* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download immune systemgd
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
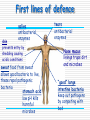
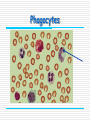
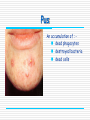
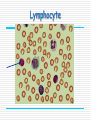
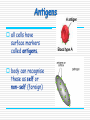
Immune system By the end of the lesson you should be able to Outline the stages in phagocytosis. Describe how antibodies work and how they are specific. First lines of defence saliva antibacterial enzymes skin prevents entry by shedding causing acidic conditions sweat food from sweat allows good bacteria to live, these repel pathogenic bacteria stomach acid low pH kills harmful microbes tears antibacterial enzymes Nose mucus linings traps dirt and microbes “good” large intestine bacteria keep out pathogens by competing with bad Pathogens = disease causing micro-organisms bacteria virus fungi, protozoa, parasite, Second lines of defence Involves white blood cells Non-specific response invading pathogens are targeted by macrophages Specific response lymphocytes produce chemicals called antibodies that target specific pathogens Phagocytes Phagocytes These are a general name for Monocytes and macrophages Provide a non-specific response to infection Phagocytosis Stages in phagocytosis 1. Phagocyte detects chemicals released by a foreign intruder (e.g. bacteria) 2. The phagocyte adheres to the foreign cell and engulfs it in a vacuole by an infolding of the cell membrane. 3. Lysosomes ( which are rich in digestive enzymes & found in the phagocytes cytoplasm) fuse with the vacuole & release their contents into it. Phagocytosis 5. The bacterium is digested by the enzymes, and the breakdown products are absorbed by the phagocyte. During infection, hundreds of phagocytes are needed. Pus is dead bacteria and phagocytes! Pus An accumulation of : dead phagocytes destroyed bacteria dead cells Lymphocyte Lymphocytes Provide a specific immune response to infectious diseases. There are 2 types: - T-cells - B-cells They produce antibodies. Antigens all cells have surface markers called antigens. body can recognise these as self or non-self (foreign) Specific response Lymphocytes detect presence of foreign antigens Stimulated to produce specific proteins called antibodies. antibodies combine with their specific antigen (like a lock and key) this renders the pathogen harmless. = primary response Immunity = the bodies ability to resist infection can be natural or acquired Immunological memory after an infection is fought off some lymphocytes become memory cells. if same pathogen returns memory cells stimulate the produce the specific antibody very rapidly. the infection is fought off before symptoms appear = secondary response vaccines can stimulate same response Immune system Can you Outline the stages in phagocytosis. Describe how antibodies work and how they are specific. This powerpoint was kindly donated to www.worldofteaching.com http://www.worldofteaching.com is home to over a thousand powerpoints submitted by teachers. This is a completely free site and requires no registration. Please visit and I hope it will help in your teaching.