* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Digestive System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
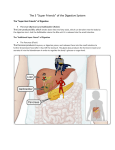
Chapter 14: The Digestive System Digestive system consists of • Muscular tube (digestive tract) – alimentary canal • Accessory organs – teeth, tongue, glandular organs 6 essential activities • • • • • • 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Ingestion Propulsion Mechanical digestion Chemical digestion Absorption Defecation Histology of the Digestive Tract • mucosa – primarily surface epithelium – lining of tract – after esophagus, simple columnar • submucosa – connective tissue • muscularis externa – smooth muscle • serosa – innermost layer (closest to viscera) Alimentary Canal Wall Structure Peristalsis Process begins in the mouth • What type of epithelial tissue is found here? • Is there any digestion in the mouth? Digestion begins in the mouth Salivary Glands • parotid glands • submandibular glands • sublingual glands • saliva – binds food into bolus – contains salivary amylase • digests starches Salivary Glands Teeth begin to process food After chewing food in the mouth • Food enters the esophagus – What is the function of the esophagus? • What type of epithelial tissue is found here? Esophagus is hollow tube From the esophagus food enters the stomach • What are the functions of the stomach? • What type of epithelial tissue is found here? • What else is unique to the histology of the stomach? Stomach Stomach • simple columnar epithelium – produces mucous • gastric glands contain cells that secrete gastric juices: – pepsinogens – digest proteins – HCl – activates enzymes – mucous – protects stomach wall – gastrin – digestive hormone Gastric Pits Does digestion occur in the stomach? Absorption? • Carbohydrates • Proteins Small Intestine • major function: responsible for 90% of absorption • divided into three regions – duodenum – jejunum – ileum Histology of the Small Intestine • Lining forms large folds called plica • epithelial tissue – projections called intestinal villi – all the cells have microvilli • villus – contains a lacteal – contains nerve and blood vessels Small Intestine Structure Small Intestine • purpose of villi, microvilli and circular folds? Pancreas • primarily an exocrine gland • triggered release by secretin • alkaline mixture of enzymes, water, and ions • travels in pancreatic duct, joins the common bile duct Pancreas Pancreatic Enzymes • pancreatic amylase – starch digestion • trypsin, chymotrypsin, carboxypeptidase – protein digestion • lipases – fat digestion • nucleases – nucleic acid digestion Liver • each lobe divided into lobules • cells called hepatocytes – produces and secrete bile Liver Liver Functions • Metabolic regulation • Hematological regulation • Bile production Metabolic Functions • all blood from digestive system flows through liver • liver regulates blood contents of – glucose – lipids – amino acids Liver’s role in glucose regulation • if levels drop, glycogen reserves in liver provide more glucose for blood – glycogenolysis - break down glycogen – also gluconeogenesis - form glucose from fats & proteins • if levels rise, glucose is stored as glycogen – glycogenesis - form glycogen from glucose Liver’s role in lipid metabolism • regulates circulating levels of triglycerides, fatty acids, and cholesterol • if levels decline, lipid stores are released • HDL: – transport cholesterol from body cells to liver • LDL: – transport cholesterol to body cells Liver’s role in amino acid metabolism? • removes excess amino acids from the bloodstream • what happens to these amino acids? Other metabolic functions of the liver • • • • Removal of waste products Vitamin storage Mineral storage Drug inactivation Bile • produced by liver • release triggered by secretin • bile salts emuslify lipids Gall bladder • Major functions: – bile storage – bile modification What regulates release of bile? • CCK (cholecsystokinin) released from the duodenum • triggered by the entry of foods high in fats into the duodenum The last part..large intestine • General functions – Reabsorption of water – Absorption of vitamins made by bacteria – Storage of fecal material Anatomy of large intestine Digestion and Absorption Chemical Digestion • What is chemical digestion? • Why is chemical digestion important? • What types of organic compounds are digested? • Where does chemical digestion occur? What is needed for these reactions? • Enzymes • What are some examples? • Where are they found? Where does most absorption occur? • • • • SI active transport capillary beds to liver via hepatic portal vein • lipids & fats absorbed by diffusion Absorption in Large Intestine • bacteria produce vitamin K & some Bs