on health. The negative effects include increased risk of liver diseases, oropharyngeal cancer, esophageal cancer and pancreatitis. Conversely moderate intake of alcohol may have some beneficial effects on gastritis and cholelithiasis. Of the total number of deaths and diseases caused by alcohol, most happen to the majority of the population who are moderate drinkers, rather than the heavy drinker minority. Chronic alcohol misuse and abuse has serious effects on physical and mental health. Chronic excess alcohol intake, or alcohol dependence, can lead to a wide range of neuropsychiatric or neurological impairment, cardiovascular disease, liver disease, and malignant neoplasms. The psychiatric disorders which are associated with alcoholism include major depression, dysthymia, mania, hypomania, panic disorder, phobias, generalized anxiety disorder, personality disorders, schizophrenia, suicide, neurologic deficits (e.g. impairments of working memory, emotions, executive functions, visuospatial abilities and gait and balance) and brain damage. Alcohol dependence is associated with hypertension, coronary heart disease, and ischemic stroke, cancer of the respiratory system, and also cancers of the digestive system, liver, breast and ovaries. Heavy drinking is associated with liver disease, such as cirrhosis. Excessive alcohol consumption can have a negative impact on aging.Recent studies have focused on understanding the mechanisms by which moderate alcohol consumption confers cardiovascular benefit.