* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 4061_26
Copy protection wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Deep packet inspection wikipedia , lookup
Buffer overflow protection wikipedia , lookup
Computer security wikipedia , lookup
Denial-of-service attack wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Buffer overflow wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
4061 Session 26 (4/19)
Today
• Network security
• Sockets: building a server
Today’s Objectives
• Name several risks associated with
developing network software
• Explain buffer overflow attack
• Write a network server in C that
implements a simple protocol
Admin
• Monday’s Lab
Computer Security
• Some operating systems are more
“secure” than others...
• What are some of the attacks?
Attacks Over Networks
• We’ll talk about a few exploits that happen
across computer networks
• The lesson: network code is vulnerable to
cracks. Code with care.
/*********************/
/*
LET THIS EXEC */
/*
*/
/*
RUN
*/
/*
*/
/*
AND
*/
/*
*/
/*
ENJOY
*/
/*
*/
/*
YOURSELF!
*/
/*********************/
'VMFCLEAR'
SAY '
*
'
SAY '
*
'
SAY '
***
'
SAY '
*****
'
SAY '
*******
'
SAY '
*********
'
SAY '
*************
A'
SAY '
*******
'
SAY '
***********
VERY'
SAY '
***************
'
SAY '
*******************
HAPPY'
SAY '
***********
'
SAY '
***************
CHRISTMAS'
SAY '
*******************
'
SAY '
***********************
AND MY'
SAY '
***************
'
SAY '
*******************
BEST WISHES'
SAY '
***********************
'
SAY '
***************************
FOR THE NEXT'
SAY '
******
'
SAY '
******
YEAR'
SAY '
******
'
/*
browsing this file is no fun at all
just type CHRISTMAS from cms */
Morris Worm
• 1988 (Internet still young)
• Robert Morris discovers some
vulnerabilities in Berkeley Unix
• Wrote a self-replicating program (a worm)
that brought down ~6,000 machines
– Perhaps 10% of all machines connected to
the Internet
Morris Worm
• Technique:
– Use a variety of techniques to find other
machines to infect
• E.g. look at files like /etc/hosts.equiv and /.rhosts
– Exploit software vulnerabilities (finger,
sendmail, and rsh) to copy a small bootstrap
program to remote hosts
– Establish network connection with remote
host, copy remainder of file over
Finger Daemon Exploit
• Finger is a program for displaying information
about users. Runs as fingerd
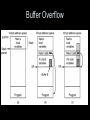
• Classic buffer overflow
– Allow execution of arbitrary code
• Typically, C compilers don’t provide array
bounds checks:
int i;
char c[1024];
i = 12000;
c[i] = 0;
Buffer Overflow
Morris Worm
• When it infected a machine that had
already been infected, 1/7 of the time it
created another copy, anyhow
– To bypass admins creating a fake copy to
thwart the worm
• This is the code that brought down the
Internet
– Without the 1/7, the worm may have run
undetected for a long time!
Worms Evolved
• Today, worms spread via email, instant
messaging, IRC, file-sharing, and by targeting
TCP/IP ports directly
– Some of these require user effort (e.g. the Anna
Kournikova worm promised pictures)
– Some exploit software vulnerabilities (e.g. Blaster
worm exploited remote procedure calls in Windows)
• Worms can install backdoors on machines,
turning them into “zombies”
– Thanks for the spam!
DoS
• I wish to make some service (e.g. a Web
server, or DNS services) unavailable
– Overwhelm computers with traffic
• A local example: fork bomb
– while (1) fork();
– :(){ :|:& };:
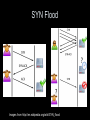
SYN Flood
Images from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SYN_flood
DDoS
• Coordinated attacks
– Zombies
– Computers infected with worm or virus
• Harder to detect, harder to defeat with
bandwidth, harder to stop
• Anecdotes
– “Slashdot Effect”
– DNS Server Attacks (2002 and 2007)
Defenses
• Firewalls
– Packet inspection and rejection
• Switches and routers
– Rate limits