* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rome - Intro
Military of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Alpine regiments of the Roman army wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Roman architecture wikipedia , lookup
Promagistrate wikipedia , lookup
Roman army of the late Republic wikipedia , lookup
Constitutional reforms of Sulla wikipedia , lookup
Cursus honorum wikipedia , lookup
Roman economy wikipedia , lookup
Roman funerary practices wikipedia , lookup
Travel in Classical antiquity wikipedia , lookup
Roman historiography wikipedia , lookup
Demography of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Roman Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Education in ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Food and dining in the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Rome (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
History of the Roman Constitution wikipedia , lookup
Roman technology wikipedia , lookup
Culture of ancient Rome wikipedia , lookup
Roman agriculture wikipedia , lookup
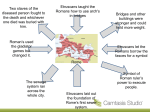
Rome - Intro CHW3M Brains and Drains Greek Brains? and Roman Drains? Public toilets at Ostia, 40 BCE Affordable Housing Institute: US. The Economics of Water: Part 5 – Roman Municipal Finance. 2012. http://affordablehousinginstitute.org/blogs/us/2008/04/theeconomics-of-water-part-5-roman-municipal-finance.html (March 29, 2012). Cloaca Maxima Wilke D. Schram. The Roman Water System. 2006. http://www.romanaqueducts.info/aquapub/tardieu_photos.htm (March 29, 2012). Timeline 700s BCE – Etruscan civilization 753 BCE – Founding of Rome 509 BCE – Roman Republic begins 44 BCE – End of Republic – beginning of Empire 476 CE – Fall of the Roman Empire in the west 1453 CE – Fall of the Roman Empire in the east Republic 44 BCE: Rome at the end of the Republic Romulus and Remus About.com. Legendary Rome Timeline. 2012. http://ancienthistory.about.com/od/romehistory/tp/Legendar y-Rome-Timeline.htm (March 29, 2012). Metropolitan Museum. Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. The Roman Republic. 2000. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/romr/hd_romr.htm (March 29, 2012). Geographic Features That Affected Rome’s Development Physical map of Europe Free Maps of the World. Physical Map of Europe. N.d., http://www.freeworldmaps.net/europe/index.html (April 2, 2012). Orientation Toward the Sea Trade Coastal trade Some natural harbours; some ports were built (e.g., Ostia – Rome’s harbour) Therefore: Eventually Rome was able to dominate the Mediterranean. No Internal Physical Barriers There were mountains but they didn’t divide like in Greece Therefore: There was more unity than in Greece after the Romans (a tribe) began expanding and conquering other territories. Agriculture Very fertile soil (due to volcanic ash) Good rivers Population growth meant that there still wasn’t enough land Need to import grain from Sicily and Egypt Therefore: Romans needed to conquer more territory in order to expand (military) Carthage potential enemy Volcano Mount Vesuvius Kidipede. Pliny the Elder. 2012. http://www.historyforkids.org/learn/romans/liter ature/elderpliny.htm (March 29, 2012). Exploring the Environment: Volcanoes. Mount Vesuvius. 2011. http://www.cotf.edu/ete/modules/volcanoes/vmtvesuvius.html (March 29, 2012). Rome – the City Well defended by 7 hills It was not directly on the sea; warships couldn’t reach it Centrally located – easy for armies to march in any direction Therefore: Strategic location; Rome could conquer in all directions throughout the Italian peninsula and then onward Rome Map 7 hills of Rome Ancient Rome. Ancient Rome Geography. N.d. http://www.ancientrome.com/geo_f.htm (March 29, 2012). The Alps These mountains separated Rome from the rest of Europe Po River was seen as a border dividing civilized Rome from northern “barbarians” Therefore: Rome felt protected by these mountains, possibly superior There were invasions, however Alps Hannibal crossing the Alps Alps Archaeology Photoblog. Hannibal In the Alps. Stanford Alpine Archaeology Project: 1994-2006. http://traumwerk.stanford.edu/archaeolog/2006/04/hannibal_in_the_alps_stanford_1.html (March 29, 2012). Etruscans They were another tribe on the Italian peninsula We know a lot about them from their tombs Highly advanced culture before the Romans Some of Rome’s 7 early kings were Etruscan Etruscan Cultural Contributions to Rome Greek alphabet Urban infrastructure Tunnels Dams Arches and vaults Religious practices Animism = spirits are everywhere Taking auspices = predicting the future by looking at the livers of animals Etruscan Cultural Contributions, con’t Funereal games = gladiator games eventually Symbols Fasces = became a Roman symbol of imperium, having the power over life and death (see page 168 in textbook) fasces Livius. Fasces. N.d., http://www.livius.org/fa-fn/fasces/fasces.html (March 29, 2012). Etruscan Art Etruscan urn, 4th or 3rd century BC Metropolitan Museum. Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. Cinerary Urn. 2000. http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/works-of-art/96.9.225a,b (March 29, 2012). First Emperor Augustus Metropolitan Museum. Heilbrunn Timeline of Art History. List of Rulers of the Roman Empire. 2000.http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/hd/roru/hd_roru.htm (March 29, 2012). Monarchical, Aristocratic or Democratic Element of Republican Government? Includes the two leaders of the armies A check on their power is that they can only serve one year in a row It looks like they might have the most power in this supposedly “balanced” system Patricians with a lot of power A check on their power is that they control where the army is sent A check on their power is that they must agree Eventually came to have some say against patricians Homework Takeup: 172-176 Name two societies that one point defeated the Romans. Name two societies the Romans defeated. What was the importance of coloniae to the Romans? How did roads help Romanize the Italian peninsula?