* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHEM121 Lecture Ch5 student
Properties of water wikipedia , lookup
Chemical bond wikipedia , lookup
Chemical equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Nanofluidic circuitry wikipedia , lookup
Hydrogen-bond catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Process chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Bioorthogonal chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Lewis acid catalysis wikipedia , lookup
Computational chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Artificial photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Click chemistry wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Transition state theory wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Water splitting wikipedia , lookup
Electrochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Chemical reaction wikipedia , lookup
Freshwater environmental quality parameters wikipedia , lookup
Physical organic chemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of molecular theory wikipedia , lookup
Chemical thermodynamics wikipedia , lookup
Gas chromatography–mass spectrometry wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Electrolysis of water wikipedia , lookup
Hypervalent molecule wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Atomic theory wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
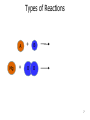
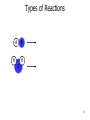
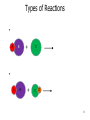
CHEM 121 Chapter 5 1 The Mole • • • • 12 eggs = 12 bagels = 6.02 x 1023 hydrogen atoms = 6.02 x 1023 water molecules = How many water molecules are in 3.5 moles of water? 2 Moles of Elements in a Formula How many moles of each element are in 1 mole of water? How many moles of each element are in 1 mole of glucose? 3 Molar Mass • • Examples: Carbon Water Atomic mass? Molecular mass? Molar mass? Molar mass? 4 Calculations with Molar Mass You measure out 10.0 g of water. How many moles of water do you have? If a piece of metal displaces 2.2 mL water, how many water molecules has it displaced? (Assume the density of water is 1.0 g/mL.) 5 Chemical Equations Physical Change: Chemical Change: Chemical Equation: 6 Types of Reactions Mg A + B + O O 7 Types of Reactions A H B O H 8 Types of Reactions • A + B C • A B + C D 9 Chemical Equations _____________ and ___________ involved in change 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Ex. Reaction of magnesium solid and oxygen 10 Reaction Equivalents C3H8 (g) + 5 O2 (g) 3 CO2 (g) + 4 H2O (g) 1 1 1 5 2 molecule C3H8 reacts with _______ molecules O2 molecule C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecule C3H8 produces _______ molcules H2O molecules O2 produces _______ molecules CO2 molecules C3H8 produces _______ molecules CO2 11 Ionic Equations • Molecular equations – • Total ionic equations – • Net ionic equations – Example: HCl and NaOH Precipitation Reactions • Type of replacement reaction • Example: Aqueous sodium iodide and lead (II) nitrate 13 Stoichiometry the study of mass relationships in chemical equations Can’t compare mass to mass Go to moles first 14 Reaction Calculations 1. 2. 3. 4. 15 Sample Problem How much carbon dioxide (in grams) is produced when 3.00 g of ethanol (C2H6O) combusts in air? How much oxygen gas is used up to combust 5.00 g of ethanol? 16 5-minute review How many grams of oxygen are needed to react with 1 mole of CH4 to create water? Hint: carbon dioxide is also a product. 17 Yields • Theoretical yield: • Actual yield: – • Percent yield: 18 Limiting Reactants What if we have: 8 scoops of ice cream 6 cherries 100 mL of syrup. How many sundaes can we make? 19 Chemical Reactions Involving a Limiting Reactant hydrazine (N2H4) and dinitrogen tetraoxide are liquids that ignite to form nitrogen gas and water vapor How many grams of nitrogen gas form when 100. g of N2H4 and 200. g of dinitrogen tetraoxide are mixed? 20 Redox Reactions • Reduction and oxidation • Movement of e- from one reactant to another • 2 Mg (s) + O2 (g) --> 2 MgO (s) • LEO GER • Reducing agent? Oxidizing agent? 21 Oxidation Numbers (O.N.) • • • • • • Any element has O.N. = 1A(1) ions = 2A(2) ions = H ion can only = Oxygen ion only = Halogen ions usually = The sum of all atoms O.N. in a compound = Examples: ZnCl2 sulfur trioxide potassium sulfate 22 3-minute review What is the O.N. of each atom in CaCO3? 23 Redox Reaction? CaO (s) + CO2 (g) → CaCO3 (s) 24 3-minute Review What’s been oxidized in each reaction? Cu (s) + AgNO3 (aq) → N2 (g) + H2 (g) → Ag (s) + Cu(NO3)2 (aq) NH3 (g) 25