* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Electric Fields 21.1
History of quantum field theory wikipedia , lookup
Introduction to gauge theory wikipedia , lookup
Time in physics wikipedia , lookup
Fundamental interaction wikipedia , lookup
Speed of gravity wikipedia , lookup
Weightlessness wikipedia , lookup
Circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Aharonov–Bohm effect wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Maxwell's equations wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electric charge wikipedia , lookup
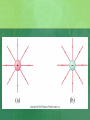
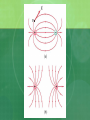
Electric Fields Chapter 21 21.1 Creating & Measuring Electric Fields The electric force varies inversely as the square of the distance between two point objects. How can a force be exerted through empty space? Michael Faraday suggested because of an electrically charged object changing the properties of space Electric Field The changed property of space is the electric field The electric field means that the interaction is not between two objects, but between an object and the field at the location of the object. Electric Field How is the electric field measured? Place a small positively charged object in the space, if there is a force on the object, there is an electric field. According to Coulomb’s law the force and the charge are directly proportional. So divide F by q (test charge) and get a vector quantity representing the electric field at a certain point. Electric Field Strength The direction of an electric field is the direction of the force on a positive test charge. The magnitude of the electric field is measured in N/C. E Fonq' q' Picturing the Electric Field Electric field is a vector quantity so use an arrow to represent the direction of a positive test charge and the number of arrows and spacing between lines represent the strength These are electric field lines