* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Drawings of di ti f
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
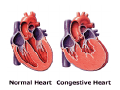
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
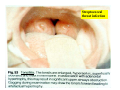
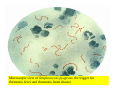
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
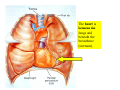
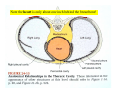
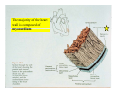
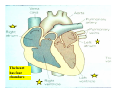
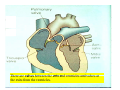
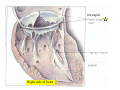
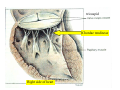
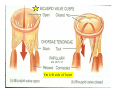
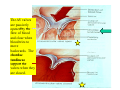
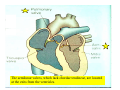
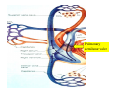
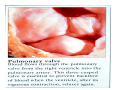
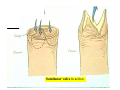
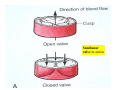
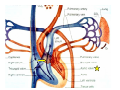
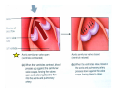
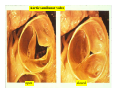
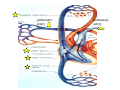
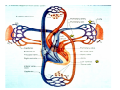
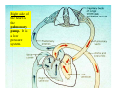
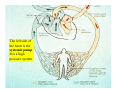
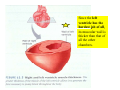
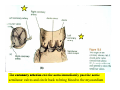
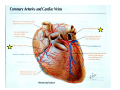
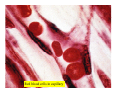
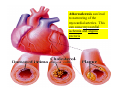
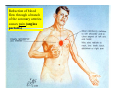
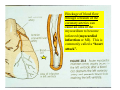
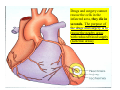
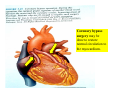
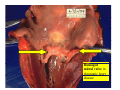
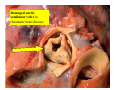
Drawings of di dissections ti off the human heart by Leonardo DaVinci done in 1510. The anatomy lesson by Dr. Nicholas Tulp, by Rembrandt in 1632 Dr. Gunter Von Hagens with ppastinated human cadaver at Body Worlds exhibit in 2009 The heart is between the lungs and beneath the b breastbone b (sternum). Note the heart is only about one inch behind the breastbone! The majority of the heart wall is composed of myocardium di The heart has four chambers There are valves Th l b t between the th atria t i andd ventricles t i l andd valves l att the exits from the ventricles. tricuspid p Right side of heart tricuspid Chordae tendineae Right side of heart On left side of heart The left AV valve is also called the “bicuspid valve”. Another name for this same valve is the “mitral valve” b because it looks l k like a Bishop’s miter. The AV valves are passively openedd by b the th flow of blood and close when blood tries to move backwards. The chordae tendineae support the valves when they are closed. The chordae t di tendineae support the AV valves when theyy are closed. Internal view of a ventricle showing the papillary muscles and th chordae the h d tendineae. t di The semilunar valves, which lack chordae tendineae, are located at the exits from the ventricles. Pulmonary semilunar valve Semilunar valve in action Semilunar valve in action Aortic semilunar valve open closed pulmonary artery pulmonary artery Right side of the heart is the p pulmonary y pump. It is a low pressure system. The left Th l f side id off the heart is the systemic y p pump. p It is a high pressure system Since the left ventricle has the hardest jjob of all,, its muscular wall is thicker than that of all the other chambers. The coronary arteries exit the aorta immediately past the aortic semilunar valves and circle back to bring blood to the myocardium Red blood cells in capillary The venous drainage from the myocardium collects in the coronary veins, which in turn flow to the coronary sinus which drains into the posterior of the right atrium. Atherosclerosis can lead to narrowing of the myocardial arteries. This can cause myocardial y ischemia and angina pectoris Reduction of blood flow through g a branch of the coronary arteries causes pain (angina pectoris) Blockage of blood flow through a branch of the coronary arteries can cause an area of the myocardium to become infarcted (myocardial infarction or MI). MI) This is commonly called a “heart attack”. Severe pain and discomfort is associated with myocardial infarctions (MIs, heart attacks) Drugs and surgery cannot rescue the cells in the infarcted area, they die in seconds. The purpose of the drugs and surgery is to rescue the nearby areas with reduced blood supply (i h i areas)) (ischemic Coronary bypass surgery may be done to restore normal circulation to the myocardium. Cross-section of the heart showing h i scarring i from f pastt heart attacks (white areas) Streptococcal throat infection Microscopic view of Streptococcus pyogenes, the trigger for rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease Damaged mitral valve in rheumatic heart disease Damaged aortic semilunar il valve l in i rheumatic heart disease