* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cells and Tissues
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Artificial cell wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Hematopoietic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal lineage marker wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Cell (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
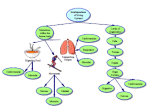
Biology The study of Living Things Characteristics of Living Things – Made of cells – Obtain and use energy – Grow and develop – Reproduce – Respond to their environment – Adapt to their environment Cells • Make up all living things • Basic units of structure and function • Humans are made of trillions of cells and there are hundreds of different types. Two Classifications of Cells • Prokaryotic Cells – 1st form of life – No nucleus – Only form Unicellular organisms (one celled) – Example: Bacteria • Eukaryotic Cells – Formed from prokaryotes – Have a nucleus – Form unicellular and multi-cellular organisms. – Example: Plants and animals Types of Living Things • Unicellular organisms – Function by itself without need of other cells for survival • Bacteria • Protozoa • Unicellular algae, fungi and yeast • pathogens • Multi-cellular organisms – Made of many cells that are specialized and work together to function and survive. • Plants and animals Cell Organelles Structure Function – Cell Membrane: Outer cell lining for protection – Cytoplasm: Liquid that organelles float in – Nucleus: Control center with DNA – Nuclear Membrane: Surrounds and protects nucleus – Vacuoles: Stores water and other nutrients in plant cells Cell Organelles Structure Function – Mitochondria: Produces energy (ATP) – Ribosomes: Makes proteins – Endoplasmic Reticulum: Transports proteins throughout cell – Golgi Apparatus: Stores, modifies and secretes proteins – Cell Wall: Gives Plant cells structure and support to maintain shape Cell Organelles Structure Function – Chloroplast: Produces energy through photosynthesis in Plant cells – Microtubules protein filaments involved in cell movement, shape, and cell division. – Centrioles contain microtubules and involved in cell division. – Lysosomes helps with animal cell digestion – Chromosomes strands of DNA inside the nucleus. Animal Cell Animal Cell Plant Cell Plant Cells Cells Make Tissues • A group of similar cells working together • 4 types: 1. 2. 3. 4. Epithelial tissue Nervous Muscle Connective Epithelial Tissue • Covers and protects underlying tissue • Ex. - Skin Nervous Tissue • Sends electrical signals through the body • Found in the brain, nerves and sense organs Muscle Tissue • Made of cells that can contract and relax to produce movement • 3 Types: Skeletal, Smooth, and Cardiac 3 Types of Muscle Tissue • Cardiac - only found in the heart • Smooth - line the wall of structures inside the body • Skeletal - makes the body move Connective Tissue • Joins, supports, protects, insulates, nourishes, and cushions organs • Keeps organs from falling apart ORGANS • Two or more tissues working together • Organs that work together make up an organ system • The body has 12 major organ systems Integumentary System • Skin, hair and nails • Main function is protection • Helps regulate body temperature • Helps remove waste from the body • Produces Vitamin D • Receives stimuli such as pressure, heat, cold and pain Muscular System • The human body contains more than 650 individual muscles • The muscular system provides movement for the body • Muscles can be voluntary or involuntary 3 Types of Muscle Tissue • Skeletal Muscle – Attached to the skeleton and moves parts of the body • Smooth Muscle – Usually involuntary and found in internal organs • Cardiac Muscle – Only found in the heart Skeletal System • Provides structure • Supports and protects the body • Allows bodily movement – attached to muscles • Produces red blood cells– an average of 2.6 million cells each second • Stores minerals – such as calcium and phosphorus Skeletal System • Bones - More than 206 bones in the human body. • Ligaments attaches bone to bone • Tendons - attaches muscle to bone • Cartilage Circulatory/Cardiovascular System • Heart, blood and blood vessels (arteries, veins and capillaries) • Transports blood (oxygen and nutrients) throughout the body Respiratory System • Nose, larynx, pharynx, trachea, lungs, bronchi • Diaphram - muscle that helps w/breathing • Takes in oxygen and releases carbon dioxide Nervous System • Central Nervous System - brain and spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System - Nerve cells (neurons) • Sends and receives messages (electrical impulses) to and from the brain. Lymphatic/Immune System • Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, thymus gland, tonsils, spleen • Returns excess fluid in the body to the bloodstream. • Helps fight against pathogens Immune System • Collection of cells, tissues and organs, including the lymphatic system • White Blood Cells called lymphocytes (B cells and T cells) produced in bone marrow. • Protects against infection by identifying and killing pathogens. Digestive System • Digestive Tract Mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus • Liver, pancreas, and gall bladder helps with digestion • Receives and breaks down food, absorbs nutrients, and excretes waste. Endocrine System • Regulates body functions • Glands and hormones – – – – – – – – Pituitary: Master gland Hypothalamus: Brain Thyroid: Metabolism Parathyroids: Regulates calcium in blood. Adrenal: Produces adrenaline Pineal: Secretes melatonin Ovaries/Testes: Reproduction Pancreas: Produces insulin to maintain blood glucose level. Urinary System • 2 Kidneys, 2 ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. • Filters and cleans blood • Produces, stores and eliminates urine. Homeostasis • Regulation of a living systems internal environment to maintain a stable constant normal condition. • Required for living systems to be healthy and function normally. • Controlled by “Feedback Mechanisms” – Receptors that either start or stop a reaction using enzymes. Feedback Mechanisms Examples • Increase in heart rate and respiration during exercise to get more oxygen to cells. • Sweating to maintain a normal body temperature. • Release of insulin by the pancreas to regulate blood glucose (sugar) levels. • Plants regulating water loss and CO2 intake for photosynthesis and other life activities.