* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name - chem.uwec.edu
Survey
Document related concepts
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
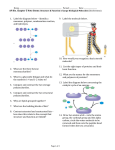
1 Name:_____________ Chem 150 Practice Exam #3 Exam 3 Directions: 1. Do not open the exam until you are told to do so. 2. Select only ONE choice for each problem and blacken or fill in the choice with a pencil (NOT ink pen). Selecting more than one choices or no selection for a problem will be counted wrong. 1 2 CHEM 150, EXAM 3: May 6, ’05 Name:__________________ Ch. 8 Lipids: 1. In which solvent would lipids be most soluble? a a. hexane b. water c. methyl alcohol d. ethyl alcohol 2. Inspect the molecules below and answer the questions that refer to these molecules. Molecules like these are classified as _______ . b O A HO B HO C HO C O H C H O H C a. b. c. d. e. triglycerides fatty acids waxes phospholipids none of the above H O D HO H H C 3. Molecule “B” in question #2 above can be referred to as _____ . d a. stearic acid b. lauric acid c. Oleic acid d. -3 fatty acid e. none of the above 4. Refer to question #2. Molecules B, C and D are said to be ________ . b a. saturated b. unsaturated c. completely hydrophobic d. completely hydrophilic 5. Because of the properties in portion A and portion B, the molecule below is said to have ______ properties. d O a. hydrophobic c. hydrophilic HO C A b. lipophobic d. amphipathic B 6. The structure CH3(CH2)12CH2COOCH2(CH2)24CH3 is best classified as a _____, b a. triglyceride b. wax c. steroid d. phospholipid e. none of the above 7. The steroid compound that is the source for the production of other steroid hormones is ____ . c a. arachidonic acid b. triglyceride c. cholesterol d. phospholipids 8. The steroid compound that is believed to be used for maintaining the correct degree of cell membrane rigidity is ____ . d a. arachidonic acid b. triglyceride c. sphingolipid d. cholesterol 2 3 Use the molecules in question #9 to answer questions # 9 – 11: 9. Which molecule is glycerophospholipid? Note: R’s represent long carbon chains. b O H C O C R O H C O C R' H A H C O O C R" H B C O H C O C R O H C O C R' H OH H C H C NH O C R H C O O + P O CH2CH2N(CH3)3 H O- H C O O P O CH2CH2NH2 H O- a. A b. B c. C d. none of the above 10. Which molecule is a lipid called sphingomyelin. c a. A b. B c. C d. none of the above 11. Which compounds form the cell membrane? d a. A only b. B only c. C only d. B and C only e. none of the above 12. Which molecule makes up oil? (Use the A, B and C as your answer choices.) c A O H H C O C O H C O C O H H C O C O H C O C H C O O C H H C O O C H C O H C O C O H C O C H B H C O O C H 13. Refer to question #12. Which molecule contains the fatty acyl groups of palmitic acid, stearic acid, and myristic acid? b a. A only b. B only c. C only d. both A and B e. none of the above 14. The effect of the hydrogenation of oils is to _____. a a. remove double bonds, increasing the degree of saturation. b. cause the oils to remain as liquids, increasing the C=C bonds. c. make the oils boil at a lower temperature d. make the oils oxidize 15. Shown below is the structure of estradiol. It belongs to what class of lipids? d a. b. c. d. phospholipids eicosanoids triglycerides steroids 3 4 16. Estradiol is considered to be a __________ hormone. a a. human female b. human male c. plant d. potato hormone 17. Shown below is a picture of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The tails of the lipids face each other because they are _____ . a a. hydrophobic c. amphipathic 18. This compound is a ______ . c b. hydrophilic d. amphoteric a. glycerolphospholipid c. glycolipid b. sphingomyelin d. triglyceride 19. What is the function of HDL? a a. transport cholesterol and phospholipids from cells to liver. b. transport cholesterol and phospholipids from liver to cells. c. digest cholesterol and phospholipids in cells. d. digest cholesterol and phospholipids in liver. ____ Ch. 12 Carbohydrates: 20. Which is the structure of glucose? d O O OH C O CH2OH H HO a). H H OH H OH OH b). C C O HO H H OH H OH c). H H H OH OH OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH C H H HO d). H H H OH H OH OH CH2OH 21. The monosaccharide below is a(n) _____ . b O C H H H H a. purine b. aldose c. enantiomer d. ketose e. glycolysis OH OH OH CH2OH 22. Which molecule contains the pyranose ring? a HOCH2 HO a). HOH2C O OH O HO b). CH2OH c). none of the above OH OH OH HO 4 5 23. Which molecule below is an aldohexose? a O H C O H HO HO H a). C OH H H OH H b). C C O HO H c). H OH H OH OH HO O CH2OH H H CH2OH d). H OH H H OH OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH H H e). H H C O OH OH OH CH2OH 24. Molecules II and IV are a pair of ________ . a O C H H H O OH OH C H HO CH2OH H O OH H a. enantiomers d. anomers H HO HO CH2OH II I C O H H HO H CH2OH III b. cis-trans isomers e. none of the above C H H OH CH2OH IV c. identical molecules 25. Which is the structure of -D-glucose? c CH2OH O HO OH O O OH OH HO OH B A a. A b. B C OH c. C d. D O HO OH OH HO CH2OH CH2OH CH2OH OH HO OH OH CH2OH D e. none of the above 26. Which is the structure of α-D-galactose? (Look up the structure on a sheet.) B CH2OH CH2OH HO O OH HO O OH OH OH OH OH A B 27. The structure of -D-ribose is shown below. Identify the anomeric carbon or hemiacetal carbon in -Dribose. a HOH2C O OH HO OH a. 1 only b. 2 and 3 c. 3 and 4 d. 1, 2 and 3 e. 1, 2, 3, and 4 5 6 28. If a molecule of sucrose is hydrolyzed (broken down to monosaccharides), what would be the monosaccharides found in the products? (Note: Do not consider the - or -forms). c a. two molecules of fructose c. one glucose and one fructose e. one fructose and one galactose b. one lactose and one glucose d. one galactose and one glucose 29. If a molecule of maltose is hydrolyzed, what would be the monosaccharides found in the products? (Note: Do not consider the - or -forms). c a. two molecules of fructose c. two molecules of glucose e. none of the above b. one fructose and one galactose d. one lactose and one glucose 30. If a molecule of lactose is hydrolyzed, what would be the monosaccharides found in the products? (Note: Do not consider the - or -forms). a a. one glucose and one galactose c. one fructose and one galactose e. none of the above b. one maltose and one fructose d. one fructose and one glucose 31. Olestra is composed of a disaccharide and several fatty acyl groups. What disaccharide is contained in the Olestra molecule? a. lactose b. maltose c. sucrose d. cellobiose e. none of the above 32. Which molecule possesses the (14) glycosidic bond? b HOCH2 O HOCH2 OH HOCH2 OH HOCH2 O O a. A only OH A b. B only OH O HO OH OH OH OH OH HO O O OH B c. both A and B Use the picture below to answer questions # 33 - 34. CH2OH 33. The molecule shown to the right can be classified as a(n) ___ . b a. monosaccharide b. disaccharide c. polysaccharide d. dipeptide e. none of the above OH O O HO 34. The glycosidic bond present on this molecule is _____ . c a. (14) b. (14) c. (16) d. (12) e. 16 CH2 OH O OH OH HO OH 35. What type of polysaccharide is shown below? a HOCH2 HOCH2 HOCH2 OH OH OH O O O O O O O OH OH OH a. b. c. d. e. amylose cellulose amylopectin glycogen starch 6 7 36. What is the biological role of amylopectin? c a. provide structural rigidity in plants c. provide energy or energy storage in plants e. form bile salts b. provide structural rigidity in animals d. provide energy or energy storage in animals 37. What is the biological role of glycogen? d a. provide structural rigidity in plants c. provide energy or energy storage in plants e. form cell membranes b. provide structural rigidity in animals d. provide energy or energy storage in animals 38. What polysaccharide provides structural protection to insects or crustaceans? e a. Cellulose b. amylose c. amylopectin d. glycogen e. chitin 39. How is the structure of cellulose different from that of amylose? b a. Cellulose has α(14) glysidic bond, but amylose has (14) glysidic bond. b. Cellulose has (14) glysidic bond, but amylose has α(14) glysidic bond. c. Cellulose has no branches, but amylose has brances. d. Cellulose has branches, but amylose has no brances. 40. How is the structure of glycogen different from that of amylopectin? c a. Glycogen has (14) and α(16) glycosidic bonds, but amylopectin has (14) bonds. b. Amylopectin has more frequency of branching than glycogen. c. Glycogen has more frequency of branching than amylopectin. d. Glycogen has α(14) and α(16) glycosidic bonds, but amylopectin has (14) bonds. 41. What type of glycosidic bond is present on this polysaccharide found in certain types of lichens? d O CH2 O O OH CH2 O HO OH OH HO O a. b. c. d. e. α(14) (14) α(16) (16) none of the above OH Ch. 13: Amino acids 51. The side chain of the amino acid phenylalanine is shown here. The side chain is classified as _____. a a. nonpolar b. polar-acidic -H2C c. polar-basic d. polar-neutral 52. The side chain of the amino acid histidine is shown here. The side chain is classified as _____. c a. nonpolar H N b. polar-acidic + c. polar-basic N -H 2C H d. polar-neutral 7 8 54. Shown here is the amino acid alanine at a pH of _____. b 53. Shown here is the amino acid alanine at a pH of _____. c H O + H3N C C CH3 O- a. b. c. d. 1 14 neutral pH both (a) and (c) H O H2N C C CH3 O- a. b. c. d. 1 14 neutral pH both (a) and (c) 55. The side chains of which pair of amino acids can form a salt bridge? Note: Look up the amino acid structure sheet. c a. Glycine and Aspartic acid b. Glutamic acid and Aspartic acid c. Lysine and Glutamic acid d. Alanine and Leucine e. none of the above 56. A zwitterion is an _____. c a. ion that is polar acidic. b. ion that is polar basic. c. ion that has both positive and negative charge. d. ion that is polar neutral. Use this molecule to answer questions #57 – 59: H2N H O H H O H H O H H O H H O H H O C C N C C N C C N C C N C C N C C H CH2 H CH2 CH2 O CH2 CH2 C OH O- OH A CH2 NH3+ 57. This molecule can be classified as a(n) _____ . c a. polysaccharide b. polypeptide c. hexapeptide d. protein 58. What is the amino acid sequence of this molecule? b a. Pro-Ser-Asp-Gly-Lys-Gly b. Gly-Lys-Gly-Asp-Ser-Pro c. Gly-Arg-Gly-Asp-Ser-Pro d. Pro-Ser-Glu-Gly-Lys-Gly e. none of the above 59. The N-terminus amino acid residue is ______ . b a. Proline b. Glycine c. Lysine d. Aspartate 60. The denaturing of a protein can be caused by _____. d a. heating b. exposing to detergents c. changing the pH d. All of these can cause denaturation 61. Which picture below best represents the structure of the Hemoglobin molecule? Note: Each circle represents a subunit. c 62. Enzymes are _____ . a a. proteins b. polysaccharides c. lipids 63. Circle all the chiral carbon atoms on this molecule. This is testing on the concept of chirality. e a). b). c). d). 8 9 d. inorganic compounds e. coordination compounds 8 CH3 N 2 1 9 3 7 O C 10 O CH3 4 6 O 5 O C 11 17 16 15 a. 4 and 5 b. 4, 5, 9, and 11 c. 2, 3, 7, 9, and 11 d. 3, 4, 5, 6, 8 and 17 e. 3, 4, 5, and 7 12 13 14 64. Evaluate this statement and see what level of protein structure it describes. “The polypeptide chain has a number of bends and twists which result in compacting it into a ball-like unique threedimensional shape.” c a. primary structure d. quaternary structure b. secondary structure e. none of the above c. tertiary structure 65. The α-helix and β-pleated sheet are both forms of the _____ structure of proteins. b a. primary b. secondary c. tertiary d. quaternary Use the picture below for questions # 66 - 69: A C B E D 66. On the structure of the protein above, the non-covalent interaction labeled by arrow “A” is called ______ . d a. salt bridge b. hydrogen bond c. disulfide bond d. hydrophobic interaction e. none of the above 67. On the structure of the protein above, the non-covalent interaction labeled by arrow “B” is called ______ . a a. salt bridge b. hydrogen bond c. disulfide bond d. hydrophobic interaction e. none of the above 9 10 68. Which arrow points to a region that has the -sheet structure? d a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 70. What would happen to the non-covalent interaction in the protein structure below if the Lysine side chain is replaced with a Glutamic acid side chain (CH2CH2COO-)? c 69. Which arrow points to a region that has the α-helical structure? e a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 71. On the picture below, what does Z represent? a y x a type of non-covalent interaction Lysine -CH2CH2H2CH2NH3+ II _ O z NO "P" is formed C CH2- Aspartic acid O a). The non-covalent interaction shown would remain intact. b). The protein structure would be broken down to individual amino acids. c). The ionic interaction would be broken and cause the protein to lose its unique structure. d). Hydrogen bond would be formed between the -CH2CH2COO- and –OOCCH2- side chains, and the protein structure would remain the same. a. Z = enzyme c. Z = products b. Z = substrate d. Z = inhibitor ____________________ 72. What is the effect of X upon binding or fitting into one of the pocket on Z in question #71? c a. stimulation of product formation (Product formed faster). b. has no effect. c. inhibition of product formation. d. X turns into product. 10