* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Poliomyelitis
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Poliomyelitis eradication wikipedia , lookup
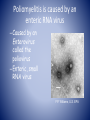
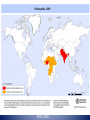
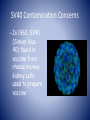
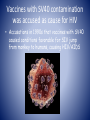
U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Poliomyelitis U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Ijeoma Ohadugha 4/1/10 Infectious Diseases http://www.immune.org.nz/site_resources/Professionals/Diseases/Polio/Polio.jpg Poliomyelitis is an infection of the CNS • poliós -Greek word “grey”, + myelós “spinal cord’ + suffix – itis “inflammation =poliomyelitis • Viral infection of the nerves of the CNS Poliomyelitis is caused by an enteric RNA virus – Caused by an Enterovirus called the poliovirus – Enteric, small RNA virus F.P. Williams, U.S. EPA Transmission by fecal-oral route http://www.co.washington.or.us/HHS/EnvironmentalHealth/PublicPools/ Risk Factors – Not being vaccinated in areas where polio is common – infants, pregnant women, immunocompromised (eg. HIV) WHO, 2008. Three basic patterns • Subclinical infection(95% of infections), Three basic patterns • Subclinical infection(95% of infections), • Nonparalytic poliomyelitis(1-2%) Three basic patterns • • • • Subclinical infection(95% of infections), Nonparalytic poliomyelitis(1-2%) Paralytic poliomyelitis(0.1–0.5%) -result of accidental transfer of virus from GI tissue to neural tissue – Spinal polio - 79% of paralytic cases— Bulbospinal polio - 19% of paralytic cases— Bulbar polio - 2% of paralytic cases Polio afflicted everyone socially as well as medically • Franklin Delano Roosevelt • “Once you’ve spent two years trying to wiggle one toe, everything is in proportion.” —Franklin D. Roosevelt, 1945 http://americanhistory.si.edu/polio/howpolio/fdr.htm Heine named polio as a clinical condition; Lansteiner discovered the virus Jakob Heine(1840) Karl Landsteiner (1909) – poliovirus enters digestive tract via mouth – Primary site of infection is epithelial and lymphoid tissue associated with the oropharynx and gut • Virus production at this site leads to a transient viremia, following which the virus may infect the CNS http://cmbi.bjmu.edu.cn/www-learn/micro-ac-uk/335/Picornaviruses.html Dual Tropism Thought to be the Cause of Poliomyelitis from Poliovirus • Reflects the distribution of the poliovirus receptor CD155 on cells lymphoid cells as well as the epithelial cells in the gut and on neurons in the CNS • Viral Tropism relies on host cell permissiveness and receptor susceptibility Virus Replicates Through Viropexis – attachment of the virus to specific cellular receptors of cells with CD155 – penetration and uncoating of the virus is energy dependent, and occurs by receptormediated endocytosis (viropexis) Interferons May Prevent Susceptibility of Most Cells with CD155 – CD155 is present on most human cells, so does not explain why it infects certain tissues – Recent studies-suggest human type I interferon receptors possibly prevent – Interferon- protein released by lymphocyte in response to pathogen to trigger immune defenses Only IPV used in US today – OPV known to in rare cases become virulent and cause iatrogenic (vaccine-induced) polio – Both used today in the world – IN US, only IPV used since 1990s from policy changes – Only cases of polio (8-10 per year) were from people with vaccine-induced polio Jonas Salk- Injected Poliovirus Vaccine(IPV) Albert Sabin – oral live attenuated virus (OPV) 1952 1957 SV40 Contamination Concerns – In 1960, SV40 (Simian Vius40) found in vaccine from rhesus monkey kidney cells used to prepare vaccine Vaccines with SV40 contamination was accused as cause for HIV • Accusations in 1990s that vaccines with SV40 caused conditions favorable for SIV jump from monkey to humans, causing HIV/AIDS Accusation now debunked, but stigma lingers for new reasons – New reasons for vaccination stigma such as rumors of sterility in some areas Treatment in the past often ineffective until Elizabeth Kenny’s procedures – crutches or wheelchair for motor muscle degeneration – “convalescent serum”-1920s – iron lung for respiratory failure – early 1940s- Sister Elizabeth Kenny’s procedureshotpacks and heating pads w/massages, still used today Present Treatments Offer Relief to Symptoms – No current cure – Respiratory apparatus – Antibiotics for UTIs, medication for urine retention – Heating pads and towels for muscle spasms & pain – Physical therapy, braces, or orthopedic surgery for recovery of muscle strength/function What still needs to be done • Eradication efforts – Get rid of stigma surrounding vaccine in Africa and other polio-afflicted places – Develop new targets for polio cure References • http://www.polioeradication.org/ • https://health.google.com/health/ref/Poliomyelitis • http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/polio/DS00572/D SECTION=risk-factors • http://www.cloudnet.com/~edrbsass/poliotimeline.ht m • http://www.vaccineinformation.org/polio/qandavax.as