* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Overview of Innate Immunity 01/19/06
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
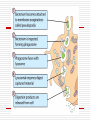
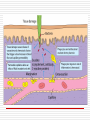
Principles of Immunology Overview of Innate Immunity 1/19/06 “Education is not preparation for life. Education is life itself.” John Dewey Review(T/F) Jenner was the first to introduce variolation Innate immune responses are specific T cells are either T-helper or Tcytotoxic cells Immunological memory results in an amanestic response All antigens are immunogens Innate Immunity Nonspecific host defenses that exist prior to exposure to an antigen. Involves the following components: Anatomic Physiologic Phagocytic Inflammatory Word List Antibody Antigen Complement Endocytosis Humoral Macrophage Monocyte Neutrophil Barriers to Antigenic Insult Anatomic Skin Mucous membranes Physiologic Temperature pH Chemical mediators Cellular and Inflammatory Components of Innate Immunity Cellular Phagocytic cells Inflammatory Vasodilation Capillary permeability Anatomic Barriers Skin Epidermis Dermal layer Sebaceous glands Normal flora Anatomic Barriers Mucous membranes Physical barrier Secretions Cilia Normal flora Physiologic Barriers Temperature Varies by species Febrile response Endogenous pyrogens pH Skin GI tract Physiologic Mediators of Innate Immunity Chemical mediators Enzymes Interferon Complement Three pathways Classical MB Lectin Alternative Physiologic Mediators of Innate Immunity(cont’d) Chemical mediators Collectins Toll-like receptors Acute phase proteins Cellular Component of Innate Immunity Phagocytic cells Monocytes Neutrophils Macrophages Non-Phagocytic cells Natural killer cells Inflammatory Response Hallmarks of inflammation Rubor Tumor Calor Dolor Primary cell Activated macrophage Inflammatory Response(cont’d) Biological effects Vasodilation Capillary permeability Phagocyte migration Inflammatory Response(cont’d) Chemical mediators of inflammation Histamine Kinin system Fibrin system