* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electrostatics Physics I Review
Condensed matter physics wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Neutron magnetic moment wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic field wikipedia , lookup
Field (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnet wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic monopole wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
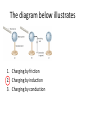
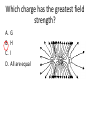
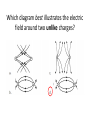
Electrostatics & Magnetism Review Physics I Electric Field lines exit __ charges and enter ___ charges. 1. 2. 3. 4. Neutral , negative Negative, Positive Positive, Negative Positive , Neutral What causes an object to become electrically charged? 1. Gain or Loss of protons 2. Gain or Loss of electrons 3. Gain or loss of neutrons One of these isolated charged spheres is copper and the other is rubber. The diagram below depicts the distribution of excess negative charge over the surface of two spheres. Which material is copper? 1. A 2. B 3. Neither If the distance between two charges is doubled, then the force of attraction or repulsion would 1. 2. 3. 4. Double. Quadruple Reduce to half. Reduce to ¼. As shown in the diagram below, a charged rod is held near, but does not touch a neutral electroscope. The charge on the knob becomes If your comb becomes negatively charged when combing your hair then which of the following occurred? 1. Hair lost electrons 2. Hair gained electrons 3. Hair lost protons 4. Hair gained protons One object has a charge of +3 C and the other is -7 C. What is the final charge on the objects after they touch? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. -4 +4 +2 -2 -10 +10 The diagram below illustrates 1. Charging by friction 2. Charging by induction 3. Charging by conduction Where is the electric force strongest on the test charge? A C++ + + Q + + ++ B 1. A 2. B 3. C What is the resulting direction at point J of the electric fields created by both charges? A. B. C. D. Right Left Zero Cannot be determined. 2. If you put a small compass in a magnetic field, the compass will a. line up in a direction parallel to the magnetic field lines. b. swing randomly. c. line up in a direction perpendicular to the magnetic field lines. d. seek electrical charge concentrations. What is the direction of the force on the negative charge in the figure? __ 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Up Down Left Right Into Page Out of page What is the direction of the force on the positive charge? A. B. C. D. E. F. Up Down Left Right Into Page Out of page Two identical charges of +3µC are 2 m apart. What force do they exert on one another? 0.02 N A charge of -5x10-5 C is 50 cm from a 3x10-5 C charge. What magnitude of force do they exert on one another? 54 N Moving electric charges are surrounded by a. only electric fields. b. only magnetic fields. c. both magnetic and electric fields. d. nothing. The magnetic field lines about a current-carrying wire form a. b. c. d. circles. radial lines. eddy currents. spirals. Which charge has the greatest field strength? A. B. C. D. G H I All are equal A positive charge enters the magnetic field below. The force on the charge is down. What is the direction of the velocity? 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Up Left Right Out of page Into Page Force A current carrying wire is placed in the magnetic field below. What is the direction of the force on the wire? N S N I 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Up Down Left Right Into page Out of page S The Earth’s Magnetic North is located at a. The South geographic pole b. The North Geographic pole. c. The equator. Which diagram best illustrates the electric field around two unlike charges?