* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 02-DEVELOPMENT OF THE CNS
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
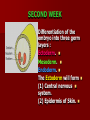
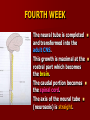
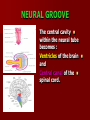
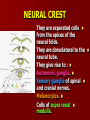
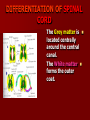
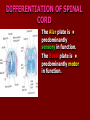
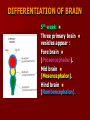
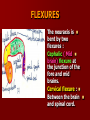
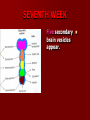
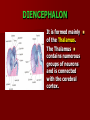
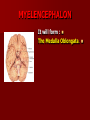
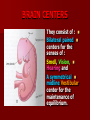
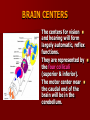
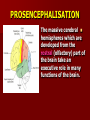
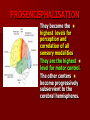
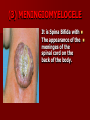
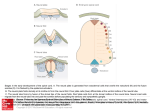
SECOND WEEK Differentiation of the embryo into three germ layers : Ectoderm. Mesoderm. Endoderm. The Ectoderm will form (1) Central nervous system. (2) Epidermis of Skin. THIRD WEEK Neural Plate : It is a dorsal midline thickening of the ectoderm overlying the notochord (Neuroectoderm) . THIRD WEEK Neural Folds : They are the elevated lateral margins of the neural plate. They are on each side of the longtudinal midline (Neural Groove). NEURAL TUBE It is formed from the apposition and fusion of the neural folds which seal the neural groove and create the tube. FOURTH WEEK The neural tube is completed and transformed into the adult CNS. This growth is maximal at the rostral part which becomes the brain. The caudal portion becomes the spinal cord. The axis of the neural tube (neuroaxis) is straight. NEURAL GROOVE The central cavity within the neural tube becomes : Ventricles of the brain and Central canal of the spinal cord. NEURAL CREST They are separated cells from the apices of the neural folds. They are dorsolateral to the neural tube. They give rise to : Autonomic ganglia. Sensory ganglia of spinal and cranial nerves. Melanocytes. Cells of supra renal medulla. DIFFERENTIATION OF SPINAL CORD The Grey matter is located centrally around the central canal. The White matter forms the outer coat. DIFFERENTIATION OF SPINAL CORD Sulcus Limitans : It is a longtudinal groove along the inner surface of the lateral walls of the developing spinal cord. It differentiates the grouping of cells (gray matter) into dorsal (Alar) plate and a ventral (Basal) plate. DIFFERENTIATION OF SPINAL CORD The Alar plate is predominantly sensory in function. The Basal plate is predominantly motor in function. DIFFERENTIATION OF BRAIN 5th week: Three primary brain vesicles appear : Fore brain (Prosencephalon). Mid brain (Mesencephalon). Hind brain (Rombencephalon). FLEXURES The neuraxis is bent by two flexures : Cephalic ( Mid brain) flexure at the junction of the fore and mid brains. Cervical flexure : Between the brain and spinal cord. SEVENTH WEEK Five secondary brain vesicles appear. PROSENCEPHALON Is divided into : Telencephalon. Diencephalon. TELENCEPHALON It is the largest brain vesicle. It has the greatest degree of development. It forms the two Cerebral Hemispheres. DIENCEPHALON It is formed mainly of the Thalamus. The Thalamus contains numerous groups of neurons and is connected with the cerebral cortex. ROMBENCEPHALON Is divided into : Metencephalon. Mylencephalon. PONTINE FLEXURE It is the third flexure that appears between the metencephalon and the myelencephalon. METENCEPHALON It is differentiated into: Pons . Cerebellum. MYELENCEPHALON It will form : The Medulla Oblongata. MESENCEPHALON It remains undifferentiated. It is in the form of its embryonic picture : Central canal surrounded by grey matter. BRAIN CENTERS They consist of : Bilateral paired centers for the senses of : Smell, Vision, Hearing and A symmetrical midline Vestibular center for the maintenance of equilibrium. BRAIN CENTERS They start to appear as expansions from the dorsal aspect of the simple tubular brain. They are composed of an outer cortex of nerve cells with underlying core of nerve fibers. BRAIN CENTERS The centers for vision and hearing will form largely automatic, reflex functions. They are represented by the four colliculi (superior & inferior). The motor center near the caudal end of the brain will be in the cerebellum. PROSENCEPHALISATION The massive cerebral hemispheres which are developed from the rostral (olfactory) part of the brain take an executive role in many functions of the brain. PROSENCEPHALISATION They become the highest levels for perception and correlation of all sensory modalities They are the highest level for motor control. The other centers become progressively subservient to the cerebral hemispheres. CONGENITAL ANOMALIES (1) Anencephaly The brain and skull are minute. It is incompatible for life. (2) SPINA BIFIDA It is underdevelopment of the lower part of the spinal cord and the nerve roots. It may be associated with underdevelopment of the bone and skin. SPINA BIFIDA The infants with Spina Bifida complain from : Paralysed, anesthetic lower limbs. Incontinence of urine and stool. (3) MENINGIOMYELOCELE It is Spina Bifida with The appearance of the meninges of the spinal cord on the back of the body.