* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download FUNCTIONAL NAME OF STRUCTURE EXAMPLE
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
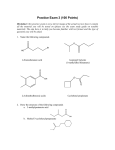
FUNCTIONAL GROUP Hydroxyl Carbonyl Carboxyl Amino Sulfhydryl Phosphate NAME OF COMPOUNDS STRUCTURE EXAMPLE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES FUNCTIONAL GROUP NAME OF COMPOUNDS Hydroxyl Alcohols (their specific names ends in –ol ) Carbonyl Ketones Aldehyde STRUCTURE EXAMPLE FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward it attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars A ketone and an aldehyde may be structural isomers with different properties, as in the case for acetone and propanal. Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions. The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ion (H+) tend to dissociate reversibly; for example, Carboxyl Carboxylic acids, or organic acids Amino Amine Sulfhydryl Thiols Phosphate Organic Phosphates Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called amino acids. Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution: Ionized, with a charge of conditions. +1, under cellular Two sulfhydryl groups can interact to stabilize protein structure (fig. 5.20) Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion (negatively charged ion). Can transfer energy between organic molecules FUNCTIONAL GROUP Hydroxyl NAME OF COMPOUNDS STRUCTURE EXAMPLE Draw and name an example Alcohols (their specific names ends in –ol ) FUNCTIONAL PROPERTIES Use the letters on the next page to designate the correct functional properties for each of the arrows in this column. Draw both types of structures Ketones Aldehyde Carbonyl ___________ acids, or organic acids Because it also has a carboxyl group, glycine is both an amine and a carboxylic acid; compounds with both groups are called _____ acids. Sulfhydryl Thiols Phosphate Organic Phosphates Draw both types of structures Draw glycine Draw and name an example AP BIOLOGY Functional Groups Quiz Match these functional properties (by letter) to the functional groups on the chart. This is only a sample. The choices will be reordered on your quiz. ) B) A _______ and an ________ may be structural isomers with different properties, as in the case for _______ and ________. (Add the missing words in correct order on the chart. ex. B) ______, _______, ______, _______) C) This group is polar as a result of the electronegative oxygen atom drawing electrons toward it. D) The covalent bond between oxygen and hydrogen is so polar that hydrogen ion (H+) tends to dissociate reversibly; for example E) Makes the molecule of which it is a part an anion (negatively charged ion). F) G) Acts as a base; can pick up a proton from the surrounding solution: H) Has acidic properties because it is a source of hydrogen ions. I) attracts water molecules, helping dissolve organic compounds such as sugars J) Can transfer energy between organic molecules K) Ionized, with a charge of +1, under cellular conditions. L) Two groups can interact to stabilize protein structure.