* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download "The Response of Dissolved Oxygen to Climate and Other Anthropogenic Change"
Fred Singer wikipedia , lookup
Climate sensitivity wikipedia , lookup
Climate change in Tuvalu wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Hotspot Ecosystem Research and Man's Impact On European Seas wikipedia , lookup
General circulation model wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on human health wikipedia , lookup
Politics of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change and poverty wikipedia , lookup
Global warming hiatus wikipedia , lookup
Climatic Research Unit documents wikipedia , lookup
Public opinion on global warming wikipedia , lookup
Attribution of recent climate change wikipedia , lookup
Media coverage of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Climate change feedback wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming wikipedia , lookup
Years of Living Dangerously wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on humans wikipedia , lookup
Physical impacts of climate change wikipedia , lookup
Instrumental temperature record wikipedia , lookup
Climate change, industry and society wikipedia , lookup
Scientific opinion on climate change wikipedia , lookup
Effects of global warming on Australia wikipedia , lookup
Surveys of scientists' views on climate change wikipedia , lookup
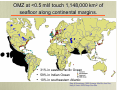
The response of dissolved oxygen to climate and other anthropogenic change. Diaz, Reay, Moore Climate Change, Oxygen, and Coastal Oceans • For temperature: Oxygen solubility, organism metabolism, and remineralisation rates • • Availability of DO resulting from altered productivity. Flood regimes • Altered precipitation and evaprotranspiration • Runoff and erosion delivering nutrients • Rising sea level • • • • Duration and intensity of summer stratification. Duration of winter ice cover. Storm frequency and intensity Shifting wind and current patterns Climate Change and Coastal Oxygen • Predictors for future oxygen budgets are not good: • Lower dissolved oxygen content of world oceans (Keeling and Garcia 2002 Proc Nat Acad Sci Sci)) • Expansion of Oxygen Minimum Zones and -Sea Res upwelling (Helly and Levin 2004 Deep Deep-Sea Res)) • Expansion of anthropogenic hypoxia (Diaz & Rosenberg Science, Rabalais et al. 2007 Estuaries & Coasts) Lower dissolved oxygen content of world oceans • Increasing temperature (Levitus et al. 2002 Science ) • Altered currents and advection (Stramma et al. 2008 Science ) • Increased biological oxygen demand (Stramma et al. 2008 Science ) At Global Scale, Ocean Temperatures are Warming: Levitus et al. Science 2002 287:2225 Expansion of Oxygen Minimum Zones • Altered precipitation and wind patterns (IPCC 2007) • Increased temperature and altered currents (Stramma et al. 2008 Science ) • Naqvi 2000 Anthropogenic nutrients ((Naqvi Nature ) OMZ at <0.5 ml/l touch 1,148,000 km2 of seafloor along continental margins. • • • 31% in eastern Pacific Ocean 59% in Indian Ocean 10% in southeastern Atlantic Diaz & Rosenberg 1995 Oceangr Mar Bio Ann Rev; Helly & Levin 2004 Deep-Sea Res Expansion OMZ and Upwelling (Grantham et al. 2004 Nature, Chan et al. 2008 Science ) www.primidi.com Oregon Coast, USA Upwelling increase linked to shifts in regional climate forcing: • Strong interannual changes in upwelling wind stress • Nutrient supply to California Coastal Current Severe inner-shelf hypoxia and anoxia since 2000, >32,000 km2 in 2006 Expansion of OMZs areas ((Naqvi Naqvi et al. 2000 Nature ) • In 2000s, first report of intensification of hypoxia in an natural upwelling zone that may be related to eutrophication. • Over the western Indian continental shelf during late summer and autumn. • 180,000 km2 Expansion of anthropogenic hypoxia • Altered precipitation and wind patterns (IPCC 2007) • Land use and Human population Tilman et al. 2001 Science ) increase ((Tilman • Anthropogenic nutrients from land and air ((Rabalais Rabalais et al. 2007 Estuaries & Coasts, Duce et al. 2008 Science) Nutrients & Hypoxia a Global Problem: •Doubling of sites first reporting hypoxia started in 1960s. •>400 systems with reports of hypoxia/anoxia •>100 eutrophic sites in danger of developing hypoxia/anoxia. •OMZ and Upwelling areas not included. Boesch 2002 Estuaries Spread of Hypoxia In the 1960s the number of systems with reports of hypoxia-related problems increased. Sanderson et al. 2002 Bioscience; Global Human Footprint Spread of Hypoxia 1970s more increase in the number of hypoxic systems. Spread of Hypoxia 1980s explosive increase in the number of hypoxic systems. Spread of Hypoxia By the 1990s most estuarine and marine systems in close proximity to population centers had reports of hypoxia or anoxia. Spread of Hypoxia 2000s numbers continue to expand. Two Part Key to Future Hypoxia




















![[1] Hypoxic hypoxia](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/019417251_1-6b5838be37430c23578b2b34b0734d1f-150x150.png)