* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1. dia
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
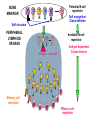
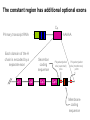
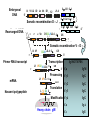
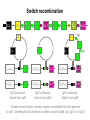
B-CELL DIFFERENTIATION IN THE PERIPHERY Ag Ag Ag Memory B-cell Activated B-cell Mature naive B-cell ISOTYPE SWITCH SOMATIC HYPERMUTATION BONE MARROW 3 2 1 4 n 5 Potential B-cell repertoire Self recognition Clonal deletion Self structure PERIPHERAL LYMPHOID ORGANS 3 2 Available B-cell repertoire n 4 Antigen dependent Clonal division Antigen – non-self 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Memory cell repertoire 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 Effector cell repertoire The molecular genetics of immunoglobulins • If the BCR and the soluble antibodies are identical, by what mechanism switch from one to the other is controlled? MEMBRANE VS SECRETED IMMUNOGLOBULIN • By what mechanism are antibodies with the same specificity but with different isotypes generated? ISOTYPE SWITCH • How could antibodies increase their affinity in the course of the immune response? SOMATIC HYPERMUTATION MEMBRANE BOUND AND SECRETED IMMUNOGLOBULIN The constant region has additional optional exons Cm Primary transcript RNA Each domain of the H chain is encoded by a separate exon Cm1 Cm2 AAAAA Secretion coding sequence Cm3 Polyadenylation site (secreted) pAs Polyadenylation site (membrane) pAm Cm4 Membrane coding sequence Membrane IgM constant region DNA Cm1 Cm2 Cm3 Cm4 Transcription 1° transcript pAm Cm1 Cleavage & polyadenylation at pAm and RNA splicing mRNA Cm2 Cm3 Cm1 Cm2 Cm3 Cm4 Cm4 AAAAA AAAAA Membrane coding sequence encodes transmembrane region that retains IgM in the cell membrane Protein Fc Secreted IgM constant region DNA Cm1 Cm2 Cm3 Cm4 Transcription 1° transcript pAs Cm1 Cm2 Cm3 Cm4 AAAAA Cleavage polyadenylation at pAs and RNA splicing mRNA Cm1 Cm2 Cm3 Cm4 Protein AAAAA Secretion coding sequence encodes the C terminus of soluble, secreted IgM Fc ISOTYPE SWITCH Antibody isotype switching Throughout the immune response the specificity of an antibody will be essentially the same (notwithstanding affinity maturation) The effector function of antibodies throughout a response needs to change drastically as the response progresses. Antibodies are able to retain Variable regions whilst exchanging Constant regions that contain the structures that interact with cells. Organisation of the functional human heavy chain C region genes J regions Cm Cd Cg3 Cg1 Ca1 Cg2 Cg4 Ce Ca2 embrionális Embryonal L1 V1 L2 V2 Ln Vn D1 - 12 DNS DNA 5' szomatikus rekombináció Somatic recombination D– D-J kapcsolódás átrendeződött Rearranged DNA DNS L1 V1 Ln Vn Cm Cδ Cg3 CM CD CG3 J1-4 J CA1Cε2 Ca1 CG1 CE2Cg1 CE1 Ca2 CG 2 CG 4 Cε1 CA2 C g1 Cg4 D1D2 J1J2-4 Cm CM Cδ CD 5' 3' szomatikus rekombináció Somatic recombination V -D-J kapcsolódás CM Cδ CD D2J1 J2-4 Cm 3' L1 V1 5' Primerprimer RNA transcript RNS-átirat mRNA mRNS 3’ Transcription transzkripció 5' L1 V1D2 J1 J2-4 Cm CM Cδ CD IgM Cγ1 IgG Cγ2 IgG Cγ3 IgG Modification Cγ4 IgG AAAA transzláció Translation L V DJ Cm C polipeptid Ig ISOTYPES Cµ 3' Processing átalakítás Cm L1 V1 D2 J1 CM naszcens Nascent polypeptide módosítás V C V–D–J NEHÉZL ÁNC (M ) Heavy chain IgM Cα IgA Cε IgE Switch regions Cm Sm Cd Cg3 Sg3 Cg1 Sg1 Ca1 Sa1 Cg2 Sg2 Cg4 Sg4 Ce Se Ca2 Sa2 • Upstream of C regions are repetitive regions of DNA called switch regions. (The exception is the Cd region that has no switch region). • The Sm consists of 150 repeats of [(GAGCT)n(GGGGGT)] where n is between 3 and 7. • Switching is mechanistically similar in many ways to V(D)J recombination, but • All recombination events are productive • Different recombination signal sequences and enzymes are involved • Requires antigen stimulation of B cell • Not a random event, but regulated by external signals such as T cell derived cytokines • Isotype switching does not take place in the bone marrow, but occurs after B cell activation in the peripheral lymphoid organs Switch recombination Cm Cd Cg3 Cg1 Ca1 Cg2 Cg4 Cd Ce Cd Ca2 Sg3 Cg3 Cg3 Cm Sg1 Cm Cg1 V23D5J4 Cg3 V23D5J4 Ca1 V23D5J4 Ca1 V23D5J4 Cg3 V23D5J4 Ca1 V23D5J4 Ca1 IgG3 produced. Switch from IgM IgA1 produced. Switch from IgG3 IgA1 produced. Switch from IgM At each recombination constant regions are deleted from the genome An IgE - secreting B cell will never be able to switch to IgM, IgD, IgG1-4 or IgA1 Model for Class Switch Recombination (CSR) AID (Activation Induced (citidin) Deaminase C →U, RNA editing enzyme) UNG excises U → abasic sites, AP-endonuclease/lyase activity → ss nicks Class switch defects - Hiper IgM syndrome type 2 in humans (autosomal) •HYPER IgM SYNDROME (Autosomal) -Intrinsic B cell defect, activation induced deaiminase (AID) deficiency. Cytidine uridine conversion. -The enyme is involved in affinity maturation and Ig. class switch