* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name___________________________________ Per____
Criticism of Twelver Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
International reactions to Fitna wikipedia , lookup
Islamofascism wikipedia , lookup
Muslim world wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Mormonism wikipedia , lookup
The Jewel of Medina wikipedia , lookup
Islamic Golden Age wikipedia , lookup
Sources of sharia wikipedia , lookup
Gender roles in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
War against Islam wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Satanic Verses wikipedia , lookup
Medieval Muslim Algeria wikipedia , lookup
Islamic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Islamic–Jewish relations wikipedia , lookup
Liberalism and progressivism within Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Afghanistan wikipedia , lookup
Soviet Orientalist studies in Islam wikipedia , lookup
Criticism of Islamism wikipedia , lookup
Censorship in Islamic societies wikipedia , lookup
Islam and violence wikipedia , lookup
Islamic missionary activity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic ethics wikipedia , lookup
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic socialism wikipedia , lookup
Historicity of Muhammad wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Bangladesh wikipedia , lookup
Political aspects of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Islamic culture wikipedia , lookup
Origin of Shia Islam wikipedia , lookup
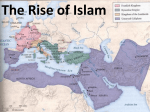
AP World History Name___________________________________ Per____ Date______________________________ Chapter 8 STUDY GUIDE- Rise of Islam 600-1200 Using complete sentences, answer the following questions on a separate sheet of paper. Page numbers are provided. 1. What was the division in the Islamic community about and who were the groups involved? P.197 2. In what region was the Sassanid Empire? P.197 3. What holy shrine is located in Mecca? According to stories connected with it, who built the shrine and what happened near the site? P.198 4. Who/what was revealed to Muhammad? P.199/200 5. Muhammad’s teachings seem to be in agreement with what religions? P.201 6. What was Muhammad’s flight to Medina called? P.201 7. What did the supremacy of the Median state depend on? P.201 8. Who was Muhammad’s successor and what was his title? P.201 9. List the 5 pillars of Islam. P.201 10. What is the Quran? P.201-2 11. Why was the Battle of Camel fought? P.202 12. What happened as a result of Husayn’s death? P.202 13. Who are the Ahl al-Sunna wa’l-Jama’s, or Sunni for short? P.202 14. List 5 regions/countries conquered by the Muslim caliphs. Pp.202-03 15. What caused the unrest that led to the fall of the Umayyad caliphate? P.203 16. Why was the Abassid period called a “golden age”? p.204 17. Why did the Abassid caliphate decline in power? P.204 18. After failing to reform their government and military, the Abassid Caliphate fell under the influence whom? P.205 19. What cultures were blended together in Umayyad Spain? P.206 20. Who was Maimonides and what did he do? P.206 21. Who were the ulama? P.207 22. Describe the change in economy, government involvement in religious matters, and population during the reign of the Seljuk Turks. P.207 23. Who recaptured Jerusalem from European Crusaders? P.208 24. What is Shari’a? p.208 25. What did the hadith deal with? And what was a problem with the hadith? P.209 26. The Shari’a embodied a vision of what? P.209 27. What did conversion to Islam entail? P.209 28. Why did converts to Islam face discrimination if they remained in their Christian, Jewish, or Zoroastrian communities? And how could they avert discrimination? P.210 29. How did urban growth help the countryside? And what were some of the main crops grown? P.210 30. What helped facilitate long-distance trade and integrate rural areas into the economy? P.210 31. Who influenced Muslim science and technology? And what were 3 major scientific advancements of Ibn al-Haytham? P.210 32. Describe 4 aspects of the life of urban women. P.210 33. What are Sufis and what was a common doctrine of Sufism? P.214-5 Shi’ites Muslims belonging to the branch of Islam believing that God vests leadership of the community in a descendant of Muhammad’s son-in-law Ali. Shi’ism is the state religion of Iran. (See also Sunnis.) (pp. 197, 496) Mecca City in western Arabia; birthplace of the Prophet Muhammad, and ritual center of the Islamic religion. Mamluks Under the Islamic system of military slavery, Turkic military slaves who formed an important part of the armed forces of the Abbasid Caliphate of the ninth and tenth centuries. Mamluks eventually founded their own state, ruling Egypt and Syria (1250–1517). Medina City in western Arabia to which the Prophet Muhammad and his followers emigrated in 622 to escape persecution in Mecca. (p. 201) caliphate Office established in succession to the Prophet Muhammad, to rule the Islamic empire; also the name of that empire. Umayyad Caliphate First hereditary dynasty of Muslim caliphs (661 to 750). From their capital at Damascus, the Umayyads ruled an empire that extended from Spain to India. Overthrown by the Abbasid Caliphate. Muslim An adherent of the Islamic religion; a person who “submits” (in Arabic, Islam means “submission”) to the will of God. (p. 201) ulama Muslim religious scholars. From the ninth century onward, the primary interpreters of Islamic law and the social core of Muslim urban societies. Sunnis Muslims belonging to branch of Islam believing that the community should select its own leadership. The majority religion in most Islamic countries. Muhammad (570–632 c.e.) Arab prophet; founder of religion of Islam. (p. 199) Islam Religion expounded by the Prophet Muhammad (570–632 C.E.) on the basis of his reception of divine revelations, which were collected after his death into the Quran. In the tradition of Judaism and Christianity, and sharing much of their lore, Islam calls on all people to recognize one creator god—Allah—who rewards or punishes believers after death according to how they led their lives. umma The community of all Muslims. A major innovation against the background of seventh-century Arabia, where traditionally kinship rather than faith had determined membership in a community. (p. 201) Quran Book composed of divine revelations made to the Prophet Muhammad between ca. 610 and his death in 632; the sacred text of the religion of Islam. Abbasid Caliphate Descendants of the Prophet Muhammad’s uncle, al-Abbas, the Abbasids overthrew the Umayyad Caliphate and ruled an Islamic empire from their capital in Baghdad (founded 762) from 750 to 1258. Ghana First known kingdom in sub-Saharan West Africa between the sixth and thirteenth centuries C.E. Also the modern West African country once known as the Gold Coast. hadith A tradition relating the words or deeds of the Prophet Muhammad; next to the Quran, the most important basis for Islamic law. Free Response Focus Questions: Answer these questions in a 5-7 sentence paragraph. In your own words. Do not simply copy from the book and memorize the response. Support your response with plenty of facts. Understand where events fall historically (global context, cause/effect, etc) 1. Explain how Islam was able to spread from Spain to India in a relatively short amount of time, dominating a wide range of territories and societies. 2. Compare and contrast the Umayyad and Abbasid caliphates, particularly regarding religion, politics and military. 3. Describe the evolution of Islamic cultural and economic development. What was its impact on Europe? 4. What does the chapter reveal about the status of Muslim women? Compare the status of Muslim women with the status of women in other parts of the world at that time.