* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
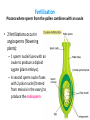
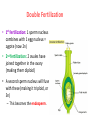
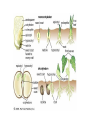
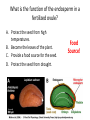
A. B. C. D. Male Structures Female Structures Neither Both Male! These are stamen with white filaments & large anthers carrying pollen. A. B. C. D. Male Structures Female Structures Neither Both Female! This is the carpel, which leads down to the ovary. A. B. C. D. Male Structures Female Structures Neither Both Both! You can see the stamen & the carpel. If flowers can have male & female parts, can they self-pollinate? Yes! • Flowers can self-pollinate OR cross-pollinate. How do plants reproduce? Plant Reproduction Alternation of Generations • Plants have 2 reproductive life cycles: – Diploid Sporophyte Generation – Haploid Gametophyte Generation • Applies to Bryophytes, Seedless Vascular Plants, Gymnosperms, & Angiosperms Sporophyte & Gametophyte Generation • Our human bodies undergo meiosis to create gametes. Once an egg is fertilized, it undergoes mitosis for the baby to grow & develop. • Plants undergo haploid gametophyte generation to create gametes. Once fertilization occurs, the plant switches to diploid sporophyte generation to grow. Diploid (2N) Sporophyte Generation • Familiar, recognizable form of a plant • Develops from a zygote • Cell replication through mitosis Haploid (N) Gametophyte Generation • Gamete cells created from meiosis • Sperm & egg cells – Pollen & ovules • Combine to form a zygote, which grows into the sporophyte generation Alternation of Generations The actual plant that you think of is the sporophyte (2n). The sporophyte undergoes meiosis to produce the gametophyte (1n). The male gametophyte is pollen & the female gametophyte is the ovule. The gametophytes (pollen & ovule) produce gametes (sperm & egg). When gametes fuse, a new sporophyte will develop. Gametophytes • Gymnosperms: cones – Pollen forms in the male pollen cones. – Ovules form in the female seed cones. • Angiosperms: flowering plants – Flower is the reproductive structure, with male (stamen) & female (carpel) parts Is pollen a male structure or a female structure? A. B. C. D. Male Structure Female Structure Neither Both Male! Pollen forms on the stamen. Pollination • Process in which pollen is spread • Plants can be self-pollinated or cross-pollinated – Wind, insects, & animals can all help pollinate The flower of an angiosperm helps attract birds & insects! Fertilization Process where sperm from the pollen combines with an ovule • 2 fertilizations occur in angiosperms (flowering plants): – 1 sperm nuclei fuses with an ovule to produce a diploid zygote (plant embryo). – A second sperm nuclei fuses with 2 polar nuclei (formed from meiosis in the ovary) to produce the endosperm. Double Fertilization • 1st fertilization: 1 sperm nucleus combines with 1 egg nucleus = zygote (now 2n) • 2nd fertilization: 2 ovules have joined together in the ovary (making them diploid) • A second sperm nucleus will fuse with these (making it triploid, or 3n) – This becomes the endosperm. Anatomy of a Seed • Endosperm: food source for the plant embryo • Cotyledon: seed leaf of plant embryo (will become the first leaves) • Seed Coat: protection Which of the following does not play a direct role in sexual reproduction? A. B. C. D. Petal Ovary Anther Style Petals! What is the function of the endosperm in a fertilized ovule? A. Protect the seed from high temperatures. B. Become the leaves of the plant. C. Provide a food source for the seed. D. Protect the seed from drought. Food Source! Video Fruits • Ripened ovary that contains angiosperm seeds - Strawberries, peaches, apples, peas, corn, beans, cucumbers, and tomatoes The ovary wall surrounding the fruit may be fleshy (like a grape) or tough (like a bean pod)! Vegetables • Other edible parts of a plant, like the roots, tubers, bulbs, stems, leaves, or flower parts The part of the carrot that you eat is the root of the plant! Plant Reproduction • In your groups, put the cards in the correct sequence of plant reproduction. • When you finish, raise your hand & I will check it! • Once it is correct, I will give you your exit ticket!