* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Monoclonal Antibodies - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Immunoprecipitation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Cooperative binding wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
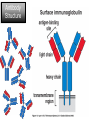
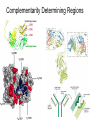
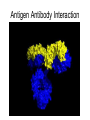
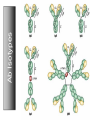
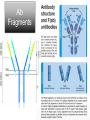
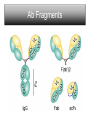
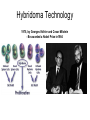
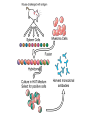
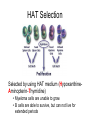
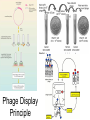
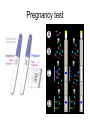
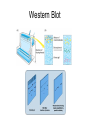
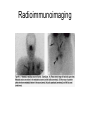
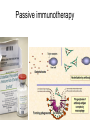
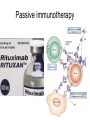
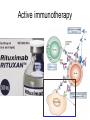
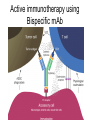
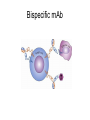
Monoclonal Antibodies Dr. Aws Alshamsan Department of Pharmaceutics Office: AA87 Tel: 4677363 [email protected] Objectives of this lecture By the end of this lecture you will be able to: 1. Define terms such as monoclonal, polyclonal, isotype, idiotype, allotype, CDR, and hybridoma 2. Compare monoclonal-antibody production methods 3. Identify different mAb types 4. List some applications of mAb in medicine Antibody Response Antibody Structure Complementarity Determining Regions Antigen Antibody Interaction Antigen Antibody Interaction Ab Isotypes Ab Fragments Ab Fragments Ab types differences Polyclonal v.s. Monoclonal Affinity and Avidity Affinity: the strength of binding between a single binding site and a single ligand. Avidity: the strength of binding between a molecule and a complex ligand, e.g. if there are multiple binding sites then the avidity may be increased by increasing the number of binding sites or by increasing the affinity of those binding sites. Affinity and Avidity, continued IgM is produced early in an immune response when the affinity for antigen often is low; as an immune response continues, antibody affinity is improved, this is combined by “class switching” to the use of smaller molecules (IgG, IgE and IgA). The increased affinity compensates for the decrease in number of binding sites in maintaining the overall avidity for antigen. Polyclonal Response • Polyclonal antibody – Antigens possess multiple epitopes – Serum antibodies are heterogeneous, • To increase immune protection in vivo • To reduces the efficacy of antiserum for various in vitro uses – To response facilitates the localization, phagocytosis, and complement-mediated lysis of antigen – To have clear advantages for the organism in vivo • Monoclonal antibody – Derived from a single clone, specific for a single epitope – For most research, diagnostic, and therapeutic purposes mAb Types mAb nomenclature Source stem Suffix o mAb xi mAb zu mAb u mAb mAb Production Hybridoma Technology Phage Display Method Hybridoma Technology 1975, by Georges Köhler and Cesar Milstein - Be awarded a Nobel Prize in1984 (1) Immunisation of a mouse (2) Isolation of B cells from the spleen (3) Cultivation of myeloma cells (4) Fusion of myeloma and B cells (using PEG) (5) Separation of cell lines (6) Screening of suitable cell lines (7) in vitro (a) or in vivo (b) multiplication (8) Harvesting HAT Selection Selected by using HAT medium (HypoxanthineAminopterin-Thymidine) • Myeloma cells are unable to grow • B cells are able to survive, but can not live for extended periods Two different pathways to synthesis nucleotide in mammalian cells (Folic acid analog) Phage Display Introduction • The display of functional foreign peptides or small proteins on the surface of bacteriophage particles. • An important tool in protein engineering • A powerful way to screen and select for peptides on the basis of binding or molecular recognition Phage Display Principle Phage Display Advantages • More efficient than hybridoma system. • Cheaper to produce recombinant antibodies using bacteria, rather than mammalian cell line. • Easier to maintain and grow bacterial cultures for recombinant antibody production. • Bypass immunization in antibody selection. • Bypass the use of animal cells for production of antibodies. • Producing the combinatorial library (ideally with 108 to 109 members) of functional antibodies to generate a larger repertoire of antibodies than those available through conventional hybridoma technology. Plantibodies • "plantibodies" are antibodies produced by genetically-engineered corps e.g. corn, potatoes and tobacco plant • "plantibodies" are cheaper and arguably safer than mammalian mAbs Clinical Applications of Monoclonal Antibodies A. Diagnosis 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Pregnancy test ELISA Western Blot Flow Cytometry Radioimmunoimaging B. Therapy A. Passive Immunotherapy B. Active Immunotherapy C. Drug Targeting Pregnancy test ELISA Western Blot Flow cytometry Radioimmunoimaging Passive immunotherapy Passive immunotherapy Active immunotherapy Active immunotherapy using Bispecific mAb Bispecific mAb Drug targeting You are now able to: Define terms such as monoclonal, polyclonal, isotype, idiotype, allotype, CDR, and hybridoma Compare monoclonal-antibody production methods Identify different mAb types List some applications of mAb in medicine