* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Gene Section WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1)
BRCA mutation wikipedia , lookup
Cancer epigenetics wikipedia , lookup
Protein moonlighting wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene therapy of the human retina wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Oncogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
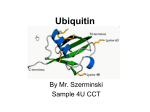
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology OPEN ACCESS JOURNAL AT INIST-CNRS Gene Section Mini Review WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) Ceshi Chen The Center for Cell Biology and Cancer Research Albany Medical College MS355/350, Mail code 165, 47 New Scotland Ave. Albany, NY 12208, USA Published in Atlas Database: January 2008 Online updated version: http://AtlasGeneticsOncology.org/Genes/WWP1ID42993ch8q21.html DOI: 10.4267/2042/38581 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Non-commercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2008 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology breast cancer cell line T47D (Flasza et al., 2002). The open reading frame for the full length WWP1 gene is 2766 bp. The transcription is increased by TGFb (Chen et al., 2007). Identity Hugo: WWP1 Other names: AIP5 (Atropin-1-interacting protein 5); Tiul1 (TGIF-interacting ubiquitin ligase 1) Location: 8q21.3 Protein Description DNA/RNA 922 amino acids; approximatively 110 kDa protein; The C2 domain at N-terminus is responsible for calcium-dependent phospholipid binding. The four WW domains in the middle are responsible for proteinprotein interaction with PY motifs. The HECT domain at the C-terminus is responsible for the ubiquitin transfer. The Cystein 890 is the catalytic center. The underlined WWP1 substrates do not have a PY motif (PPXY). A smaller WWP1 protein isoform was detected in two prostate cancer cell lines PC-3 and LAPC-4 (Chen et al., 2007a). Protein structure: The HECT domain of WWP1 (see Figure 2C.) (Verdecia et al., 2003). Description The WWP1 gene encompasses 26 exons which span approximatively 142 kb of DNA. BAC clone RPCI459L5 contains the complete human WWP1 genome sequence. Transcription WWP1 mRNA is strongly or modestly expressed in human heart, muscle, placenta, kidney, liver, pancreas and testis (Mosser et al., 1998; Komuro et al., 2004). The size of the WWP1 mRNA is about 4.2 kb (Chen et al., 2007). There are multiple splicing isoforms in the Figure 1. Boxes represent exons. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2008;12(5) 393 WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) Chen C Figure 2A: WWP1 protein. Figure 2B: Exogenous WWP1 expression in the 22Rv1 prostate cancer cell line was detected under a confocal microscopy. The endosomes are indicated by GFP-Rab5. Figure 2C: Protein structure of WWP1. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2008;12(5) 394 WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) Chen C Expression Mutations The WWP1 protein is lowly expressed in normal prostate and breast but is frequently upregulated in prostate and breast cancers due to the gene amplification. Somatic The WWP1 gene is rarely mutated in human prostate cancer (Chen et al., 2007a). Two sequence alterations were detected in prostate cancer xenografts. One was 2393A→T (Glu798Val) in CWR91 and the other was 721A→T (Thr241Ser) in LuCaP35. Additionally, some mutations in the HECT domain decrease the E3 ligase activity (Verdecia et al., 2003). Localisation Predominately on membrane structures in cytoplasm and occasionally in nucleus (see Figure 2B.). Function WWP1 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase. WWP1 negatively regulates the transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-b) signaling by targeting its molecular components, including TGF-beta receptor 1 (TbR1) (Komuro et al., 2004), Smad2 (Seo et al., 2004), and Smad4 (Moren et al., 2005) for ubiquitin mediated degradation. In addition, WWP1 has been reported to target the epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC) (Malbert-Colas et al., 2003), Notch (Shaye and Greenwald, 2005), Runx2 (Jones et al., 2006; Shen et al., 2006), KLF2 (Zhang et al., 2004), and KLF5 (Chen et al., 2005) for ubiquitinmediated proteolysis. Recently, WWP1 has been demonstrated to inhibit p53 activity through exporting p53 from the nucleus after ubiquitination (Laine and Ronai, 2007). Overall, WWP1 may play a pro-survival role in several tumor types including breast (Chen et al., 2007b) and prostate (Chen et al., 2007a). WWP1 has also shown to promote virus budding (Martin-Serrano et al., 2005; Heidecker et al., 2007). Implicated in Prostate cancer Disease The WWP1 gene is amplified in 31-44% prostate cancer cell lines/xenografts/tumors. Consistently, the WWP1 mRNA and protein is up-regulated in these samples compared to immortalized prostate epithelial cell lines. WWP1 knock-down increases the TGFbinduced CDK inhibitor p15 expression and decreases PC-3 prostate cancer cell growth in vitro. These results suggest that WWP1 may be an oncogene in prostate cancer. Breast cancer Disease The WWP1 gene is amplified in 41-51% breast cancer cell lines/tumors. Consistently, the WWP1 mRNA and protein is up-regulated in breast cancer cells compared to immortalized breast epithelial cell lines. WWP1 knock-down induces growth arrest and apoptosis in MCF7 and HCC1500 breast cancer cell lines. Forced expression of WWP1 promotes MCF10A and 184B5 immortalized breast epithelial cell proliferation in an E3 ligase independent manner. Homology WWP1 belongs to the C2-WW-HECT E3 family which contains 8 other members (Chen and Matesic, 2007). The WWP1 gene is highly-conserved among species (from human to c. elegant). Figure 3. WWP1 protein expression in normal breast epithelial cells and breast cancer cells by immunohistochemical staining. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2008;12(5) 395 WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1) Chen C Morén A, Imamura T, Miyazono K, Heldin CH, Moustakas A. Degradation of the tumor suppressor Smad4 by WW and HECT domain ubiquitin ligases. J Biol Chem 2005;280(23):22115-22123. References Mosser EA, Kasanov JD, Forsberg EC, Kay BK, Ney PA, Bresnick EH. Physical and functional interactions between the transactivation domain of the hematopoietic transcription factor NF-E2 and WW domains. Biochemistry 1998;37(39):1368613695. Shaye DD, Greenwald I. LIN-12/Notch trafficking and regulation of DSL ligand activity during vulval induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. Development 2005;132(22):50815092. Flasza M, Gorman P, Roylance R, Canfield AE, Baron M. Alternative splicing determines the domain structure of WWP1, a Nedd4 family protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;290(1):431-437. Jones DC, Wein MN, Oukka M, Hofstaetter JG, Glimcher MJ, Glimcher LH. Regulation of adult bone mass by the zinc finger adapter protein Schnurri-3. Science 2006;312(5777):12231227. Malbert-Colas L, Fay M, Cluzeaud F, Blot-Chabaud M, Farman N, Dhermy D, Lecomte MC. Differential expression and localisation of WWP1, a Nedd4-like protein, in epithelia. Pflugers Arch 2003;447(1):35-43. Shen R, Chen M, Wang YJ, Kaneki H, Xing L, O'keefe RJ, Chen D. Smad6 interacts with Runx2 and mediates Smad ubiquitin regulatory factor 1-induced Runx2 degradation. J Biol Chem 2006;281(6):3569-3576. Verdecia MA, Joazeiro CA, Wells NJ, Ferrer JL, Bowman ME, Hunter T, Noel JP. Conformational flexibility underlies ubiquitin ligation mediated by the WWP1 HECT domain E3 ligase. Mol Cell 2003;11(1):249-259. Chen C, Matesic LE. The Nedd4-like family of E3 ubiquitin ligases and cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 2007;26(3-4):587604. Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Dong XY, Sethi P, Zhou W, Zhou Z, Petros J, Frierson HF Jr, Vessella RL, Atfi A, Dong JT. Ubiquitin E3 ligase WWP1 as an oncogenic factor in human prostate cancer. Oncogene 2007;26(16):2386-2394. Komuro A, Imamura T, Saitoh M, Yoshida Y, Yamori T, Miyazono K, Miyazawa K. Negative regulation of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta) signaling by WW domaincontaining protein 1 (WWP1). Oncogene 2004;23(41):69146923. Chen C, Zhou Z, Ross JS, Zhou W, Dong JT. The amplified WWP1 gene is a potential molecular target in breast cancer. Int J Cancer 2007;121(1):80-87. Seo SR, Lallemand F, Ferrand N, Pessah M, L'Hoste S, Camonis J, Atfi A. The novel E3 ubiquitin ligase Tiul1 associates with TGIF to target Smad2 for degradation. EMBO J 2004;23(19):3780-3792. Heidecker G, Lloyd PA, Soheilian F, Nagashima K, Derse D. The Role of WWP1-Gag Interaction and Gag Ubiquitination in Assembly and Release of Human T-Cell Leukemia Virus Type 1. J Virol 2007;81(18):9769-9777. Zhang X, Srinivasan SV, Lingrel JB. WWP1-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of the lung Kruppel-like factor, KLF2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;316(1):139-148. Laine A, Ronai Z. Regulation of p53 localization and transcription by the HECT domain E3 ligase WWP1. Oncogene 2007;26(10):1477-1483. Chen C, Sun X, Guo P, Dong XY, Sethi P, Cheng X, Zhou J, Ling J, Simons JW, Lingrel JB, Dong JT. Human Kruppel-like factor 5 is a target of the E3 ubiquitin ligase WWP1 for proteolysis in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2005;280(50):4155341561. This article should be referenced as such: Chen C. WWP1 (WW domain containing E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1). Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol.2008;12(5):393-396. Martin-Serrano J, Eastman SW, Chung W, Bieniasz PD. HECT ubiquitin ligases link viral and cellular PPXY motifs to the vacuolar protein-sorting pathway. J Cell Biol 2005;168(1):89101. Atlas Genet Cytogenet Oncol Haematol. 2008;12(5) 396