* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Worms - walker2012
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
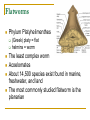
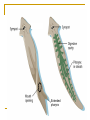
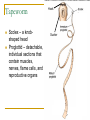
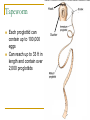
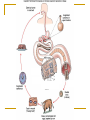
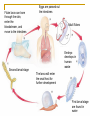
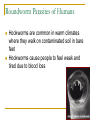
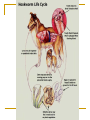
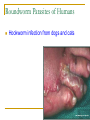
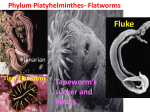
Worms Chapters 26.3, 26.4, and 27.2 Animal Classification Invertebrates Sponges Cnidarians Worms Mollusks Arthropods Echinoderms - Phylum Platyhelimenthes - Phylum Nematoda - Phylum Annelida Animals (cold-blooded) Fishes Amphibians Reptiles Endotherms Birds Mammals Ectotherms Vertebrates (warm-blooded) Flatworms Phylum Platyhelimenthes (Greek) platy = flat helmins = worm The least complex worm Acoelomates About 14,500 species exist found in marine, freshwater, and land The most commonly studied flatworm is the planarian Nervous Control Most of the nervous system is located in its head The nervous system consists of two nerve cords that run the length of the body Nerve cords Nervous Control Eyespots can detect the presence or absence of light Sensory cells can detect chemicals and movement in water Sensory cells Eyespots Sensory cells Nervous Control Ganglion A small swelling of the nerve cord Receives messages from the eyespots and sensory pits, then communicates with the rest of the body Ganglia Reproduction Most flatworms are hermaphroditic Can reproduce sexually and asexually Sexual reproduction Two planarians will exchange sperm Internal fertilization occurs Zygotes are then released in water where they will hatch Reproduction Asexual reproduction Planarians can regenerate when damaged Regeneration – The replacement or regrowth of missing body parts Feeding and Digestion in Planarians A planarian feeds on dead or slow-moving organisms Planarians are not parasitic To eat, a planarian extends its pharynx from its mouth Pharynx – a tube-like, muscular organ (also known as the throat) Extended pharynx Feeding and Digestion in Planarians Enzymes breakdown the food outside the body, and then food particles are sucked into the digestive tract Food is digested in individual cells Waste leaves through its one opening (mouth) Feeding and Digestion in Planarians Excretory system – eliminates waste from the body Flame cells – excess water is removed from the body Feeding and Digestion in Parasitic Flatworms Parasitic flatworms have mouthparts with hooks that keep them attached to their hosts Hook Sucker Feeding and Digestion in Parasitic Flatworms Parasitic flatworms don’t need a digestive system because they obtain nutrients from food that has been digested by their host Hook Sucker Tapeworm Scolex – a knobshaped head Proglottid – detachable, individual sections that contain muscles, nerves, flame cells, and reproductive organs Hook Sucker Tapeworm Each proglottid can contain up to 100,000 eggs Can reach up to 33 ft in length and contain over 2,000 proglottids Hook Sucker Fluke larva can bore through the skin, enter the bloodstream, and move to the intestines Eggs are passed out the intestines Adult flukes Embryo develops in human waste Second larval stage The larva will enter the snail host for further development First larval stage are found in water Roundworms Phylum Nematoda Greek word nema = thread Found in soil, animal, freshwater, and marine environments More than 12,000 species exist Nearly all plant and animals are affected by parasitic roundworms Pseudocoelomates Have a complete digestive system with two openings (mouth and anus) Free-living species have well-developed eyespots whereas parasitic species have underdeveloped eyespots Roundworm Parasites of Humans Ascaris is the most common roundworm infection in humans worldwide More common in subtropical areas Children become infected more often than adults Timmy plays in a sandbox… Roundworm Parasites of Humans Pinworms are the most common roundworm parasites in the U.S. Children are the commonly infected Eggs can survive two weeks on the surfaces Roundworm Parasites of Humans During night, female pinworms lay eggs around the anus of host Taping the anus before bedtime is one method used to eliminate pinworms Roundworm Parasites of Humans Trichinella can be ingested in raw or undercooked pork or wild game (turkey) Trichinella can be controlled by properly cooking meat Roundworm Parasites of Humans Hookworms are common in warm climates where they walk on contaminated soil in bare feet Hookworms cause people to feel weak and tired due to blood loss Roundworm Parasites of Humans Hookworm infection from dogs and cats