* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Sample – Firewall PowerPoint
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Proxy server wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Airborne Networking wikipedia , lookup
Wake-on-LAN wikipedia , lookup
Windows Vista networking technologies wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
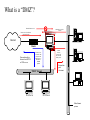
Firewall Fundamentals The 3 Components of Information Protection - “CIA” Confidentiality Integrity Availability These qualities of information must be preserved. They are the “3 legged stool” of good information protection. Physical Security Systems and networks cannot be considered secure without controls to physical access. This can be a significant issue if non-employees are allowed on-site unaccompanied. You may need “multiple layers” of protection • A firewall may protect your network and data from others on the Internet – What about modems on desktops that may connect to the Internet, bypassing the firewall? • A firewall may allow viruses to pass with “permitted” files. • “Mobile Code” -- JAVA & Active/X • How do you enforce your standards? • Planning for response if you are attacked You can’t build a house without the blueprints... The first step in protecting your information is determining your direction. • Develop basic security policies • Put “controls” in place to implement policies. – Controls may be procedures / processes – Controls may be physical One control may be a “firewall” • What is a firewall? – “A firewall is a system or group of systems that enforces an access control policy between 2 networks.” © Marcus J. Ranum - 1995 • Firewalls can be used to isolate your network from the Internet. • Firewalls can also be implemented in your network at places other than the Internet. Firewalls • Firewalls can restrict traffic between the Internet and a private network, between 2 departments, between business partners, etc. External Network Internal Network (Internet, Corp. Dept., Business Partner, etc.) Firewall What does a Firewall do? • Firewalls examine each data packet “passing through” the firewall • Firewalls can control access based on a number of parameters, depending on the type of firewall -– – – – – Source address Destination address Protocol Port Number Application What does a Firewall do? • Depending on the type of firewall, they can – block packets – allow packets – restrict packets • “DMZ” – You may want your Web Server in a “DMZ” • Allows Internet users to access your Web Server • Keeps Internet users off your Internal LAN What is a “DMZ”? Inbound Internet Access Outbound Access from Intranet Return Access from Intranet Originated Packets Internet Router Internet Access to "Public" Web Server & other DMZ systems -No access to Intranet systems Return data path to Internet from WWW or DNS servers Return data path to Intranet "DMZ" Sub-net Web Server Intranet Access to "Public" Web Server & other DMZ systems Intranet Firewall DNS Server Other Intranet systems The OSI Model & 3 Basic Firewall Types Application Application Layer Proxy a . k .a Layer Presentation 7 Firewalls examples include Sidewinder G 2, Norton Enterprise Firewall , CyberGuard Session Transport Stateful Inspection examples include Check Point Network Data Link Physical Packet “Firewall” examples include any Cisco , Netscreen , Pix , etc . a .k . a Routers with ACLs , Nortel , etc router Packet Filter • Advantages • Generally faster than other firewalls because they perform fewer evaluations • Can provide NAT -- Network Address Translation • Least Expensive • Disadvantages • Limited capabilities -- typically only Source & Destination •Cannot address protocol subsets other than IP -- most TCP only, not UDP. This can impact DNS. •Cannot perform checks on higher-level protocols • No “value add” features such a s URL filtering, HTTP caching, authentication, anti-spoofing, etc. Applications Applications Applications Presentation Presentation Presentation Sessions Sessions Sessions Transport Transport Transport Network Network Network DataLink DataLink DataLink Physical Physical Physical Circuit Proxy Firewall • Forces the client and the server to address their packets to the proxy. Intercepts and re-addresses all packets • Advantages – More control than a Packet Filter – Client has no way to learn the server IP address – SOCKS 5 allows optional user authentication & encryption • Disadvantages – Requires client modifications – Still a relatively high level of granularity-- Does not address packet contents – No anti-spoofing Applications Applications Presentation Presentation Sessions Sessions Transport Transport Network PROXY Network DataLink DataLink Physical Physical “Stateful Inspection” • Advantages • Operates at 2nd/3rd layer in the OSI stack -- faster than Application Proxy • Application independent • More granularity then Circuit Proxy or Packet Filter • Disadvantages • Less granularity than Application Proxy Applications Applications Presentation Applications Presentation Sessions Presentation Sessions Transport Sessions Transport Network Transport Network Network DataLink DataLink DataLink Physical Physical Physical INSPECT Engine State Tables Security Market Growth Worldwide Firewall Market ($MM / Year) 1999 -- Gartner Group says “the current firewall marketplace will generally disappear into router functions.” 1400 1200 1000 Compound Annual Growth Rate = 24% ? ? 800 600 400 200 0 1998 Source: Datamonitor 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 If you think technology can solve your security problems, then you don’t understand the problem and you don’t understand the technology. Firewall Market “Shakeout” • Less than 10 years ago, there was no commercial firewall market. • Today, there are dozens of firewall vendors. • The market is experiencing a shakeout and consolidation. • Will the vendor you select today be in business next year? Additional Firewall “Features” • Network Address Translation – Allows use of “Private” Addresses on the internal network. Large internal networks can operate with only a few “Public” Addresses – The firewall can “translate” internal “Private” Addresses to “Public” Addresses before sending them out to the Internet, “hiding” the internal addresses – No need to re-number internal networks, if set up per IETF RFC-1918 – One-to-One or Many-to-One translation. • Does the firewall support Remote Management? • Encryption – IPSEC Standard -- Check with vendors regarding inter-operability • Virus Checking can significantly impact performance. – Will the virus checker deal with compressed files? • Can you do URL Screening at the Internet firewall? • Can you control “portable code” -- Java/Active-X -- at the firewall? VPN Gateways • “VPN Gateways” are essentially specialized firewalls – Access control and encryption on the same box – Requires client software or a 2nd gateway on the “far” end – Provides an encrypted session from the client to the gateway • prevents “eavesdropping” • allows the use of public networks like the Internet for private business communications, at significantly less cost than leased-lines. “Personal Firewalls” • Where is the “edge” of your network? • Business data my reside on employee’s home PCs, laptops, etc. • “Fat Pipe” connections may expose this information – DSL – Cable Modems • Tools are available to protect this data at the system communication interface • Require any “home” VPN connection to also have a personal firewall • Protects “home” PCs while connected to the Internet Firewall Performance Issues • Hardware vs. Software firewalls – Proprietary “Black Boxes” – Unix vs. NT / RISC vs. “X86” • CPU Speed; Memory; Disk Capacity • The Number of Interfaces on the firewall may impact performance – n*(n-1) possible routes (n = number of interfaces) • 3 interfaces - 6 routes • 6 interfaces - 30 routes • 8 interfaces - 56 routes • Additional applications on the firewall, such as encryption, may impact performance significantly Is it really working? • Test the installation/configuration to see if it is doing what you expect it to do. • Consider having the test conducted by someone other than the person/group responsible for the installation, configuration & operation of the firewall. • What do you want to test? – The firewall? – The system configuration? – The rule set on the firewall? – The security of your network? • Retest regularly Firewall Administration • Need a knowledgeable firewall administrator(s) – Network knowledge • Routing issues • DNS issues – – – – Platform O/S knowledge Mail System knowledge Knowledge of the Selected Firewall Knowledge of the Business • Need to review firewall logs regularly – Some systems do not provide logging • Without logging, how do you tell what is happening on your system? – Purge logs periodically • Depending on the system, if the logs “fill up” the disk, the system may shut down. Firewalls are no guarantee of Information Protection... • E-mail attachments • Modems • “Sneaker net” • Hard Copy • …… Firewalls are only one security tool. They are not a cure all, but can be a key part of your total Information Protection Program. Summary Select the firewall that best contributes to your policy goals Firewalls are only 1 tool in your security toolkit Continue to manage the firewall after installation -- it’s not a “set it & forget it” tool Security of distributed systems is only as strong as the security of the weakest system on the network.