* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Math 7 Scope and Sequence By
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical proof wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematical notation wikipedia , lookup
Discrete mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and architecture wikipedia , lookup
Mathematical model wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics and art wikipedia , lookup
History of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
List of important publications in mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Secondary School Mathematics Curriculum Improvement Study wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
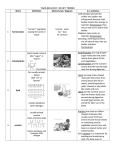
Math 7 Scope and Sequence By Mardonnia Silva and Jeanne Sidoroff BETA Campus Math 7 -Year At a Glance First Semester Three Weeks Topics/ Concepts TEKS Resource: Passport to Math Book2 1st 3 weeks 2nd 3 weeks 3rd 3 weeks 4th 3 weeks 5th 3 weeks 6th 3 weeks Basic MATH Number Theory and Relationships Fractions and their Operations Algebra and Integers (Part 1) Algebra and Integers (Part 2) Ratios And Proportions Ch. 6 2D, 3B, 4A, 6D, 8C, 13D, 14A, 15B Problem-Solving Strategies Ch. 1 2F, 2G, 13A, 13B, 13C, 14A, 14B Second Semester Three Weeks Topics/ Concepts Math 7/Advance Solving Equations Ch. 2 1A, 1B, 1C, 2E, 13D, 15A, 15B Ch. 3 1B, 2A, 2B, 2E, 14A Ch. 4, Ch. 10 1A, 2C, 2G, 4B, 4C, 5A, 7A, 11B, 13C, 13D, 14A, 14B Ch. 10 2C, 2E, 14A, 15A, 15B Math 7/Advance 1st 3 weeks 2nd 3 weeks 3rd 3 weeks 4th 3 weeks 5th 3 weeks 6th 3 weeks Percents and Decimals Plane Geometry (Part 2) Data Analysis and Statistics Probability and Statistics Problem Solving Linear Functions and Equations Plane Geometry (Part 1) Solid Geometry TEKS Resource: Passport to Math Book2 Ch. 7, Ch. 8 2A, 2B, 2F, 2G, 3A, 4A 4B, 6A, 6B, 6D, 7A, 7B, 9A, 11B, 13A, 13C, 14A, 15A, 15B Ch. 8, Ch.9 4A, 4B, 4C, 6C, 8A, 8B, 8C, 9A, 11A, 13A, 13C, 15A, 15B TAKS LEVEL REVIEW Ch. 5, Ch. 11 2F, 2G, 4C, 10A, 11A, 11B, 12A, 12B, 13A, 13B, 13C, 14A, 15B Ch. 11 2F, 2G, 4C, 10A, 11A, 11B, 12A, 12B, 13A, 13B, 13C, 14A, 15B 13A, 13B, 13C, 13D, 14A, 14B, 15A, 15C Ch. 12 2C, 2F, 4C, 5A, 13B, 14A, 15A, 15B Basic Math/Problem Solving Strategies (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 1st 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections Determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem Basic Operations: Decimals and Whole Numbers Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Ways to solve real world problems 1.1-1.9 Place Values 2F 2G Problem Solving Strategies Solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school 13A, 13B, 13C, Communicates about 14A, mathematics through informal 14B and mathematical language, representations, and models Uses logical reasoning to make conjectures and verify conclusions 15A 15B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 6 Number Relationships (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 2ND 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Compare and order integers and positive rational numbers Order of Operations 1A Powers and Exponents Convert between fractions, decimals, whole numbers, and 1B percents mentally, on paper, or with a calculator Simplify numerical expressions involving order of operations and exponents Select tools such as real objects, manipulatives, paper/pencil, and technology or techniques such as mental math, estimation, and number sense to solve problems 2E Number Patterns • Divisibility • Prime Factorization Fractions in Simplest Form A Division Model of Fractions Greatest Common Factors 13D The student uses logical 15A reasoning to make conjectures 15B and verify conclusions Ordering Numbers on a Number Line Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 2.1-2.8 TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 6 Fractions and Operations (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 3rd 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Convert between fractions, 1B decimals, whole numbers, and percents mentally, on paper, or with a calculator Represent multiplication and division situations involving fractions and decimals with concrete models, pictures, words, and numbers Use addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division to solve problems involving fractions and decimals Simplify numerical expressions involving order of operations and exponents 2A Finding L C M Mixed Numbers and Improper fractions Add Subtraction Fractions with common denominators Dividing Fractions and Mixed Numbers 2E Communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient 14A tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models 3.1-3.7 Adding subtracting Mixed Numbers Distributive Property 2B Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 6 Algebra and Integers (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 4th 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Compare and order integers Use models for integers and connect the actions to algorithms Determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem 1A Patterns, Tables, and Expressions 2C Scatter Plots and Coordinate Planes Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 2G Integers and Number Line 4.1-4.7 Adding Integers Graph data to demonstrate relationships such as conversions, perimeter, and area Describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence 4B Solving Addition Equations Solving Subtraction Equations 4C Use concrete models to solve 5A equations and use symbols to record the actions Select tools or techniques to solve problems and verify conclusions Communicates through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models Subtracting Integers 13D 14A 14B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 6 Algebra and Integers (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 5th 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Use models to add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers and connect the actions to algorithms 2C Absolute Value of a Number All Operations of Integers Simplify numerical expressions involving order of operations and exponents 2E Communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models 14A Make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and non-examples 15A Validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships 15B Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Patterns using a Table of Values 10.1-10.8 Coordinate Plane (4 Quadrants) Integers and Exponents Scientific Notation with negative powers. TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 6 Ratios and Proportions (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 6th 3 WEEKS – 1ST SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Use division to find unit rates and ratios in proportional relationships such as speed, density, price, recipes, and student-teacher ratio 2D Ratios and Rates Solving Proportions Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Word Problems Using Proportions Estimate and find solutions to application problems involving proportional relationships such as similarity, scaling, unit costs, and related measurement units Generate formulas involving conversions, perimeter, area, circumference, volume, and scaling Use critical attributes to define Writing Proportions Similar Polygons Scale Drawings 4A 6D similarity Use geometric concepts and properties to solve problems in fields such as art and architecture Select tools or techniques to solve problems and verify conclusions Communicates through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models 6.1-6.7 3B 8C 13D 14A 15B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 2, 6 Percents & Decimals/ Plane Geometry (part 1) (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 1st 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (1st page) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Assessments Resources TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Represent multiplication and division situations involving fractions and decimals with concrete models, pictures, words, and numbers Use addition, subtraction, multiplication Select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections Determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem Estimate and find solutions to application problems involving percent Graph data to demonstrate relationships in familiar concepts such as conversions, perimeter, area, circumference, volume, and scaling 2A Percents, Fractions, and Decimals Finding Percent of a Number Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Large and Small Percents Percent EQUATION 7.1-7.7 8.1-8.3 2B Circle Graphs Simple Interest 2F Percent Increase and Decrease 2G Intersecting Lines and Angle Measures Transversal, Translations, and Tessellations 3A Circumference Area of Parallelogram, Trapezoid, and Circle 4B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 Percents & Decimals/ Plane Geometry (part 1) (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 1st 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (2nd page) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Assessments Resources TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Use angle measurements to classify 6A pairs of angles as complementary or supplementary Use properties to classify shapes including triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, and circles 6B Use critical attributes to define similarity 6D Percents, Fractions, and Decimals Finding Percent of a Number Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Large and Small Percents Percent EQUATION 7.1-7.7 8.1-8.3 Circle Graphs Locate and name points on a coordinate plane using ordered pairs of integers Graph translations on a coordinate plane Simple Interest Percent Increase and Decrease 7A Intersecting Lines and Angle Measures 7B Transversal, Translations, and Tessellations Circumference Estimate measurements and solve application problems involving length (including perimeter and circumference), area, and volume 9A Area of Parallelogram, Trapezoid, and Circle TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 3, 4, 6 Plane Geometry (part 2) & Solid Geometry (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 2nd 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Generate formulas involving conversions, perimeter, area, circumference, volume, and scaling Graph data to demonstrate relationships in familiar concepts such as conversions, perimeter, area, circumference, volume, and scaling Describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence 4A Area of Quadrilaterals: Parallelogram and Trapezoid Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 4B The Pythagorean Theorem 8.4-8.8 9.1-9.7 Characteristics of Polyhedrons Spatial Visualization 4C Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Volume of Prisms and Cylinders Use properties to classify solids, including pyramids, cones, prisms, and cylinders 6C Sketch a solid when given the top, side, and front views 8A Make a net (two-dimensional model) of the surface area of a solid 8B Use geometric concepts and properties to solve problems in fields such as art and architecture Area of Triangles 8C TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 2,3, 4, 6 Plane Geometry (part 2) & Solid Geometry (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 2nd 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (2nd page continued) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Assessments Resources TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Estimate measurements and solve application problems involving length (including perimeter and circumference), area, and volume Select and use an appropriate representation for presenting collected data and justify the selection Identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types to solve a problem Make conjectures from patterns or 9A Area of Quadrilaterals: Parallelogram and Trapezoid The Pythagorean Theorem 11A Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 8.4-8.8 9.1-9.7 Characteristics of Polyhedrons Spatial Visualization 13A Surface Area of Prisms and Cylinders Volume of Prisms and Cylinders 13C 15A sets of examples and non-examples Validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships Area of Triangles 15B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 2,3, 4, 6 Data Analysis and Statistics (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 3rd 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections Determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem Describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence Construct sample spaces for compound events (dependent and independent) 2F Describe a set of data using mean, median, mode, and range Choose among mean, median, mode, or range to describe a set of data and justify the choice for a particular situation Frequency Table 5.1-5.6 2G Histogram 4C Box-n-Whisker Plot 10A Using appropriate graph Misleading graph Select and use an appropriate 11A representation for presenting collected data and justify the selection Make inferences and convincing arguments based on an analysis of given or collected data Central Tendency Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Mean, Median, Mode, and Range of data 11B 12A 12B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 5, 6 Data Analysis and Statistics (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 3rd 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (PART 2 continued) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics Use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness Select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types to solve a problem Communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships 13A 13B Central Tendency Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Frequency Table 5.1-5.6 Mean, Median, Mode, and Range of data Histogram Box-n-Whisker Plot Using appropriate graph Misleading graph 13C 14A 15B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 5, 6 Probability and Statistics (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 4th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections Determine the reasonableness of a solution to a problem Describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence Construct sample spaces for compound events (dependent and independent) 2F Permutations and Probability 2G Describe a set of data using mean, median, mode, and range Choose among mean, median, mode, or range to describe a set of data and justify the choice for a particular situation Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Combinations and Probability 11.1-11.7 Making Predictions 4C Expected Value Venn Diagrams and Probability 10A Select and use an appropriate 11A representation for presenting collected data and justify the selection Make inferences and convincing arguments based on an analysis of given or collected data Counting Techniques 11B 12A 12B Mean, Median, and Mode TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 5, 6 Probability and Statistics (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 4th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (PART 2 continued) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Identify and apply mathematics to everyday experiences, to activities in and outside of school, with other disciplines, and with other mathematical topics 13A Counting Techniques Permutations and Probability Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell Combinations and Probability 11.1-11.7 Use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness Select or develop an appropriate problem-solving strategy from a variety of different types to solve a problem Communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models Validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships Making Predictions 13B Expected Value Venn Diagrams and Probability Mean, Median, and Mode 13C 14A 15B TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 5, 6 Problem-Solving / TAKS Review (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 5th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Represent and use numbers in a variety of equivalent forms Adds, subtracts, multiplies, or divides to solve problems and justify solutions 1A-15B Number, Operation, Quantitative Reasoning Patterns, Relationships, and Algebraic Thinking Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Solve problems involving proportional relationships Represent a relationship in numerical, geometrical, verbal, and symbolic form Use equations to solve problems Compare and classify shapes and solids using geometric vocabulary and properties Use coordinate geometry to describe location on a plane Use geometry to model and describe physical world Solves application problems involving estimation and measurement Measurement Probability and Statistics Processes and Mathematical Tools Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Problem-Solving / TAKS Review (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 5th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (2nd page) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Recognize that a physical or mathematical model can be used to describe the probability of real-life events Understand that the way a set of data is displayed influences its interpretation Use measures of central tendency and range to describe a set of data Solve problems connected to everyday experiences, investigations in other disciplines, and activities in and outside of school Communicate about mathematics through informal and mathematical language, representations, and models Use logical reasoning to make conjectures and verify solutions 1A-15B Number, Operation, Quantitative Reasoning Patterns, Relationships, and Algebraic Thinking Geometry and Spatial Reasoning Measurement Probability and Statistics Processes and Mathematical Tools Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 Linear Functions and Equations (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 6th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Use models to add, subtract, multiply, and divide integers and connect the actions to algorithms Select and use appropriate operations to solve problems and justify the selections Describe the relationship between the terms in a sequence and their positions in the sequence 2C Equations and Variables Inverse Operations 2F Addition and Subtraction Equations Multiplication and Division Equations 4C Two-Step Equations Linear Functions Use concrete models to solve equations and use symbols to record 5A the actions Use a problem-solving model that incorporates understanding the problem, making a plan, carrying out the plan, and evaluating the solution for reasonableness 13B Communicate mathematical ideas using language, efficient tools, appropriate units, and graphical, numerical, physical, or algebraic mathematical models 14A Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 12.1-12.6 TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 6 Linear Functions and Equations (Approximate Time: 3 weeks) 6th 3 WEEKS – 2nd SEMESTER (PART 2 continued) Objectives/concepts TEKS Topics (not in sequential order) Suggested Resources Assessments TAKS Objectives The student is expected to: Make conjectures from patterns or sets of examples and non-examples Validate his/her conclusions using mathematical properties and relationships 15A Equations and Variables Inverse Operations 15B Addition and Subtraction Equations Multiplication and Division Equations Two-Step Equations Linear Functions Passport to Mathematics Book 2 McDougal Littell 12.1-12.6 TEKSING with TAKS DeBorde/ Thompson 1, 2, 6