* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exam 3: Plants and Fungi Supplemental Instruction Iowa State
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
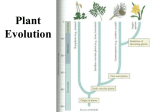
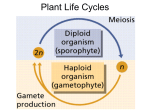
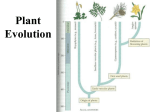
Leader: Course: Supplemental Instruction Instructor: Iowa State University Date: 1. Seedless vascular plants need to be able to support their above-ground body, what material is incorporated in their cell walls in order to do so? Cellulose Peptidoglycan Lignin Actin Exam 3: Plants and Fungi 2. The most closely related, extant group of organisms to members of kingdom Plantae is charophycean algae. True False 53. A ______ is a unique structure to zygomycota in the _________ reproduction? zygosporamgia, asexual zygosporamgia, sexual basidocarp, sexual basidiocarp, asexual 3. All plants have waxy cuticles, sporopollenin, cellulose, and seeds at some point in their life cycles. True False In moving to land, plants had to overcome which of the following challenges? Less available CO2 in the atmosphere than in the oceans Desiccation Lack of structural support Both b and c Plants undergo alternation of generations in which _________. The sporophyte generation alternates with the gametophyte generation - mention multicellularity The vascular generation alternates with the nonvascular generation Male plants alternate with female plants Antheridia alternate with archegonia ____________ protect(s) pollen grains from environmental damage. Sporopollenin Lignin Cuticles Stomata 13. The gametophyte state of the plant life cycle is most conspicuous in _______. Ferns Mosses - bryophyta, gametophyte dominate Horsetails Seed plants 14. Which of the following produce eggs and sperm? Megaphylls Fern sporophytes Moss gametophytes Megaspores Moss sporangia 15. Fertilization in moss occurs when sperm swim from a(n) ______ and down the neck of a(n) _______. Antheridium; sporangium Antheridium; archegonium Archegonium; antheridium Sporangium; archegonium 17. Ferns and mosses are limited mostly to most environments because _________. They lack cuticles and stomata They lack vascular tissue They have swimming sperm Their seeds do not store water 19. Heterosporous plants produce ___________. Megaspores that develop into female gametophytes and microspores that develop into male gametophytes Megaspores that develop into male gametophytes and microspores that develop into female gametophytes Megaspores that bear antheridia and microspores that bear archegonia Spores that produce both archegonia and antheridia 20. Sori can be found in which of the following? Mosses Pterophytes - what are sori? Lycophytes Charophyceans Karyogamy is ____________ in a ____________. nuclie fuse, plant nuclie fuse, fugni when there are two different nuclei, plant when there are two different nuclei, fungi 21. Which of the following adaptations is common to all seed plants? Reduced gametophytes Pollen Ovules All of the above 23. Which one of the following is true of seed plants, but not true of seedless plants? The sporophyte is dependent on the gametophyte The sporophyte is large, and the gametophyte is small and independent The gametophyte is reduced and dependent on the sporophyte A film of water is necessary for sperm to come in contact with eggs 24. The eggs of seed plants are fertilized within ovules, and the ovules then develop into __________. Seeds Gametophytes Fruit Ovaries 25. What gymnosperm phylum is characterized by large cones and fern-like leaves? Anthophyta Gnetophyta Coniferophyta Cycadophyta - looks like palm trees! 26. What is located in the scalelike structures packed densely in pollen cones? Sporophyte Sporangia Megasporocytes Developing pollen tubes Sexual reproduction is ____________ than asexual reproduction and yeilds genetically ________ offspring. faster, identical faster, different slower, identical slower, different 28. In ovulate cones megasporocytes undergo _____ and produce _____ megaspores Mitosis; diploid Meiosis; diploid Mitosis; haploid Meiosis; haploid - same with sporophytes and microsporophytes 51. During what stage of fungal reproduction are diploid cells produced? Karyogamy Meiosis Dikaryotic stage Plasmogamy 29. Which types of angiosperms would most likely be wind-pollinated rather than animalpollinated? Oak and maple trees Roses and tiger lilies None of the choices are correct. Plants with flowers are not wind-pollinated 30. The portion of a flower that receives the pollen is the ________. Filament Ovary Stigma Style 31. A pea pod is formed from ________. A pea inside the pod is formed from ________. An ovule; a carpel An ovary; an ovule An ovary; a pollen grain Endosperm; an ovary 32. The pollen tube releases two sperm cells into the embryo sac. The result of this is the __________. Union of the two sperm nuclei; forming a zygote Union of one sperm nucleus with the egg nucleus while the other sperm nucleus unites with two nuclei of another megagametophyte cell, forming a triploid nucleus Union of one sperm nucleus with the egg nucleus and the disintegration of the other sperm nuclei. Fusion of both sperm nuclei with the egg nucleus and the formation of a triploid zygote 33. The triploid nucleus of the embryo sac develops into the ________. Endosperm Fruit Carpel Seed 34. Which of the following characterizes eudicots Pollen grains with three openings, floral parts in multiples of three, netlike veins Two cotyledons, netlike veins, taproot usually present Scattered vascular bundles, netlike veins, floral parts in multiples of five Leaves with parallel veins, taproot usually present, vascular bundles arranged in rings. 36. Charophytes are related to plants in all of the following ways EXCEPT: They have an apical meristem Formation of Phragmoplast Peroxisome enzymes Rose-shaped complexes that synthesize cellulose 38. What generation(s) of the hepatophytes can photosynthesize? The gametophyte only - gametophyte dominant The sporophyte only The gametophyte and the sporophyte All haploid cells can photosynthesize in hepatophytes 39. Which of the following characteristics do mosses, liverworts, and hornworts share? a. reproduction in gametangia; embryos b. vascular tissues, true leaves, and a waxy cuticle c. seeds Fern gametophytes are _____. photosynthetic diploid organisms produced from haploid gametes part of the asexual life cycle free-living, multicellular organisms - but sporophyte dominate found on the underside of fern leaves (fronds) 41. Which of the following is not common to all phyla of vascular plants? The development of seeds alternation of generations dominance of the diploid (sporophyte) generation xylem and phloem sporophyte that is independent of the gametophyte 45. In vascular plants, a. xylem conducts nutrients (sugars) - mainly up, water b. phloem conducts nutrients (sugars) - up down c. xylem is made of cellulose d. phloem and xylem both conduct nutrients (sugars) 47. Fungi are _____________ organisms. Chemoautotrophic Mixotrophic Chemoheterotrophic Photoheterotrophic 48. Fungi that consist of a continuous hyphae with hundreds or thousands of nuclei are known as _______________. Septic Coenocytic - aspetic Dikaryon Chytrids 49. The hyphae of parasitic fungi that are modified to penetrate and absorb nutrients from host tissue are called Haustoria Asci Mycorrhizae - specialized to share Septa 6. How are gametes produced in plants? By mitosis of gametophyte cells By meiosis of gametophyte cells By meiosis of sporophyte cells By mitosis of spores By meiosis of spores 50. Which choice below generally represents the correct order of events in fungal sexual reproduction? Karyogamy, meiosis, plasmogamy, germination Meiosis, plasmogamy, karyogamy, germination Plasmogamy, meiosis, germination, karyogamy Plasmogamy, karyogamy, meiosis, germination 51. Which feature below is unique to ascomycota? Asci (spore-producing sacs) Zoospores (flagellated spores) Cell walls made of chitin Conidia (asexual spores) 54. An basida is _______________. A structure used in the sexual reproduction of basidiomycota A structure used in the asexual reproduction of basidiomycota A structure used in the sexual reproduction of ascyomycota A structure used in the asexual reproduction of ascomycota 55. Lichens are ______________. Mutualistic associations of fungi and plant roots Predatory fungi The sexual state of deuteromycetes Symbiotic associations of photosynthesizers and fungi 42. Peat moss is ecologically important because It can be used in agriculture to prevent flooding It can store water and nutrients so different animals can feed on it It captures carbon dioxide and helps fight global warming 43. Walking in a forest I find a plant whose dominant stage is the gametophyte, it must be a(n) Angiosperm Gymnosperm Pterophyte Bryophyte 44. Which of the following is diploid? a. the archegonia of a moss b. a cell in the gametangia of a moss c. a cell that is part of the stalk of a moss sporophyte d. a spore produced by a sporophyte 56. An ascus is _______________. A saclike structure containing spores An asexual spore-producing structure on a stalk A club-shaped cell with spores on its outer surface A cup-shaped structure containing many spore-producing cells on the gill of a mushroom 60. Some species of _____________ are among the largest and oldest individuals on Earth. Conifers Cycadophyta Gymnosperms Both 1 and 2 Both 1 and 3 12. In fungi, the function of the mycelium is _____. a. dispersal to distant habitats b. defense c. obtaining food d. surviving a period of food shortage e. movement 10. _____ fungi are decomposers. a. Mutualistic b. Parasitic c. Absorptive d. Saprobic e. Mycorrhizal 2. The adaptive advantage associated with the filamentous nature of fungal mycelia is primarily related to a. the ability to form haustoria and parasitize other organisms. b. avoiding sexual reproduction until the environment changes. c. the potential to inhabit almost all terrestrial habitats. d. the increased probability of contact between different mating types. e. an extensive surface area well suited for absorptive nutrition. 43. The diploid generation of the plant life cycle always _____. a. produces spores b. is called the gametophyte c. is larger and more conspicuous than the haploid stage d. develops from a spore e. produces eggs and sperm 40. An ovule consists of a. Megasporangium b. Megaspore c. Integuments d. All of the above 33. Which of the following is a land plant that produces flagellated sperm and has a sporophytedominant life cycle? a. fern b. moss c. liverwort d. charophycean e. hornwort 30. The _____ in the archegonium grows into a _____. a. Zygote, gametophyte b. Spore, gametophyte c. Zygote, sporophyte d. Spore, sporophyte Refer to the figures on the board and place the correct letter next to each name: Xyloem B Plasmogamy F seed D anther C Megaspore K Megasporocyte G germination M Megasporangium L Ovule O Phloem A Microspore H Karyogamy N Microsporangium J Asexual reproduction P Ovary Q Microsprocytes I pollen tube R stigma E Style S