* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome_Intro_March_2015
Legislative assemblies of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Executive magistrates of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Switzerland in the Roman era wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Roman Republican governors of Gaul wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Elections in the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitution of the Roman Republic wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
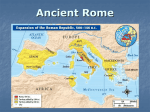
Rome - Intro CHW3M Ms. Gluskin York Mills CI A Practical and Monumental Civilization Public toilets at Ostia, 40 BCE Affordable Housing Institute: US. The Economics of Water: Part 5 – Roman Municipal Finance. 2012. http://affordablehousinginstitute.org/blogs/us/2008/04/theeconomics-of-water-part-5-roman-municipal-finance.html (March 29, 2012). Cloaca Maxima, sewer Wilke D. Schram. The Roman Water System. 2006. http://www.romanaqueducts.info/aquapub/tardieu_photos.htm (March 29, 2012). Familiar To Many People… Colosseum, amphitheatre in Rome Keith Hopkins, The Colosseum: Emblem of Rome, BBC History, 2011, http://www.bbc.co.uk/history/ancient/romans/colosseum_01.shtml (April 1, 2013). Aqueduct in Segovia, Spain PBS, Building Big, Tunnel Basics, Ancient Roman Aqueduct, 2001, http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/buildingbig/tunnel/aqueduct.html (April 1, 2013). Historical Thinking Concepts Evidence Mostly secondary sources Historical Perspectives Trial of the Assassins of Julius Caesar Continuity & Change Roman Emperor PPT Assignment Cause & Consequence Timeline of Republic 700s BCE – Etruscan civilization 753 BCE – Founding of Rome Monarchy 509 BCE – Roman Republic begins Republic = form of government with no monarchy Timeline of Empire 44 BCE – End of Republic – beginning of Empire 476 CE – End of the empire in the west 1453 – End of the empire in the east Republic 44 BCE: Rome at the end of the Republic Romulus and Remus, legendary founders of Rome About.com. Legendary Rome Timeline. 2012. http://ancienthistory.about.com/od/romehistory/tp/Legendar y-Rome-Timeline.htm (March 29, 2012). Metropolitan Museum. Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. The Roman Republic. 2000. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/romr/hd_romr.htm (March 29, 2012). Theme #1: Growth & Expansion Expansion began from the city of Rome (red dot) circa 500 BCE and extended to the purple, pink and yellow areas by the end of the republic (44 BCE) W.W. Norton Publishing, Ralph's World Civilizations Chapter 9, 1997, Geographic Features That Affected Rome’s Development Physical map of Europe Free Maps of the World. Physical Map of Europe. N.d., http://www.freeworldmaps.net/europe/index.html (April 2, 2012). Orientation Toward the Sea Trade Navy Therefore: Eventually Rome was able to dominate the Mediterranean. No Internal Physical Barriers There were mountains but they didn’t divide like in Greece Therefore: There was more unity than in Greece after the Romans (a tribe) began expanding and conquering other territories. Agriculture Very fertile soil (due to volcanic ash) Good rivers Population growth meant that there still wasn’t enough land Need to import grain from Sicily and Egypt Therefore: Romans needed to conquer more territory in order to expand (military) Carthage potential enemy The Alps These mountains separated Rome from the rest of Europe Po River was seen as a border dividing civilized Rome from northern “barbarians” Therefore: Rome felt protected by these mountains, possibly superior There were invasions, however Alps Hannibal crossing the Alps Alps Archaeology Photoblog. Hannibal In the Alps. Stanford Alpine Archaeology Project: 1994-2006. http://traumwerk.stanford.edu/archaeolog/2006/04/hannibal_in_the_alps_stanford_1.html (March 29, 2012). Theme #2: Romanization Romanization = spread of Roman values and culture Roman bath in Bath, England Bath and Northeast Somerset Council, The Roman Baths, Bath, N.d. http://www.romanbaths.co.uk/ (March 30, 2013). Theme #3: Importance of Citizenship Privileges of citizenship – see pages 176177 in textbook Ruins of Forum Romanum, where citizens came to meet National Geographic News, Photo Gallery: Ancient Rome Reborn in 3-D, Oct. 28, 2010, http://news.nationalgeographic.com/news/2007/08/photogalleries/rome-reborn/photo8.html (March 30, 2013). Privileges of Roman Citizenship Protected in law from random power of magistrates Child of father citizen is citizen (if…) Less taxes, no tribute payment Slave freed by citizen is citizen (if…) Theme #4: Struggle of the Orders – Patricians vs. Plebeians The Plebeians went on strike in the 400s BCE (plebeian secession) The Twelve Tables (law code from the 400s BCE) Table VIII. 2. If one has maimed the limb and does not compromise with the injured person, let there be retaliation. If one has broken a bone of a freeman with his hand or with a cudgel, let him pay a penalty of three hundred coins. If he has broken the bone of a slave, let him have one hundred and fifty coins. If one is guilty of insult, the penalty shall be twenty-five coins. Table XI.1. Marriages should not take place between plebeians and patricians. [Later struck down.] Oliver J. Thatcher, ed., The Library of Original Sources (Milwaukee: University Research Extension Co., 1901), Vol. III: The Roman World, pp. 9-11. In Paul Halsall, Ancient History Sourcebook: The Roman Republic: The Twelve Tables http://www.fordham.edu/halsall/ancient/12tables.html (June 1998), August 10, 2002 Theme #5: Complicated Form of Government in Republic Elements of monarchy – but they hate kings [2 Consuls and other magistrates] Elements of aristocracy – but not 100% pure power for them [Senate] Elements of democracy – but not direct democracy like in Athens [committees and tribunes] Balanced Government? 2 Consuls + other magistrates Monarchical Committees Councils, Tribunes Aristocratic Democratic Magistrates (gov’t officials) Magistrates want to climb the Cursus Honorum Census and censorship Army Justice, relations between Romans and non-Romans Roads, water, etc. Censors Consuls Praetors Aediles Quaestors Financial matters Why is dictator not on the cursus honorum? Theme #6: State Religion The concrete dome of the Pantheon, a temple originally built to honour all of the Roman gods. Later it was turned into a Christian Church in the 600s CE after the empire became Christian (300s CE). McGill Architecture, Pantheon Rome, 2005, http://www.arch.mcgill.ca/prof/sijpkes/abc-structures2005/Lectures-2005/term-work/50-questions/sixthfive.html (March 30, 2013). Rome.info, Roman Pantheon, 2003-2009, http://www.rome.info/pantheon/ (April 1, 2013). Etruscans They were another tribe on the Italian peninsula just north of Rome Highly advanced culture Some of Rome’s 7 early kings were Etruscan Etruscan urn, 4th or 3rd century BCE Metropolitan Museum. Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. Cinerary Urn. 2000. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/works-of-art/96.9.225a,b (March 29, 2012). Etruscan Cultural Contributions to Rome Greek alphabet Urban infrastructure Tunnels Dams Arches and vaults Religious practices Animism = spirits are everywhere Taking auspices = predicting the future by looking at the livers of animals Kevin J. McGowan, Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Frequently Asked Questions About Crows, 2010, Etruscan Cultural Contributions, con’t Funereal games = gladiator games eventually Symbols Fasces = became a Roman symbol of imperium, having the power over life and death (see page 168 in textbook) fasces Livius. Fasces. N.d., http://www.livius.org/fa-fn/fasces/fasces.html (March 29, 2012). Homework Day 1: Take notes on 172-176: Importance of Gauls, Sicily and southern Spain Carthaginians, Hannibal Scipio Africanus Addition of eastern territory Coloniae Via Appia Homework Takeup: 172-176 Name two societies that at one point defeated the Romans. Name two societies the Romans defeated. What was the importance of coloniae to the Romans? How did roads help Romanize the Italian peninsula? Monarchical, Aristocratic or Democratic Element of Republican Government? Includes the two leaders of the armies A check on their power is that they can only serve one year in a row It looks like they might have A check on their power is the most power in this that they control where the supposedly “balanced” army is sent system Patricians with a lot of power A check on their power is that they must agree Eventually came to have some say against patricians Roman Social Customs Beliefs: Superstitious Greeks and Etruscans, added their own Auspices, military, elections, gods Astrology, zodiac Pontifex Maximus, calendar Animal sacrifices Family Life and Morality: Family Paterfamilias, household, wife, children, slaves Potestas Property Adoption Love Recognized Education Together Latin Home, in public 16, Forum No education Girls