* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Psychology
Art therapy wikipedia , lookup
Primal therapy wikipedia , lookup
Transtheoretical model wikipedia , lookup
Status dynamic psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Depression in childhood and adolescence wikipedia , lookup
Homework in psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Reminiscence therapy wikipedia , lookup
Control mastery theory wikipedia , lookup
Behaviour therapy wikipedia , lookup
Residential treatment center wikipedia , lookup
Dodo bird verdict wikipedia , lookup
Adherence management coaching wikipedia , lookup
Behavioral theories of depression wikipedia , lookup
Adventure therapy wikipedia , lookup
Emotionally focused therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dyadic developmental psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Equine-assisted therapy wikipedia , lookup
Treatments for combat-related PTSD wikipedia , lookup
Lifetrack Therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Reality therapy wikipedia , lookup
Solution-focused brief therapy wikipedia , lookup
Psychotherapy
A planned
emotionally charged,
confiding interaction
between a trained,
socially sanctioned
healer and a
sufferer.
Therapy
Psychotherapy
Treatment of emotional and behavioral problems through
psychological techniques, rather than biological
approaches to treatment
Involves conversations, verbal interactions b/w person
with a disorder and someone who’s been trained to
correct that disorder
Eclectic Approach
an approach to psychotherapy that, depending on the
client’s problems; uses blended technique, pulls from
various forms of therapy
Therapy - Psychoanalysis
Psychoanalysis
Freud believed the patient’s free associations, defense
mechanisms, resistances, dreams, and transferences (and
the therapist’s interpretations of them) released previously
repressed feelings often from childhood
Historical reconstruction, allows patient to gain self-insight
significantly decreased use in recent years, takes time,
very expensive
Resistance
blocking flow of free associations to consciousness, often
anxiety-laden material
Any unconscious behaviors by patient that hinder the
progress of therapy (being late, missing sessions, anger at
therapist.)
Therapy- Psychoanalysis
Interpretation
analyst offers insights, alternative way of looking at dream
meanings, resistances, other behaviors based on patient’s
possible unconscious needs and desires in order to
promote insight
Transference
based on therapist’s neutral relationship with patient
patient transfers to therapist the emotions, feelings,
perceptions linked with other relationships
Ex: love or hatred for a parent
signs of transference include falling in love or being hostile to
therapist
lacking confidence in one's own ability, worth, or fitness; timid;
shy
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uZq_U2hbnvs&feature=related
Humanistic Therapy
Client-Centered Therapy - Carl Rogers
therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a
genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate
clients’ growth, unconditional positive regard, self
actualization
focuses on clients’ own point of view, not therapists’
interpretations, acts as psychological mirror, boosts self
awareness, focused on present and future – NOT past
Active Listening
empathic listening in which the listener echoes, restates,
and seeks clarification, acknowledges client’s feelings
understands emotion and content of clients’ statements
Behavior Therapy
Behavior Therapy
applies learning principles to the elimination of
unwanted, troubling behaviors
assumes both normal and abnormal behaviors are
learned and can be replaced w/ constructive behaviors
Counterconditioning
procedure that conditions new, more adaptive
responses to stimulus that triggers unwanted behaviors
based on Pavlov’s Classical Conditioning
includes systematic desensitization (gradual), exposure
therapy and aversive conditioning
Behavior Therapy
Systematic Desensitization
type of exposure therapy; counterconditioning
associates a pleasant, relaxed state with exposure
to gradually increasing anxiety-triggering stimuli
commonly used to treat phobias
Aversive Conditioning
type of counterconditioning that associates an
unpleasant state or stimulus with an unwanted
behavior; aversive response to a harmful stimuli
Nausea drug in drinks ---> alcoholics
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KZag1zlecGI
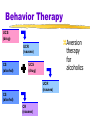
Behavior Therapy
Systematic Desensitization
Behavior Therapy
UCS
(drug)
Aversion
therapy
for
alcoholics
UCR
(nausea)
CS
(alcohol)
UCS
(drug)
UCR
(nausea)
CS
(alcohol)
CR
(nausea)
Behavior Therapy
Token Economy
operant conditioning procedure that rewards
desired behavior, can also punish
inappropriate behavior via “fines”
patient exchanges a token of some sort,
earned for exhibiting the desired behavior,
for various privileges/treats
Often used in institutional settings (schools,
hospitals, prisons, with disturbed children,
schizophrenics and AP Psych classrooms)
Behavior Therapy
Token Economy Criticisms
Dependent on extrinsic rewardswhat happens when the reinforces
stop?
Subjective-Is it right for one
human being to control another’s
behavior, is behavior modification
too authoritarian?
Cognitive Therapy
Emphasizes recognizing and changing negative
thoughts and maladaptive beliefs (depression,
anxiety).
Teaches new, more adaptive ways of thinking
and acting (no more self-blame, criticism)
Goal – change, restructure client’s thinking
process
Person’s emotional reactions are produced not
by the event (job loss) but by the person’s
thoughts in response to the event
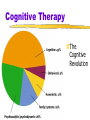
Cognitive Therapy
The
Cognitive
Revolution
Cognitive Therapy
Lost job
Internal beliefs:
I’m worthless.
It’s hopeless.
Depression
Lost job
A cognitive
perspective
on
psychological
disorders
Internal beliefs:
My boss is a jerk.
I deserve something better.
No
depression
Cognitive Therapy
Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (C.B.T.)
Aaron Beck identified patterns of thinking that correlated with symptoms
of depression. To understand depression and related illness, he
developed the Beck Depression Inventory, Beck Anxiety Inventory, and
the Scale for Suicide Ideation. Best known for cognitive approach to
treatment of disorders, especially depression, did much of the initial
research on the theory that distorted or inaccurate thoughts are
precursor in the development/continuation of depression.
CBT exposes and confronts the client’s dysfunctional thoughts; a
popular, integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy (changing
self-defeating thinking) with behavior therapy (changing behavior)
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3Y8VKs3__cA&feature=related
Cognitive Therapy
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy- focuses
on uncovering irrational beliefs which may lead to
unhealthy negative emotions, replacing them with
more productive rational alternatives
Albert Ellis’ REB theory - it is generally irrational
and self-defeating to get all worked up about
someone else's behavior
RET is a direct, confrontational form of therapy that
challenges client’s irrational beliefs. Replace
irrational thoughts with those that are appropriate
and less distressing.
RET therapists – a warm client/therapist is not
necessary
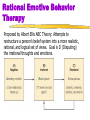
Rational Emotive Behavior
Therapy
Proposed by Albert Ellis ABC Theory: Attempts to
restructure a person’s belief system into a more realistic,
rational, and logical set of views. Goal is D (Disputing)
the irrational thoughts and emotions.
Group Therapies
Family Therapy
treats the family as a system; often less
expensive and less time intensive than
individual therapy
views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as
influenced by or directed at other family
members; no one is an island
attempts to guide family members toward
positive relationships
improve communication
Who Practices Therapy?
To whom do
people turn
for help for
psychological
difficulties?
Who Practices Therapy?
Clinical Psychologists
Trained to diagnose, test and treat
individuals with psychological disorders
Most are psychologists with Ph.D. and
expertise in research, assessment, and
therapy, supplemented by supervised
internship
About half work in agencies and institutions,
half in private practice
Who Does Therapy?
Clinical or Psychiatric Social Worker
Two-year Master of Social Work graduate
program plus postgraduate supervision
prepares some social workers to offer
counseling and psychotherapy, mostly to
people with everyday personal and family
problems.
About half have earned the National
Association of Social Workers’ designation of
Clinical Social Worker.
Who Does Therapy?
Counselors
Marriage and family counselors
specialize in problems arising
from family relations.
Pastoral counselors provide
counseling to countless people.
Abuse counselors work with
substance abusers and with
spouse and child abusers and
their victims.
Who Does Therapy?
Psychiatrists
Medical doctors who specialize in the
treatment of psychological disorders
Not all psychiatrists have had extensive
training in psychotherapy, as MD’s they can
prescribe medications
Tend to see those with the most serious
problems
Many have a private practice
Biomedical Therapies
Psychopharmacotherapy
Treatment of the mental disorders with medication
Anti mania (Lithium Carbonate)
provides an effective drug therapy for the mood swings of
bipolar (manic-depressive) disorder, 80% effective, dosage
must be exact and constantly monitored
Anti psychotic (Clozapine, Thorazine, Haldol)
used in the treatment of schizophrenia for disorganized and
psychotic thinking. Used to help treat false perceptions (e.g.
hallucinations, paranoia or delusions.), 60-70% of patients
show improvement. Can cause tardive dyskinesia – tremors,
muscle movements.
Biomedical Therapies
The emptying of U.S. mental hospitals
State and county
mental hospital 700
residents, in 600
thousands
500
Introduction of antipsychotic drugs
Rapid decline
in the mental
hospital
population
400
300
200
100
0
1900 1910 1920 1930 1940 1950 1960 1970 1980 1990
Year
Biomedical Therapies
Biomedical Therapies
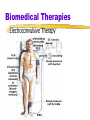
Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT)
therapy for severely depressed patients in which a brief electric
current is sent through the brain of an anesthetized patient.
Routinely used in 1940’s - 50’s for schizophrenia and
sometimes mania. Not commonly used now, no one knows
why/how it worked, the seizure that resulted may temporarily
change the biochemical balance in the brain.
Psychosurgery
surgery that removes or destroys brain tissue in an effort to
change behavior, only used for serious disorders
Lobotomy - frontal lobes surgically separated from brain
centers controlling emotion, now-rare psychosurgical
procedure once used to calm uncontrollably emotional or
violent patients (left impaired intellect, loss of motivation,
personality changes). Left patients permanently lethargic.
The Placebo Effect
Any substance that is not known to have any pharmacological
effects (produces no meaningful changes in an organism, either
chemical, biological, etc.) that is made to look like an active ("real")
drug
Sometimes the act of taking a pill produces an effect if the person
believes the pill is active
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zihdr36WVi4
Biomedical Therapies
Electroconvulsive Therapy
Biomedical Therapies ECT
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9L2B-aluCE
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=44sU
rJytcLI – Patient after ECT
And we’re done
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iQgMXOW0FLU&feat
ure=email