* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Cell Recorded Lectures
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide phosphate wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Mir-92 microRNA precursor family wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
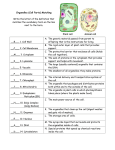
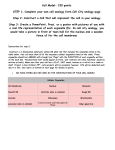
‘The Cell’ Recorded Lectures Student Self-Evaluation After listening and taking notes to the recorded lectures, quiz yourself. Make a note of any topics you do not understand or want the instructor to review. The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 1 (~21 min.): 1. List the three statements included in the Cell Theory. 2. List, in order, the levels of biological organization in the human body. The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 2 (~25 min.): 1. Proteins that speed up the rate of chemical reactions are called 2. What are the three main components of the cell (plasma) membrane? 3. Proteins have three main functions in the plasma membrane. In general, what are they? 1 4. Why are many chemical reactions performed at membranes? The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 3 (~31 min.): 1. Sub-cellular components in the cytoplasm that perform some function(s) for the cell as a whole are called . 2. What organelle may be found on the surface of the ER or in the cytoplasm? 3. The building blocks of proteins are called Many of these are bonded together to form a protein. 4. Organelles in the cell that are the sites of protein synthesis are called . 5. What organelle is composed of protein rods and cylinders; they function in movement & cell structure? 6. Which genetic disorder results in a loss of cellular functional shape due to a loss of connections between the plasma membrane and the cytoskeleton? Red blood cells balloon out and, therefore, have difficulty moving through small capillaries. 7. List the organelles discussed in the Part 3 Recorded Lecture. 2 The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 4 (~26 mn.): 1. Genes determine what a cell can make. 2. How many total chromosomes are found in most human cells? 3. What organelle contains 46 chromosomes in humans? 4. A chart with a picture of all of a person’s chromosomes is called a… 5. A section of DNA containing the instructions for making one protein is called a 6. Pairs of chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father, are called Chromosomes or . 7. Each person obtains one member of each homologous pair from his/her and one member from his/her These are the maternal and paternal members of each homologous pair. . 8. How many chromosomes did you get from your father? 9. How many chromosomes did you get from your mother? 10. What is the difference between the terms locus, gene, and allele? 3 11. How are homologous chromosomes alike? 12. How are homologous chromosomes different? 4 The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 5 (~22 min.): 1. Membrane-bound ‘sacs’ are called . 2. How are the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi body alike? 3. How are the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and the Golgi body different? 4. The term used for the DNA that is found in cells the majority of the time, when the DNA is ‘active’ (proteins are being produced from the instructions in the DNA), and, therefore, is less coiled? See the illustration of the uncoiling chromosome in the Lecture Guide. 5. What form are the chromosomes found in only during the cell division process and, therefore, are the most highly coiled (see illustration of the uncoiling chromosome)? 5 The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 6 (~36 min.): 1. What organelle is affected by Tay Sachs and Pompe Disease? What specifically is defective or missing in each of these diseases? 2. What organelle is used to acquire energy from glucose? 3. What organelle contains about 40 digestive enzymes? 4. Which genetic disorder results in an inability to break down glycogen in lysosomes? It builds up in tissues and usually results in an early death. 5. Which genetic disorder results in blindness? Why? 6. Explain why many researchers believe mitochondria were at one time singlecelled organisms (like bacteria) that were incorporated into and remained in a larger cell. 7. From whom do you inherit your mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA)? 6 The Cell Recorded Lecture Part 7 (~45 min.): 1. Groups of similar cells performing similar functions are called the 2. Write the letter of the description with the appropriate tissue. Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Epithelial tissue Connective tissue a. b. c. d. Examples are blood, fat, cartilage, and bone Movement Line the surfaces of the body Sends electrical & chemical signals to coordinate & control body activities 3. What genetic disorder results in a defective gene for dystrophin? 4. In order to form all of the different types of cells in the body, different genes are turned on and off in different cells. This process of forming different types of cells is called… OR 5. The first cell formed after fertilization is called the This is the ‘fertilized egg. . 6. What does the sperm contribute to the first cell formed after fertilization? 7. What does the egg contribute to the first cell formed after fertilization? 7 8. What genetic disorder is lethal to males and results in a variety of symptoms for females (such as marbled skin, vesicles that turn wart-like, loss of hair, seizures…)? 9. What types of human cells do NOT have 46 chromosomes? Why? 10. Match the following letter to the appropriate term: Multipotent a. able to develop into any type of cell, including an complete new organism Totipotent b. able to develop into many different types of cells Pluripotent c. able to develop only into a few different types of cells Specialized d. not able to develop into any other types of cells 11. Describe four different times when a gene might be expressed or ‘turned on’. 8 12. Describe the process which results in the specialization of cells and when this occurs during development. Questions concerning the ‘Organization of Cell Activities: Synthesis and Modification of a Protein’ 1. List the organelles described in the lecture that may be used to form a functional protein. These organelles synthesize, alter and transport proteins so that they are able to carry out their intended function for the cell/body. Make sure the organelles are in the CORRECT ORDER. 9 2. What are the functions of the above organelles in the process to synthesize, alter and transport proteins? 3. Describe why and how portions of membranes are able to ‘pinch off’. 10 The following questions concern the analogy between making a birthday cake for an eight-year old girl and synthesizing a protein in the cell. Questions 1-5- Use the choices below. a. Gene b. ER c. Chromosome d. Oven e. Recipe card 1. An analogy was made between a cookbook while baking a cake and a when synthesizing a protein. 2. An analogy can be made between the mitochondria when synthesizing a protein and a when baking a cake. 3. An analogy was made between icing a birthday cake and the synthesizing a functional protein. when 4. An analogy was made between the copy of the instructions in the DNA when synthesizing a protein and a when making a birthday cake. 5. An analogy was made between one recipe in the cookbook and one synthesizing a functional protein. when Continued… 11 6. Which one of the following is the reason for the correct analogy in question number 1? a. They contain many original instructions for different recipes or proteins. b. They contain the original instructions for one cake and one protein. c. They both modify the cake or protein. d. They both provide energy. e. They contain copies of the original instructions. 7. Which one of the following is the reason for the correct analogy in question number 2? a. They contain many instructions for different recipes or proteins. b. They contain the original instructions for one cake and one protein. c. They both modify the cake or protein. d. They both provide energy. e. They contain copies of the original instructions. 8. Which one of the following is the reason for the correct analogy in question number 3? a. They contain many instructions for different recipes or proteins. b. They contain the original instructions for one cake and one protein. c. They both modify the cake or protein. d. They both provide energy. e. They contain copies of the original instructions. 12 9. Which one of the following is the reason for the correct analogy in question number 4? a. They contain many instructions for different recipes or proteins. b. They contain the original instructions for one cake and one protein. c. They both modify the cake or protein. d. They both provide energy. e. They contain copies of the original instructions. 10. Which one of the following is the reason for the correct analogy in question number 5? a. They contain many instructions for different recipes or proteins. b. They contain the original instructions for one cake and one protein. c. They both modify the cake or protein. d. They both provide energy. e. They contain copies of the original instructions. Questions which may appear on the last exam (Exam 4) Know the functions each cell organelle described in the lectures. Structure determines . 13 Practice labeling the cell. 14