* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 1 - WordPress.com
Multilevel security wikipedia , lookup
Cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Unix security wikipedia , lookup
Cyberwarfare wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Computer and network surveillance wikipedia , lookup
Post-quantum cryptography wikipedia , lookup
Information security wikipedia , lookup
Distributed firewall wikipedia , lookup
Wireless security wikipedia , lookup
Airport security wikipedia , lookup
Cyber-security regulation wikipedia , lookup
Mobile security wikipedia , lookup
Security-focused operating system wikipedia , lookup
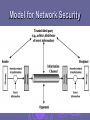
“Network Security” Introduction My Introduction Obaid Ullah Owais Khan B.E (I.T) – Hamdard University(2003), Karachi Network Engineer, Pakistan Standards & Quality Control Authority (PSQCA), Government of Pakistan E-mail: [email protected] Course Overview Course: Network Security Time: 06:00 – 07:00 pm on Thursday, Friday & Saturday Classroom: Lab 2 , FUUAST Prerequisite: Computer Networks, Discrete Mathematics. Resources Textbook Network Security Essentials: Applications and Standards, 4th ed., by William Stallings, Pearson Education, Inc., 2011. Cryptography and Network Security: Principles and Practice, Fifth Edition, by William Stallings, Prentice-Hall, 2011 Internet Searching Semester Pattern Lectures Slide Book Research Papers Presentations Quiz Mid-term and Final exams Grading Policy (Tentative) grading policy Quiz (best 1 out of 2) : 10% Attendance and class participation: 10% Research paper and Presentation: 10% Midterm : 20% Final exams: 50% Course Outline Introduction Cryptography • Symmetric encryption and message confidentiality • Public-key cryptography and message authentication Network security applications • Key distribution and user authentication • Transport-level security • Wireless network security • Electronic mail security • IP security System security • Intruders • Malicious software • Firewalls Topical Surveys We will try to read surveys in network security-related topics, e.g.: Demonstration on how to use a network security tool Comparison of security standards or algorithms Potential security weakness in systems, and possible solutions or countermeasures … Computer Security the protection afforded to an automated information system in order to attain the applicable objectives of preserving the integrity, availability and confidentiality of information system resources (includes hardware, software, firmware, information/data, and telecommunications) [NIST95] Key Security Concepts Levels of Impact can define 3 levels of impact from a security breach Low • effectiveness of the functions is noticeably reduced • minor damage to organizational assets and financial loss Moderate • effectiveness of the functions is significantly reduced • major damage to organizational assets and financial loss High • is not able to perform one or more of its primary functions • major damage to organizational assets and financial loss Computer Security Challenges 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. not simple must consider potential attacks involve algorithms and secret info must decide where to deploy mechanisms battle of wits between attacker / admin requires regular monitoring regarded as impediment to using system OSI Security Architecture ITU-T X.800 “Security Architecture for OSI” defines a systematic way of defining and providing security requirements Aspects of Security consider 3 aspects of information security: security attack security mechanism security service note terms threat – a potential for violation of security attack – an assault on system security, a deliberate attempt to evade security services Passive Attacks Passive Attacks (2) Traffic Analysis Passive attacks do not affect system resources Two types of passive attacks Eavesdropping, monitoring Release of message contents Traffic analysis Passive attacks are very difficult to detect Message transmission apparently normal • No alteration of the data Emphasis on prevention rather than detection • By means of encryption Active Attacks (1) Masquerade Active Attacks (2) Replay Active Attacks (3) Modification of Messages Active Attacks (4) Denial of Service Active attacks try to alter system resources or affect their operation Modification of data, or creation of false data Four categories Masquerade Replay Modification of messages Denial of service: preventing normal use • A specific target or entire network Difficult to prevent The goal is to detect and recover Security Services (X.800) Authentication - assurance that communicating entity is the one claimed have both peer-entity & data origin authentication Access Control - prevention of the unauthorized use of a resource Data Confidentiality –protection of data from unauthorized disclosure Data Integrity - assurance that data received is as sent by an authorized entity Non-Repudiation - protection against denial by one of the parties in a communication Availability – resource accessible/usable Security Mechanism feature designed to detect, prevent, or recover from a security attack no single mechanism that will support all services required however one particular element underlies many of the security mechanisms in use: cryptographic techniques Model for Network Security Model for Network Security using this model requires us to: 1. 2. 3. 4. design a suitable algorithm for the security transformation generate the secret information (keys) used by the algorithm develop methods to distribute and share the secret information specify a protocol enabling the principals to use the transformation and secret information for a security service Model for Network Access Security Model for Network Access Security using this model requires us to: 1. 2. select appropriate gatekeeper functions to identify users implement security controls to ensure only authorised users access designated information or resources